Abstract
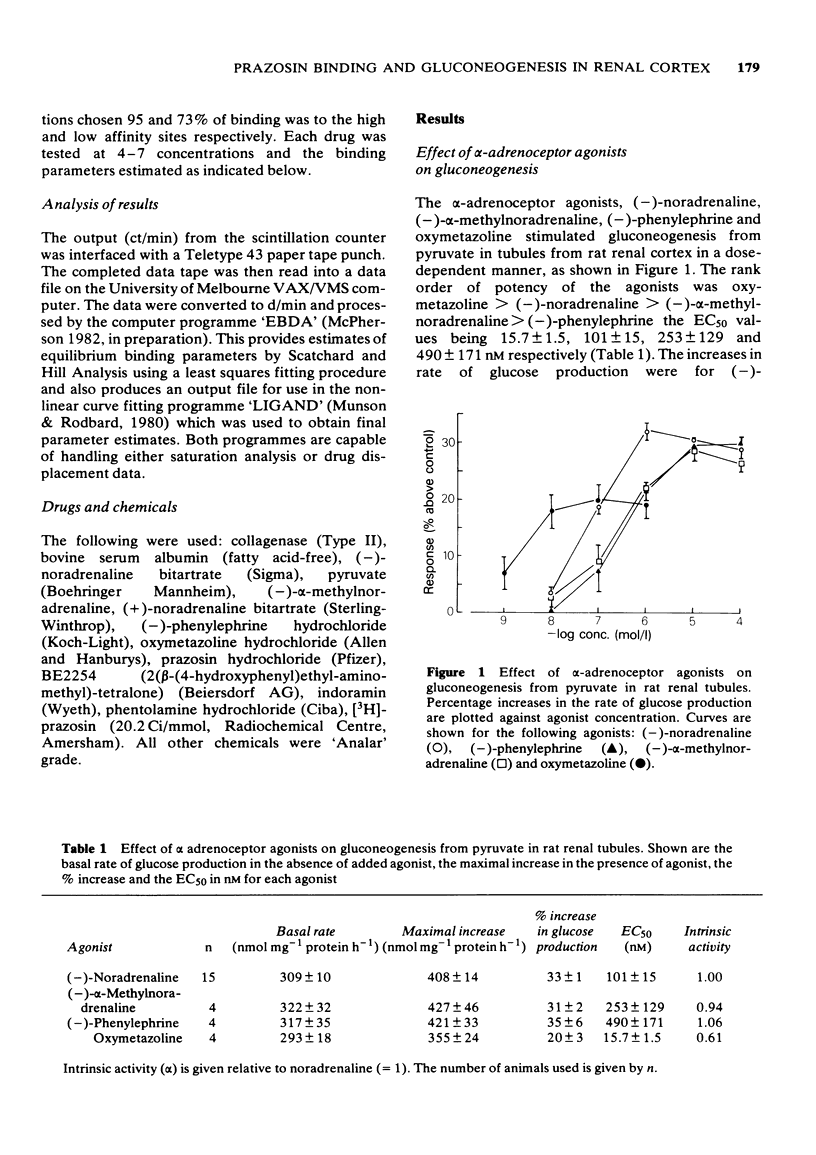
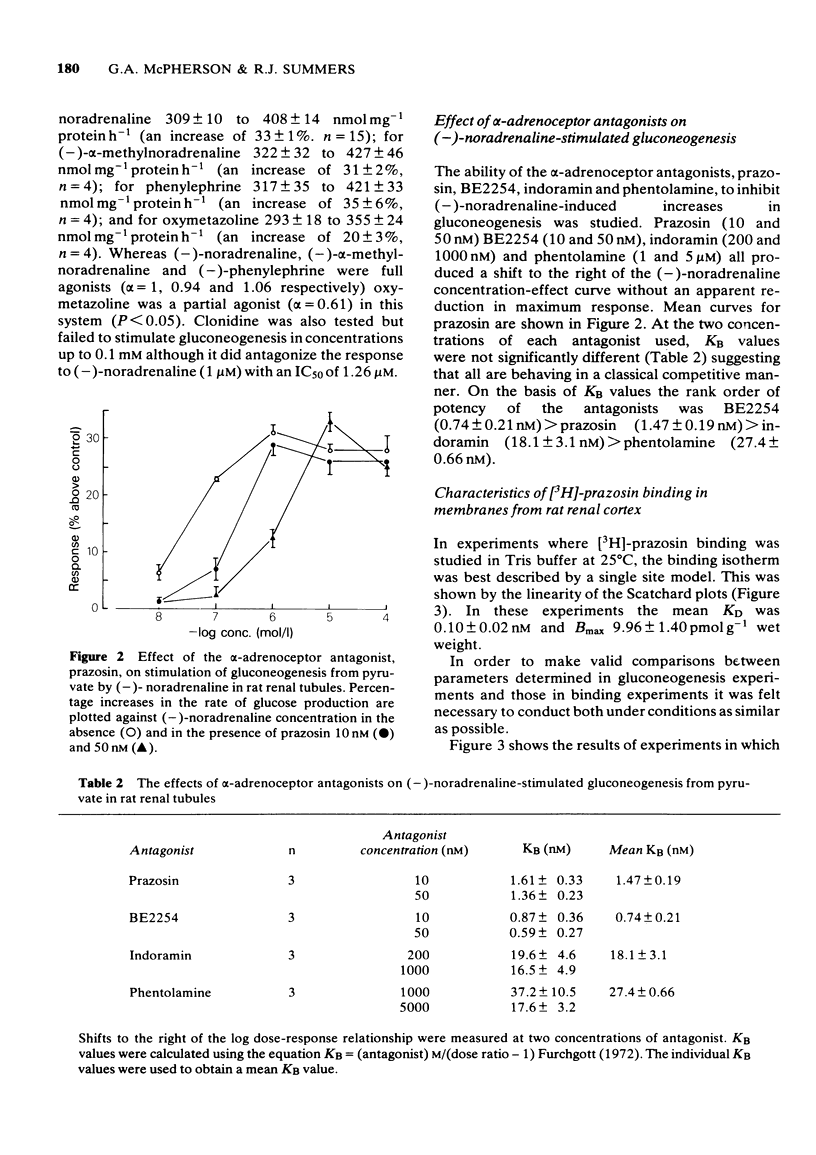
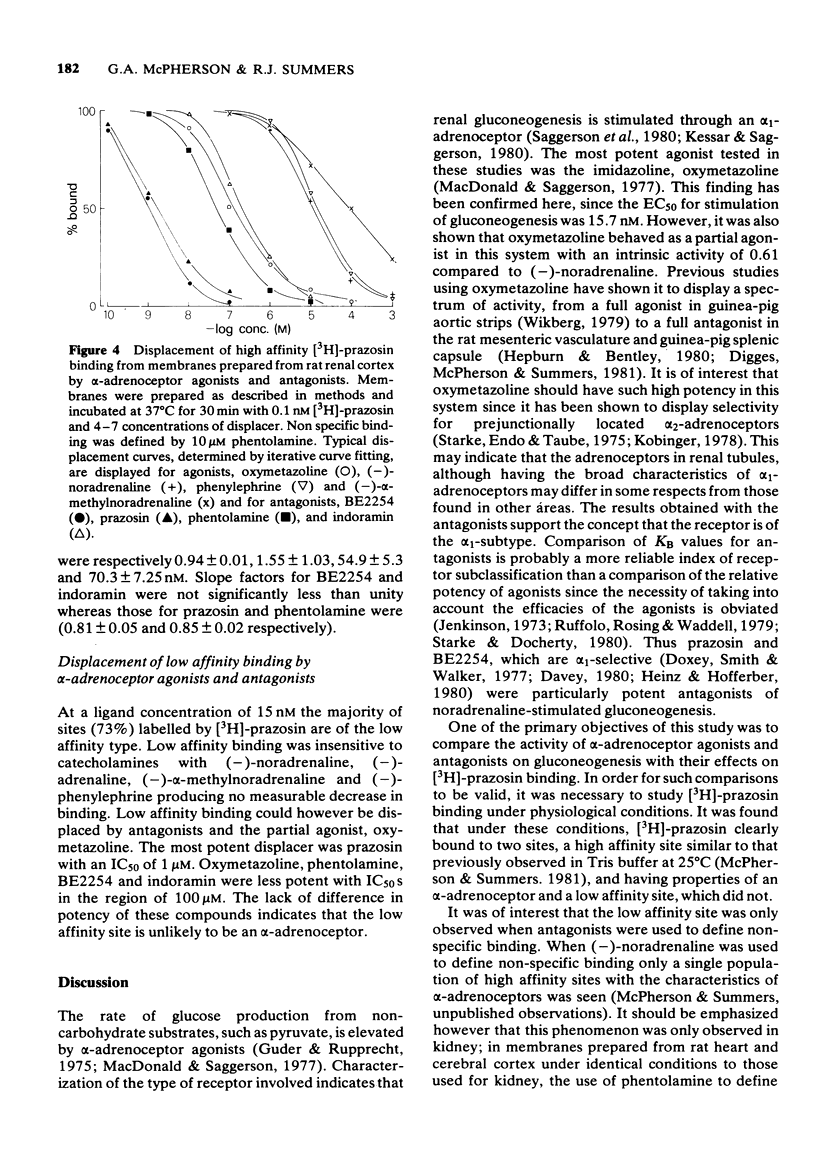
1 A comparison has been made of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor controlling gluconeogenesis in tubules from rat renal cortex and [3H]-prazosin binding in membranes prepared from the same tissue under physiological conditions. 2 In renal tubules the alpha-adrenoceptor agonists, oxymetazoline, (--)-noradrenaline, (--)-alpha-methylnoradrenaline and (--)-phenylephrine, stimulated gluconeogenesis from pyruvate. Oxymetazoline was the most potent agonist (EC50 15.7 nM) but produced only 61% of the maximum response elicited by (--)-noradrenaline. 3 The alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists, BE2254, prazosin, indoramin and phentolamine inhibited (--)-noradrenaline-mediated increases in gluconeogenesis. The alpha 1-adrenoceptor selective compounds, BE2254 and prazosin, were the most effective antagonists with KB values of 0.74 and 1.47 nM respectively. 4 [3H]-prazosin binding to membranes prepared from rat renal cortex in physiological saline at 37 degrees C was best described by a two site model. High affinity, but not low affinity sites had characteristics consistent with alpha-adrenoceptors. 5 High affinity [3H]-prazosin binding could be completely displaced by the alpha-adrenoceptor agonists, oxymetazoline, (--)-noradrenaline, (--)-phenylephrine, and (--)-alpha-methylnoradrenaline. Slope factors for the displacement curves were all significantly less than unity. The concentrations of agonists required to displace [3H]-prazosin binding were markedly higher than those required to stimulate gluconeogenesis. 6 High-affinity [3H]-prazosin binding was also displaced by the alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists, prazosin, BE2254, phentolamine and indoramin. Slope factors for the displacement curves were close to unity. Ki values calculated from the binding experiments were very similar to KB values obtained in the gluconeogenesis studies. These results suggest that in rat renal cortex the alpha 1-adrenoceptor labelled by [3H]-prazosin is probably that which stimulates gluconeogenesis.
