Abstract
1 In homogenates of rat brain, the binding characteristics of tritiated opiates and opioid peptides were examined and the relative capacities of μ-, δ- and κ-binding sites of the opiate receptor determined by saturation analysis.
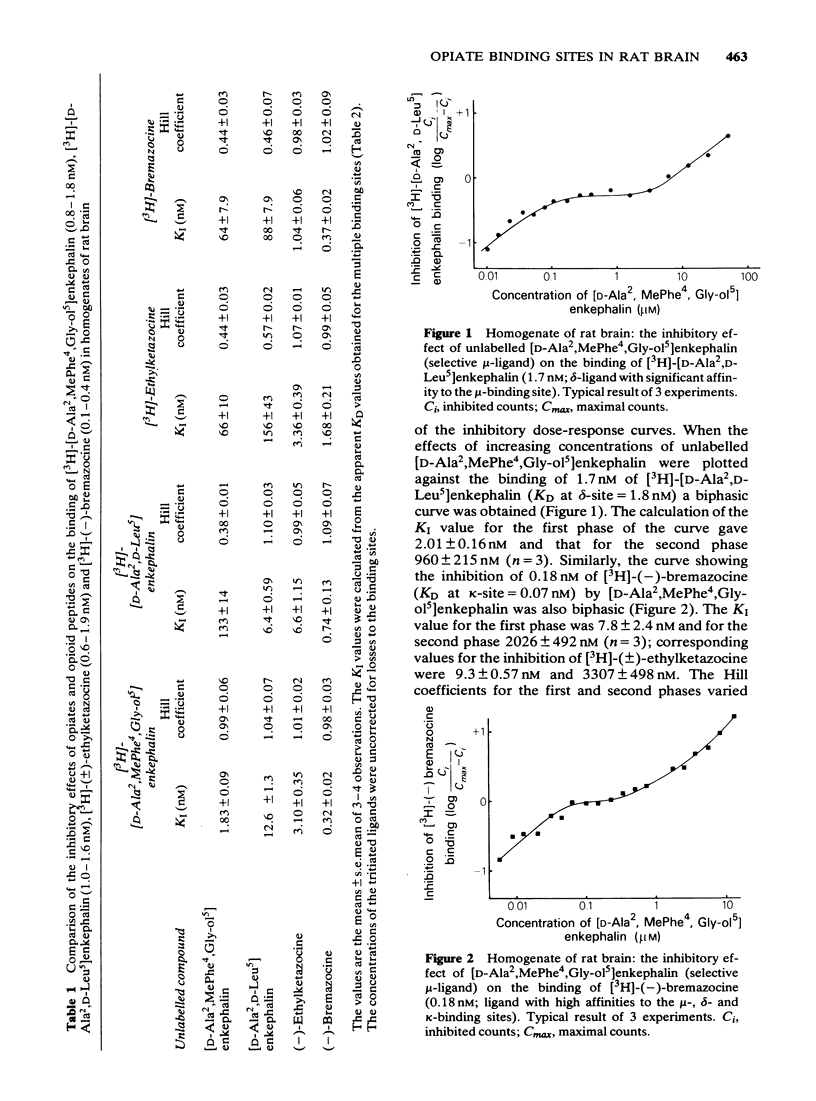
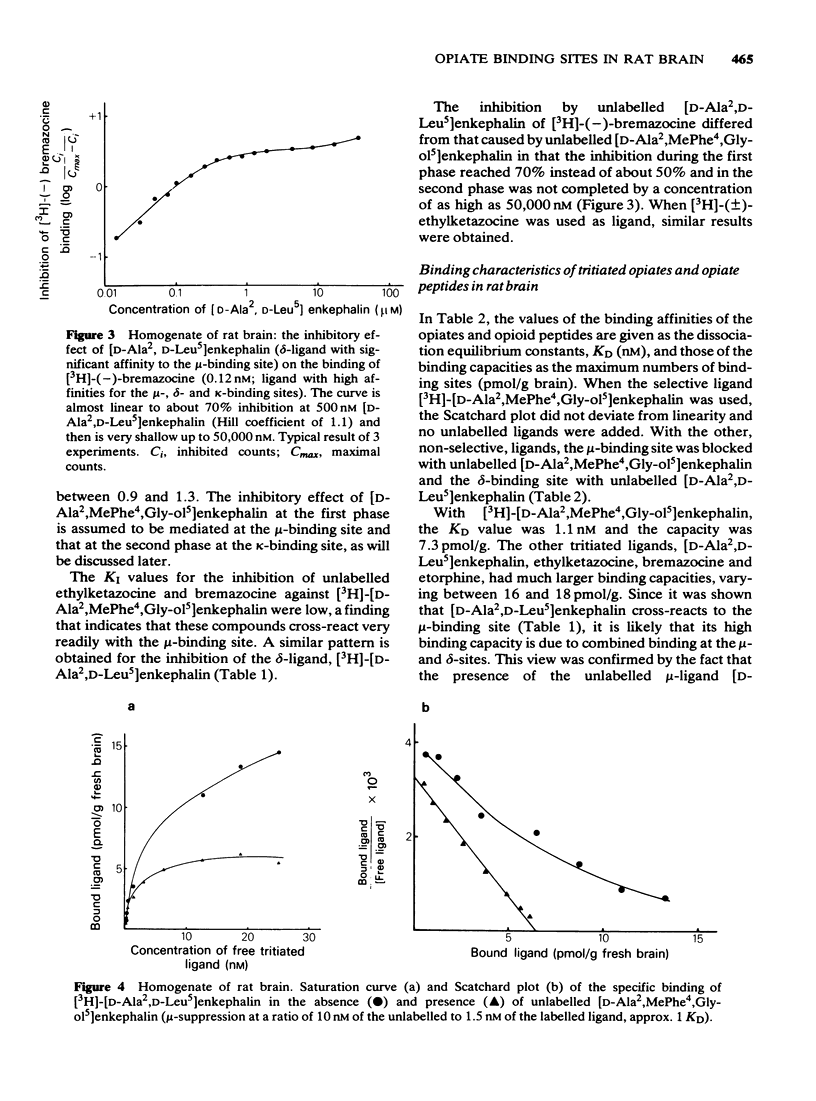
2 In competition experiments, binding of the selective μ-ligand [3H]-[D-Ala2,MePhe4,Gly-ol5]enkephalin at the μ-site was displaced by [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]enkephalin with rather low affinity (KI = 12.6 nM) and more readily by the ketazocine-like compounds (-)-ethylketazocine (KI = 3.1 nM) and (-)-bremazocine (KI = 0.32 nM), which also displaced the binding of [3H]-[D-Ala2,D-Leu5]enkephalin from the δ-site. In contrast, the binding to the κ-site was easily displaced by ethylketazocine (1.0 nM) and bremazocine (0.37 nM) but not by the μ-ligand [D-Ala2,MePhe4,Gly-ol5]enkephalin (KI = 2000-3000 nM) or the δ-ligand [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]enkephalin (KI > 20,000 nM).
