Abstract
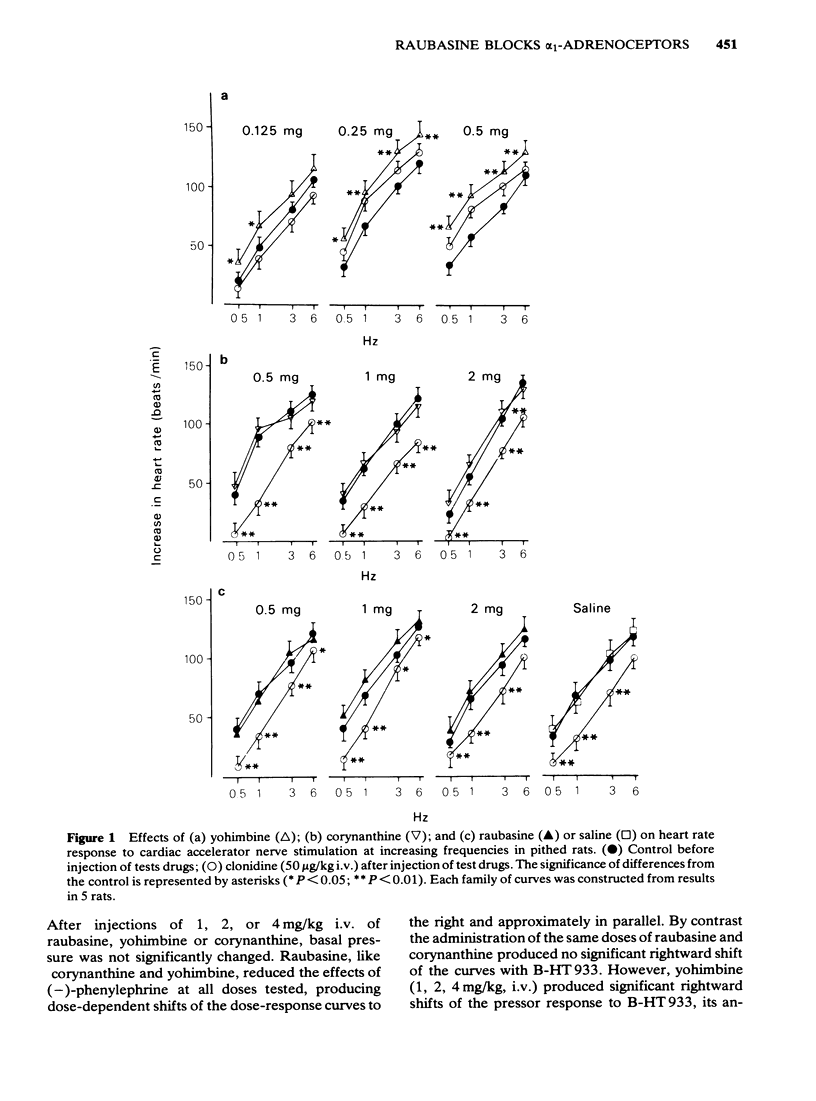
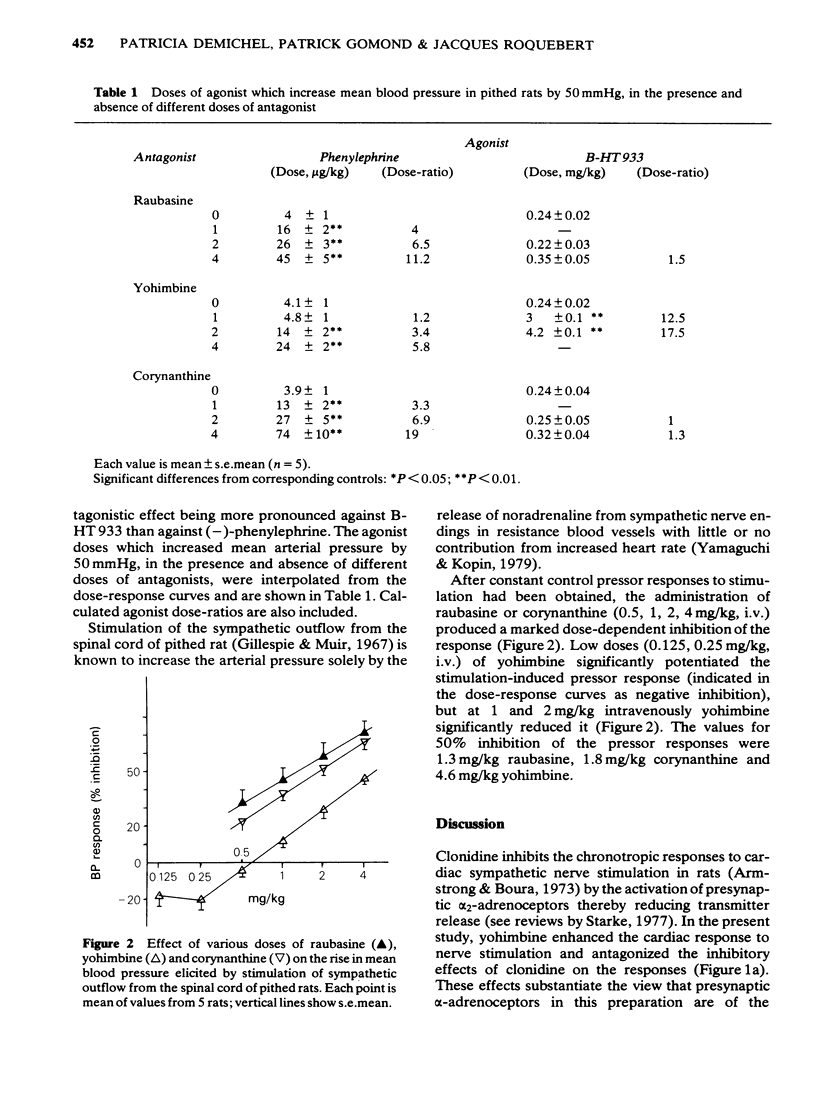
1 Raubasine was compared with yohimbine and corynanthine in pithed rats. Antagonist activity at alpha 1-adrenoceptors was evaluated on the pressor response to electrical stimulation of the spinal sympathetic outflow and to phenylephrine administration, both being reduced by raubasine in the dose range 1 to 4 mg/kg. Corynanthine was quantitatively similar, but yohimbine was not only less potent but also in doses of 0.125 to 0.5 mg/kg enhanced the effects of electrical stimulation. 2 Antagonist activity at alpha 2-adrenoceptors was determined against the inhibitory effects of clonidine on tachycardia induced by electrical stimulation of cardiac sympathetic nerves and against the pressor responses to B-HT-933 injection. Raubasine up to 4 mg/kg, like corynanthine, did not affect the pressor responses to B-HT-933 nor did it reduce the inhibitory effect of clonidine. By contrast yohimbine reduced the response to BHT-933 and antagonized clonidine as well as enhancing the tachycardia caused by electrical stimulation. 3 The results indicate that, in vivo, raubasine, like corynanthine, is a selective antagonist at alpha 1-adrenoceptors and that yohimbine is more potent in blocking alpha 2-than alpha 1-adrenoceptors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. M., Boura A. L. Effects of clonidine and guanethidine on peripheral sympathetic nerve function in the pithed rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Apr;47(4):850–852. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthelsen S., Pettinger W. A. A functional basis for classification of alpha-adrenergic receptors. Life Sci. 1977 Sep 1;21(5):595–606. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demichel P., Gomond P., Roquebert J. Pre- and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor blocking activity of raubasine in the rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Dec;74(4):739–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., MacDonald A., McGrath J. C. Further sub-classification of alpha-adrenoceptors in the cardiovascular system, vas deferens and anococcygeus of the rat [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;67(3):421P–422P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. A comparison of pre- and post-junctional potencies of several alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the cardiovascular system and anococcygeus muscle of the rat. Evidence for two types of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;312(2):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00569718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Muir T. C. A method of stimulating the complete sympathetic outflow from the spinal cord to blood vessels in the pithed rat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 May;30(1):78–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb02114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRONEBERG G. Pharmakologie des Rauwolfia-Alkaloids Raubasin (gamma-Yohimbin-Ajmalicin). Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1958;233(1):72–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobinger W., Pichler L. Pharmacological characterization of B-HT 933 (2-amino-6-ethyl-4,5,7,8,-tetrahydro-6H-oxazolo-[5,4-d]-azepindihydrochloride) as a hypotensive agent of the "clonidine-type". Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;300(1):39–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00505078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Presynaptic regulation of catecholamine release. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Jul 1;23(13):1793–1800. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichler L., Placheta P., Kobinger W. Effect of azepexole (B-HT 933) on pre- and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors at peripheral and central nervous sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Jul 25;65(2-3):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roquebert J., Gomond P., Demichel P. Activité antinoradrénergique de la raubasine sur l'aorte thoracique et le canal déférent isolés de rat. J Pharmacol. 1981 Nov-Dec;12(4):393–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Endo T., Taube H. D. Relative pre- and postsynaptic potencies of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;291(1):55–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00510821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., Van Zwieten P. A. Postsynaptic alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the circulatory system of the pithed rat: selective stimulation of the alpha 2-type by B-HT 933. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 May 2;63(2-3):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzell R., Tanaka T., Starke K. Pre- and postsynaptic effects of yohimbine stereoisomers on noradrenergic transmission in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;308(2):127–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00499054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi I., Kopin I. J. Differential inhibiton of alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenoceptor-mediated pressor responses in pithed rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Aug;214(2):275–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi I., Kopin I. J. Plasma catecholamine and blood pressure responses to sympathetic stimulation in pithed rats. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):H305–H310. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.237.3.H305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


