Abstract
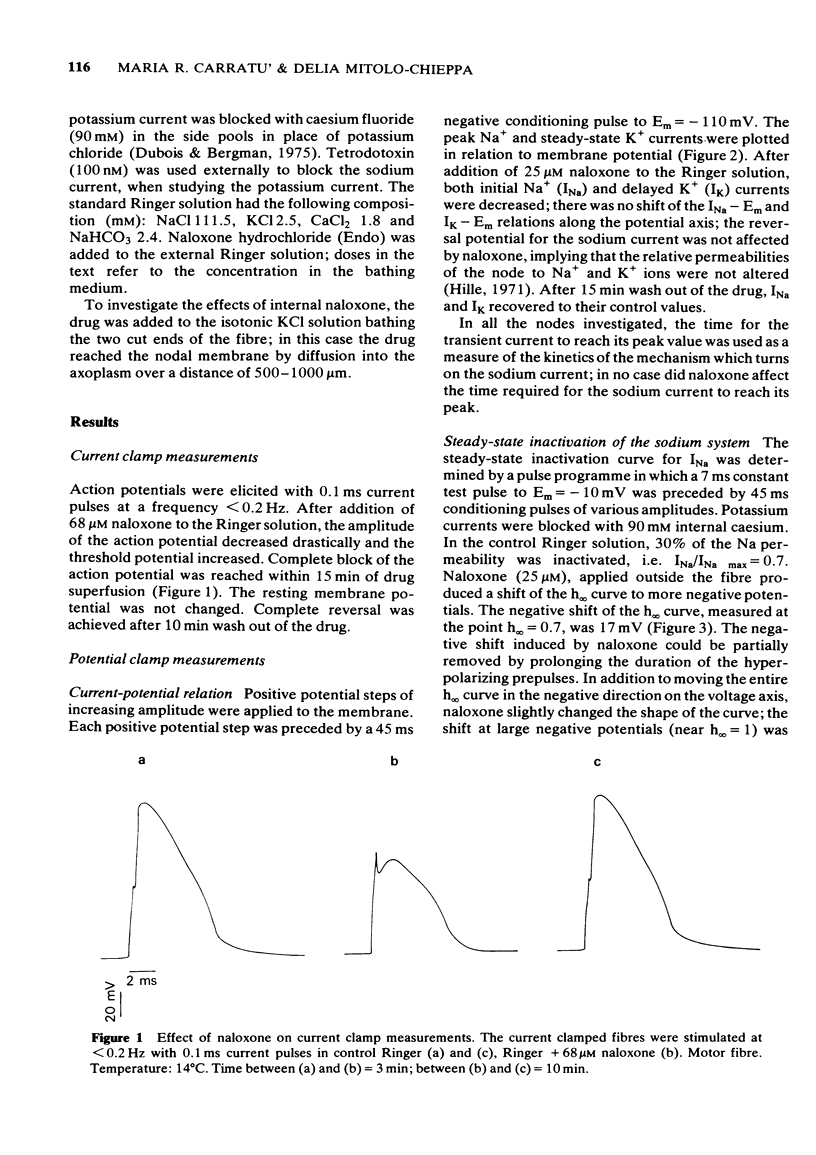
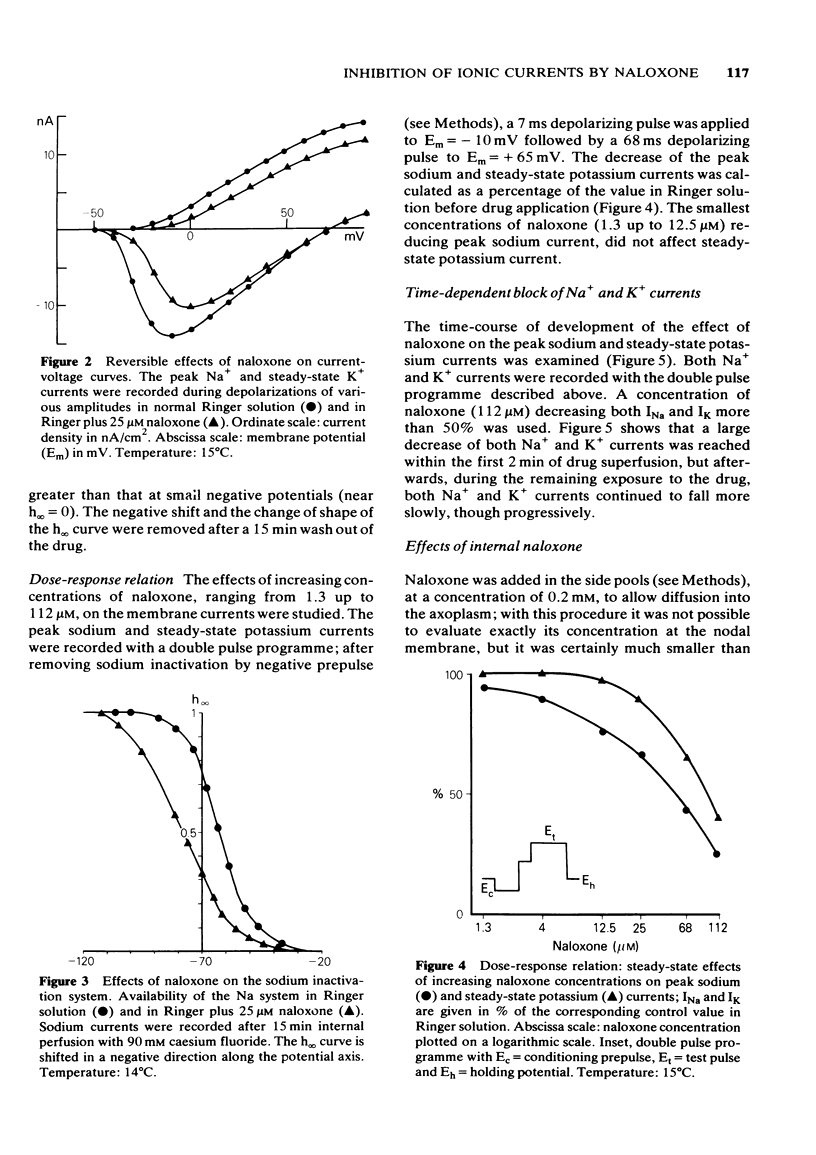
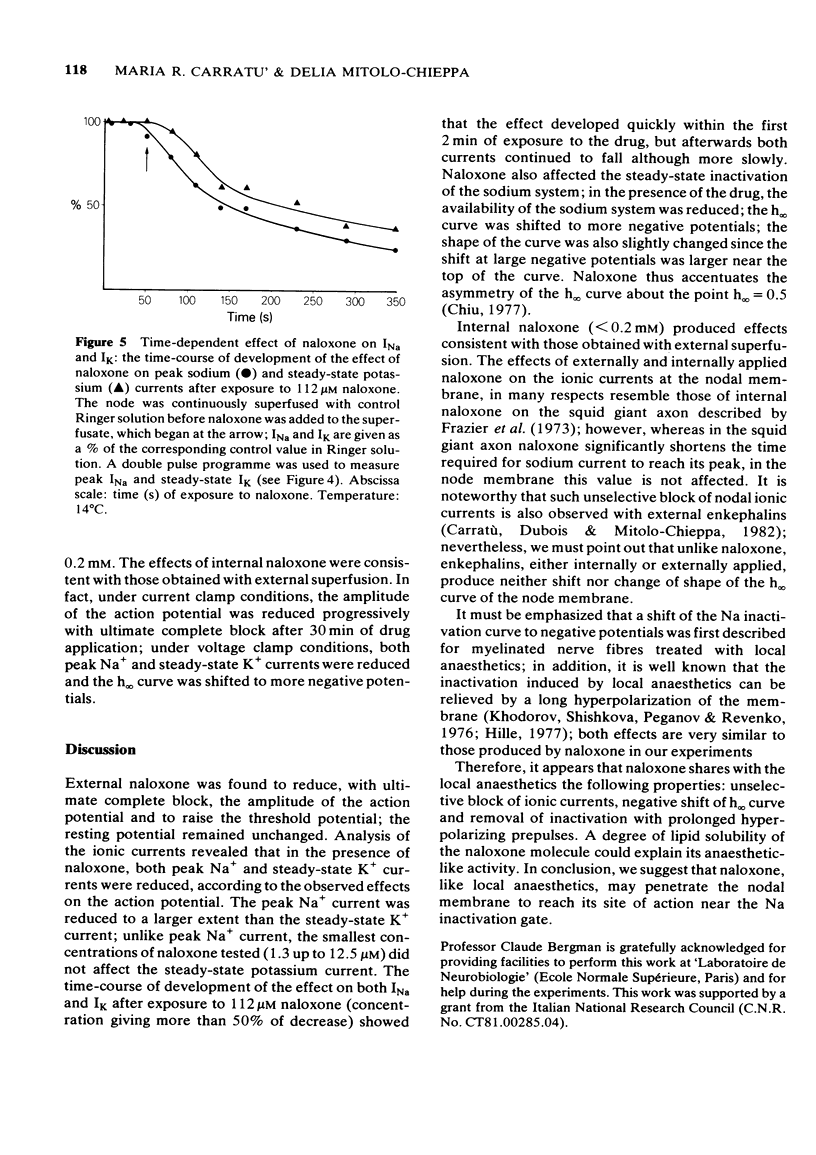
1 Myelinated nerve fibres of frog sciatic nerve were investigated under current and voltage clamp conditions. In the presence of 68 microM external naloxone, the action potential was completely, though progressively, blocked within 15 min of drug superfusion. The resting potential remained constant. 2 Under voltage clamp conditions both peak Na+ and steady-state K+ currents were decreased reversibly by external naloxone. Both currents were reduced in a dose-dependent manner but, whereas sodium current was affected by the smallest concentrations of naloxone (1.3 up to 12.5 microM), potassium current was decreased only by higher concentrations (25 up to 112 microM). 3 The time-course of development of the effect on both Na+ and K+ currents after exposure to 112 microM naloxone (a concentration giving more than 50% of decrease) showed that the effect develops quickly within the first 2 min of exposure to the drug, but afterwards both currents continue to fall more slowly, though progressively. 