Abstract
1--The longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus strip preparation of the guinea-pig ileum was used to study the binding of [3H]-diazepam and the effect of benzodiazepines on its contraction. 2--Scatchard analysis of binding indicated a single class of binding sites with KD = 43 nM and Bmax = 229 fmol/mg prótein. Binding was of peripheral type based on the much greater binding affinity of Ro5-4864 as compared to clonazepam. Binding of [3H]-diazepam reached equilibrium at 10 min and dissociated rapidly (T1/2 = 1.3 min). The KD derived from the rate constants agreed with that from the Scatchard analysis. 3--Benzodiazepines produced a dose-dependent decrease in the electrically induced contractions of the longitudinal muscle strip, but their potencies in this effect did not correlate with their binding affinities. 4--Diazepam antagonized the contractions of the longitudinal muscle strip induced by K+, Ca2+, histamine and carbachol. The inhibition of Ca2+-induced contractions was reversed by increasing the concentration of Ca2+ in the medium.
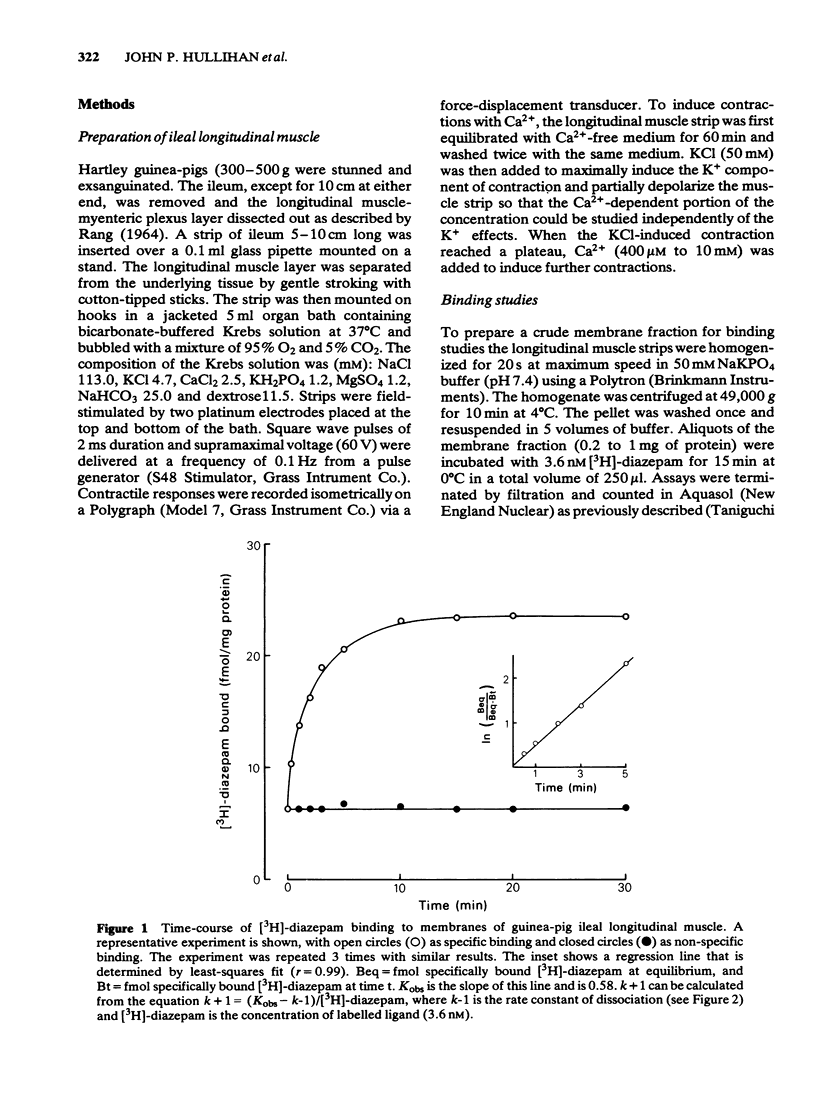
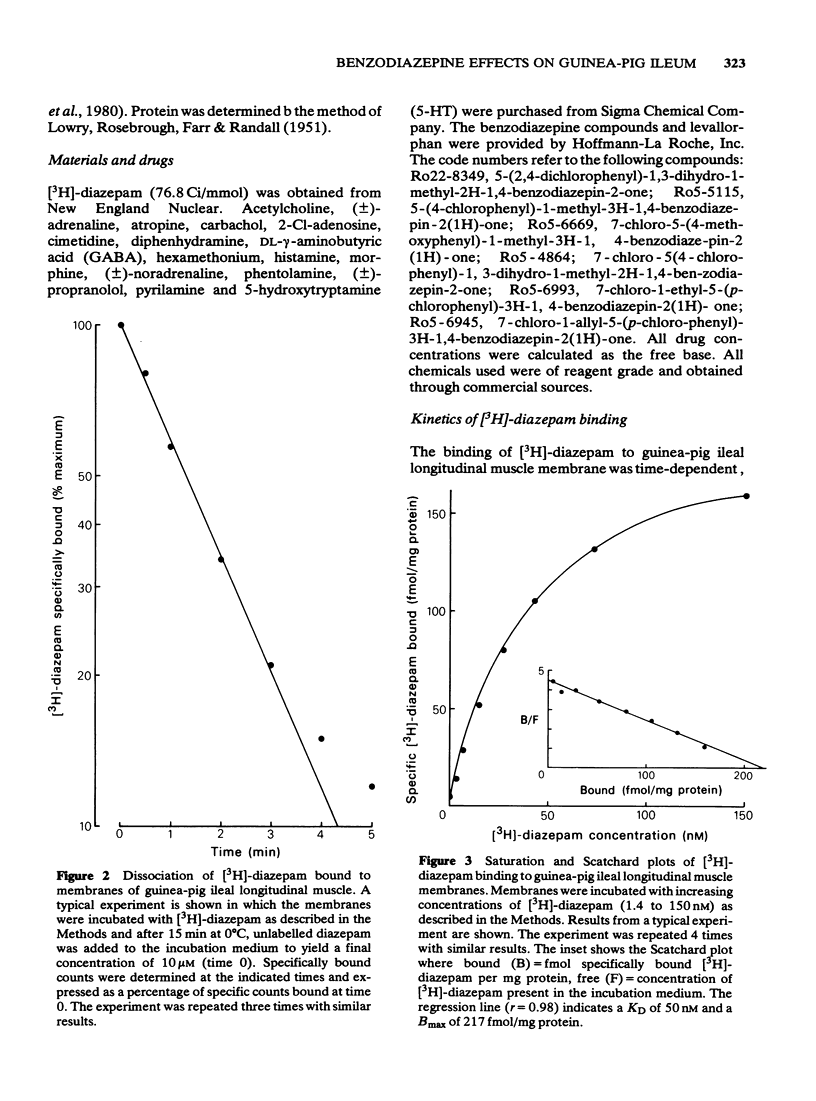