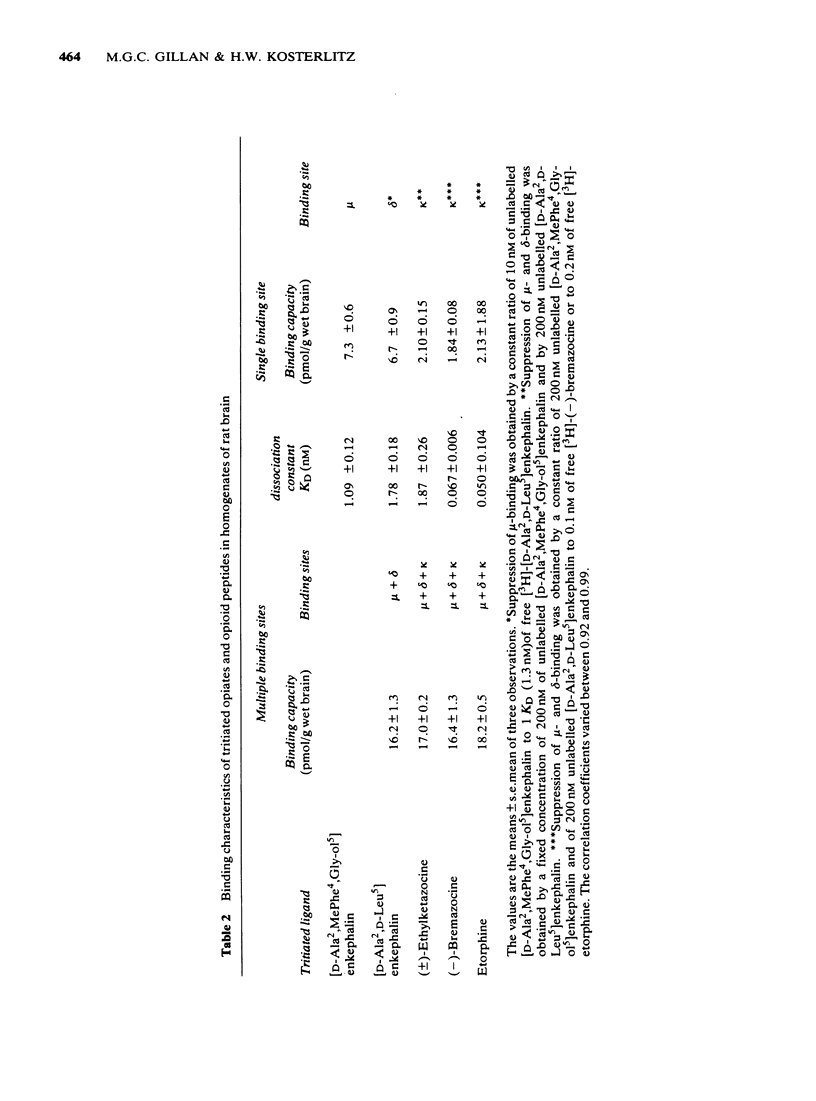
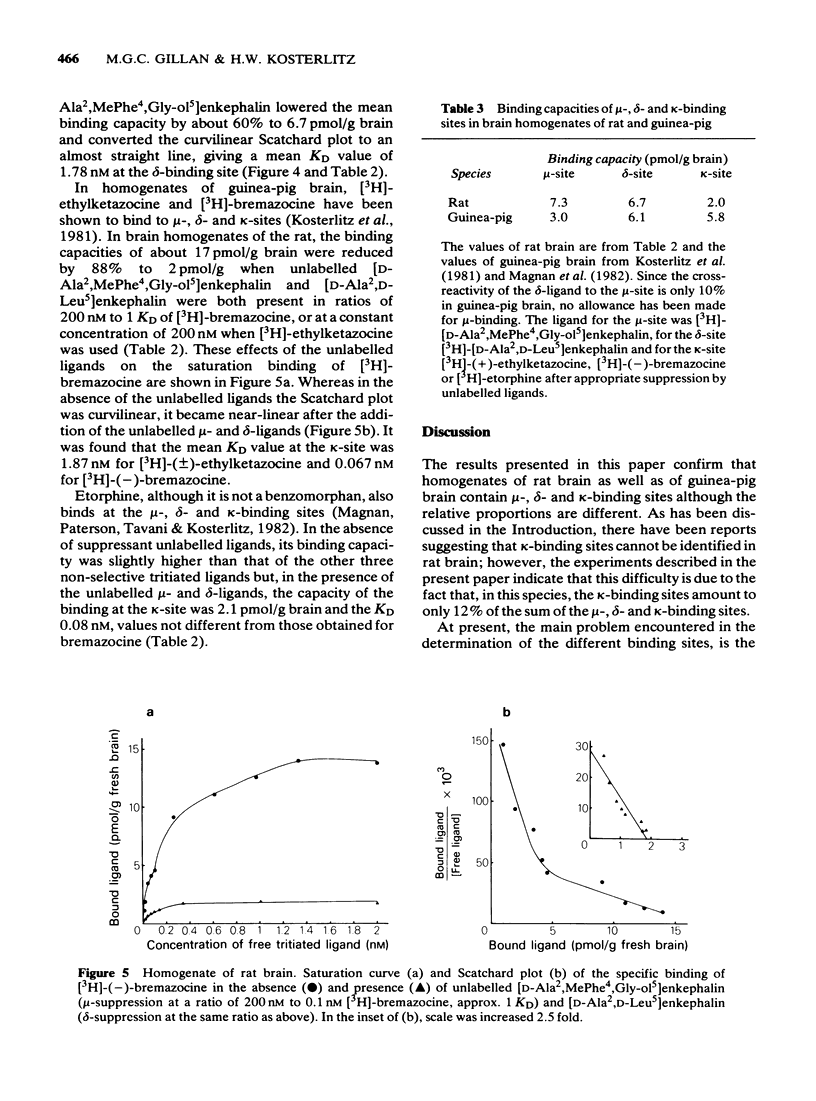
3 The dissociation equilibrium constant (KD) and the binding capacity (pmol/g) of the μ-binding site were determined with the selective μ-ligand [3H]-[D-Ala2,MePhe4,Gly-ol5]enkephalin. For the δ-site, [3H]-[D-Ala2,D-Leu5]enkephalin was used in the presence of unlabelled [D-Ala2,MePhe4,Gly-ol5]enkephalin in order to suppress cross-reactivity to the μ-binding site. For the estimation of κ-binding, [3H]-(±)-ethylketazocine or [3H]-(-)-bremazocine were used in the presence of unlabelled μ- and δ-ligands for the suppression of cross-reactivities to the μ- and δ-binding sites.
4 In rat brain the capacity of the μ-binding site was 7.3 pmol/g brain, that of the δ-binding site 6.7 pmol/g brain and that of the κ-binding site 2.0 pmol/g brain. Thus, the κ-binding site had the lowest value whereas in the guinea-pig brain the capacity of the μ-binding site was lower than that of the δ- or κ-binding site.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang K. J., Hazum E., Cuatrecasas P. Novel opiate binding sites selective for benzomorphan drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4141–4145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillan M. G., Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J. Comparison of the binding characteristics of tritiated opiates and opioid peptides. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;70(3):481–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb08727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa B. K., Land A. C., Lord J. A., Morgan B. A., Rance M. J., Smith C. F. Analogues of beta-LPH61-64 possessing selective agonist activity at mu-opiate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 9;70(4):531–540. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90364-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. W., Sethy V. H. High affinity binding of [3H]ethylketocyclazocine to rat brain homogenate. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Aug 22;66(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90303-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller J. M., Simon E. J. 3H-ethylketocyclazocine binding: lack of evidence for a separate kappa receptor in rats CNS. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Dec 20;60(4):389–390. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90249-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller J. M., Simon E. J. Specific, high affinity [3H]ethylketocyclazocine binding in rat central nervous system: lack of evidence for kappa receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Sep;214(3):516–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J. Characterization of opioid receptors in nervous tissue. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Oct 29;210(1178):113–122. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J., Robson L. E. Characterization of the kappa-subtype of the opiate receptor in the guinea-pig brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;73(4):939–949. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb08749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnan J., Paterson S. J., Tavani A., Kosterlitz H. W. The binding spectrum of narcotic analgesic drugs with different agonist and antagonist properties. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Jun;319(3):197–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00495865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W. Multiple opiate receptors: [3H]ethylketocyclazocine receptor binding and ketocyclazocine analgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3691–3694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römer D., Büscher H., Hill R. C., Maurer R., Petcher T. J., Welle H. B., Bakel H. C., Akkerman A. M. Bremazocine: a potent, long-acting opiate kappa-agonist. Life Sci. 1980 Sep 15;27(11):971–978. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Goodman R. R. Multiple neurotransmitter receptors. J Neurochem. 1980 Jul;35(1):5–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb12483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. L., Charleson S. E., Lane D., Hudgin R. L. Multiple opiate receptors: differential binding of mu, kappa and delta agonists. Neuropharmacology. 1981 Dec;20(12A):1215–1220. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(81)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