4 Experiments with constant test pulses to Em = - 10 mV and conditioning prepulses of various amplitudes, showed that the Na inactivation curve, h infinity (Em), was shifted in a negative direction along the potential axis; the shape of the curve was also slightly changed in the presence of naloxone since the shift was larger near the top of the curve. All the observed effects were reversible after returning to the standard Ringer solution. 5 Internal naloxone (less than 0.2 mM) reduced the amplitude of the action potential as well as peak Na+ and steady-state K+ currents; the sodium inactivation curve, h infinity (Em), was shifted to more negative potentials. 6 A possible anaesthetic-like activity of naloxone on the nodal membrane is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chiu S. Y. Inactivation of sodium channels: second order kinetics in myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(3):573–596. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M., Bergman C. Cesium induced rectifications in frog myelinated fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Apr 2;355(4):361–364. doi: 10.1007/BF00579857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M., Bergman C. The steady-state potassium conductance of the Ranvier node at various external K-concentrations. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Aug 29;370(2):185–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00581693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier D. T., Ohta M., Narahashi T. Nature of the morphine receptor present in the squid axon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Apr;142(4):1209–1214. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Local anesthetics: hydrophilic and hydrophobic pathways for the drug-receptor reaction. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):497–515. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to organic cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Dec;58(6):599–619. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.6.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonner W. A new voltage clamp method for Ranvier nodes. Pflugers Arch. 1969;309(2):176–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00586967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