Full text
PDF

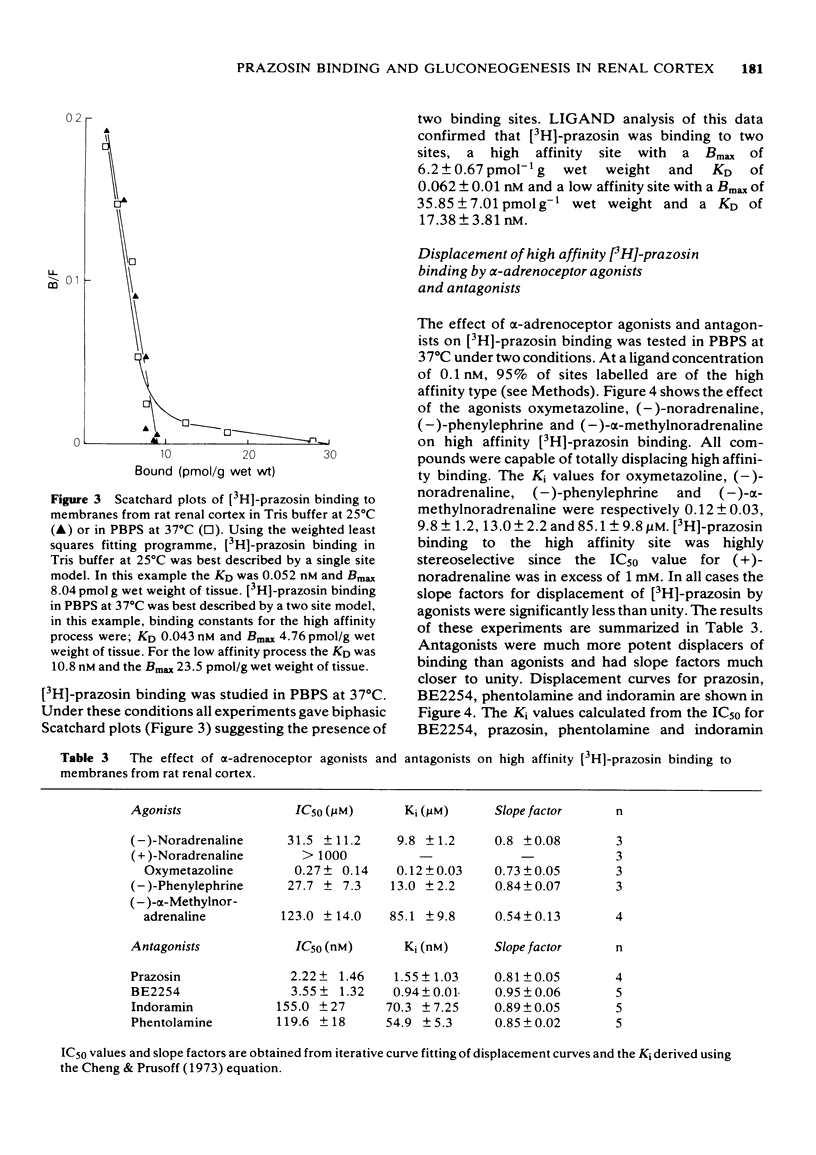


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. J., Karliner J. S., Dollery C. T. Human lung adrenoreceptors studied by radioligand binding. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Jun;58(6):457–461. doi: 10.1042/cs0580457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambridge D., Davey M. J., Massingham R. Prazosin, a selective antagonist of post-synaptic alpha-adrenoceptors [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;59(3):514P–515P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digges K. G., McPherson G. A., Summers R. J. Pharmacological investigation of alpha-adrenoreceptors in guinea-pig splenic capsule. J Auton Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;1(4):313–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1981.tb00461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Smith C. F., Walker J. M. Selectivity of blocking agents for pre-and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 May;60(1):91–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb16752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengrass P., Bremner R. Binding characteristics of 3H-prazosin to rat brain alpha-adrenergic receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 May 1;55(3):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guder W. G., Rupprecht A. Metabolism of isolated kidney tubules. Independent actions of catecholamines on renal cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate levels and gluconeogenesis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 17;52(2):283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guder W. G., Schmidt U. The localization of gluconeogenesis in rat nephron. Determination of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in microdissected tubules. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Mar;355(3):273–278. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1974.355.1.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz N., Hofferber E. Zur Pharmakologie des alpha-Rezeptoren-Blockers BE 2254 (HEAT). Arzneimittelforschung. 1980;30(12):2135–2139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornung R., Presek P., Glossmann H. Alpha adrenoceptors in rat brain: direct identification with prazosin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;308(3):223–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00501386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson D. H. Classification and properties of peripheral adrenergic receptors. Br Med Bull. 1973 May;29(2):142–147. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessar P., Saggerson E. D. Evidence that catecholamines stimulate renal gluconeogenesis through an alpha 1-type of adrenoceptor. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 15;190(1):119–123. doi: 10.1042/bj1900119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobinger Central alpha-adrenergic systems as targets for hypotensive drugs. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;81:39–100. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald D. W., Saggerson E. D. Hormonal control of gluconeogenesis in tubule fragments from renal cortex of fed rats. Effects of alpha-adrenergic stimuli, glucagon, theophylline and papaverine. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 15;168(1):33–42. doi: 10.1042/bj1680033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Summers R. J. [3H]prazosin and [3H]clonidine binding to alpha-adrenoceptors in membranes prepared from regions of rat kidney. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;33(3):189–191. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miach P. J., Dausse J. P., Cardot A., Meyer P. 3H-Prazosin binds specifically to 'alpha 1'-adrenoceptors in rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 May;312(1):23–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00502569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Rosing E. L., Waddell J. E. Receptor interactions of imidazolines. I. Affinity and efficacy for alpha adrenergic receptors in rat aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Jun;209(3):429–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D., Kessar P., Carpenter C. A. Regulation of renal gluconeogenesis by alpha-adrenergic action. Int J Biochem. 1980;12(1-2):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. M., Graham R. M., Sagalowsky A., Pettinger W. A. Renal alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenergic receptors: biochemical and pharmacological correlations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Nov;219(2):400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Endo T., Taube H. D. Relative pre- and postsynaptic potencies of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;291(1):55–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00510821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf B., Kraus H. Gluconeogenesis in kidney cortex slices of the guinea pig. Its relation to acidosis and to calcium. Curr Probl Clin Biochem. 1977 Oct 23;8:329–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. J., Jarrott B., Louis W. J. Selectivity of a series of clonidine-like drugs for alpha 1 and alpha 2 adrenoceptors in rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Dec;20(3):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U'Prichard D. C., Charness M. E., Robertson D., Snyder S. H. Prazosin: differential affinities for two populations of alpha-noradrenergic receptor binding sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Jul 1;50(1):87–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