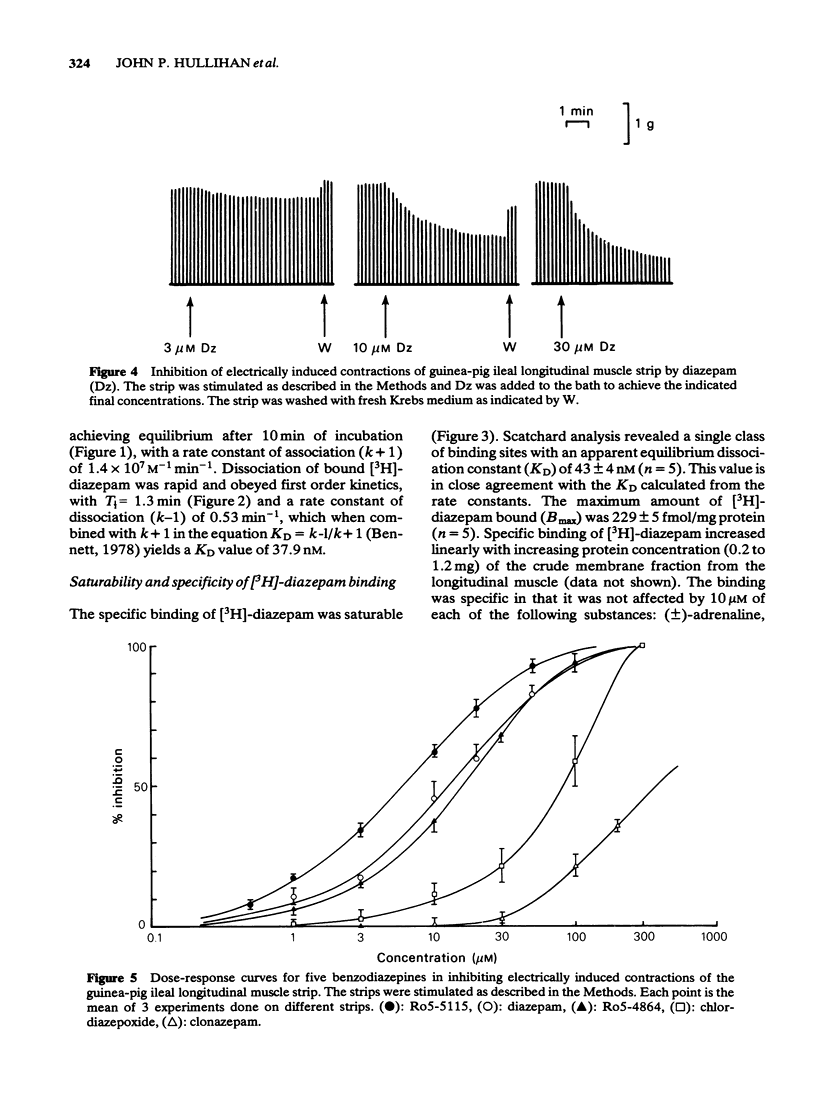
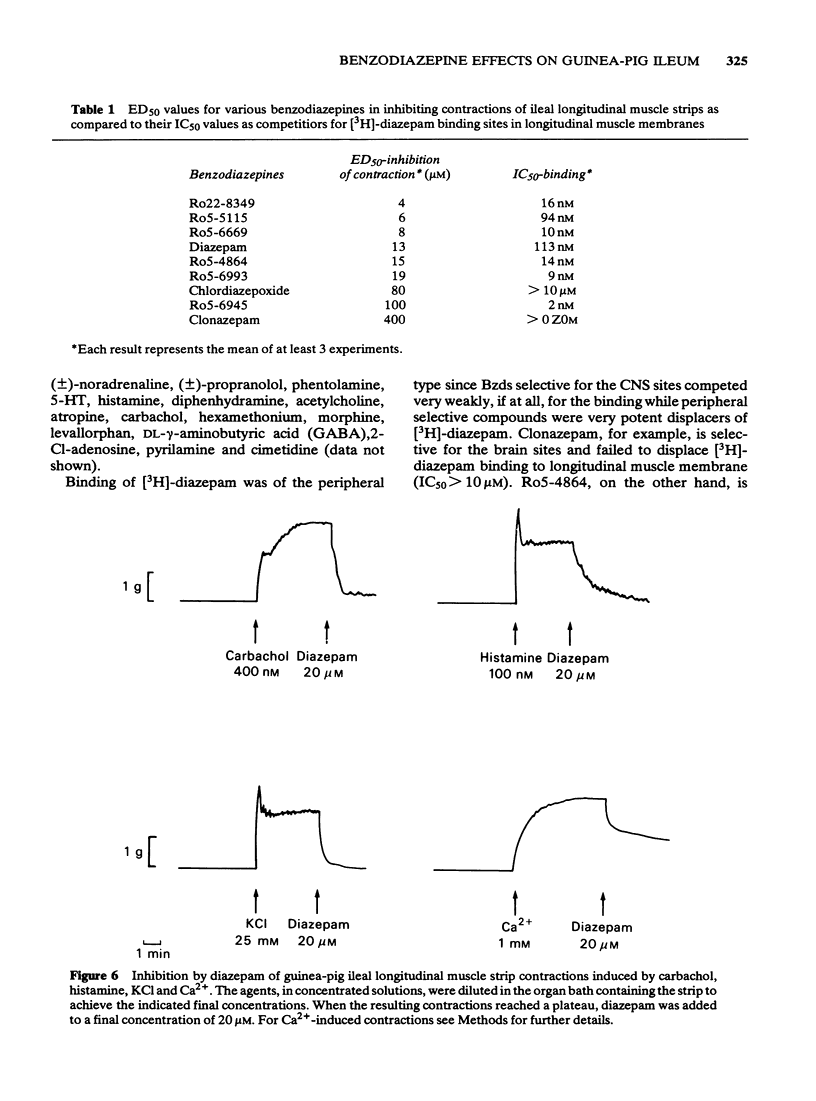
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H)diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies L. P., Huston V. Peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites in heart and their interaction with dipyridamole. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(2-3):209–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackerer C. R., Kochman R. L., Bierschenk B. A., Bremner S. S. The binding of [3H]diazepam to rat brain homogenates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Aug;206(2):405–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANG H. P. STIMULANT ACTIONS OF VOLATILE ANAESTHETICS ON SMOOTH MUSCLE. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Apr;22:356–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Brastrup C. Benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):732–734. doi: 10.1038/266732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syapin P. J., Skolnick P. Characterization of benzodiazepine binding sites in cultured cells of neural origin. J Neurochem. 1979 Mar;32(3):1047–1051. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallman J. F., Paul S. M., Skolnick P., Gallager D. W. Receptors for the age of anxiety: pharmacology of the benzodiazepines. Science. 1980 Jan 18;207(4428):274–281. doi: 10.1126/science.6101294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Wang J. K., Spector S. Properties of [3H] diazepam binding to rat peritoneal mast cells. Life Sci. 1980 Jul 14;27(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90460-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Wang J. K., Spector S. [3H]Diazepam binding sites on rat heart and kidney. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):589–590. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90164-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. K., Taniguchi T., Spector S. Properties of [3H]diazepam binding sites on rat blood platelets. Life Sci. 1980 Nov 17;27(20):1881–1888. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zbinden G., Randall L. O. Pharmacology of benzodiazepines: laboratory and clinical correlations. Adv Pharmacol. 1967;5:213–291. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60658-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


