Abstract
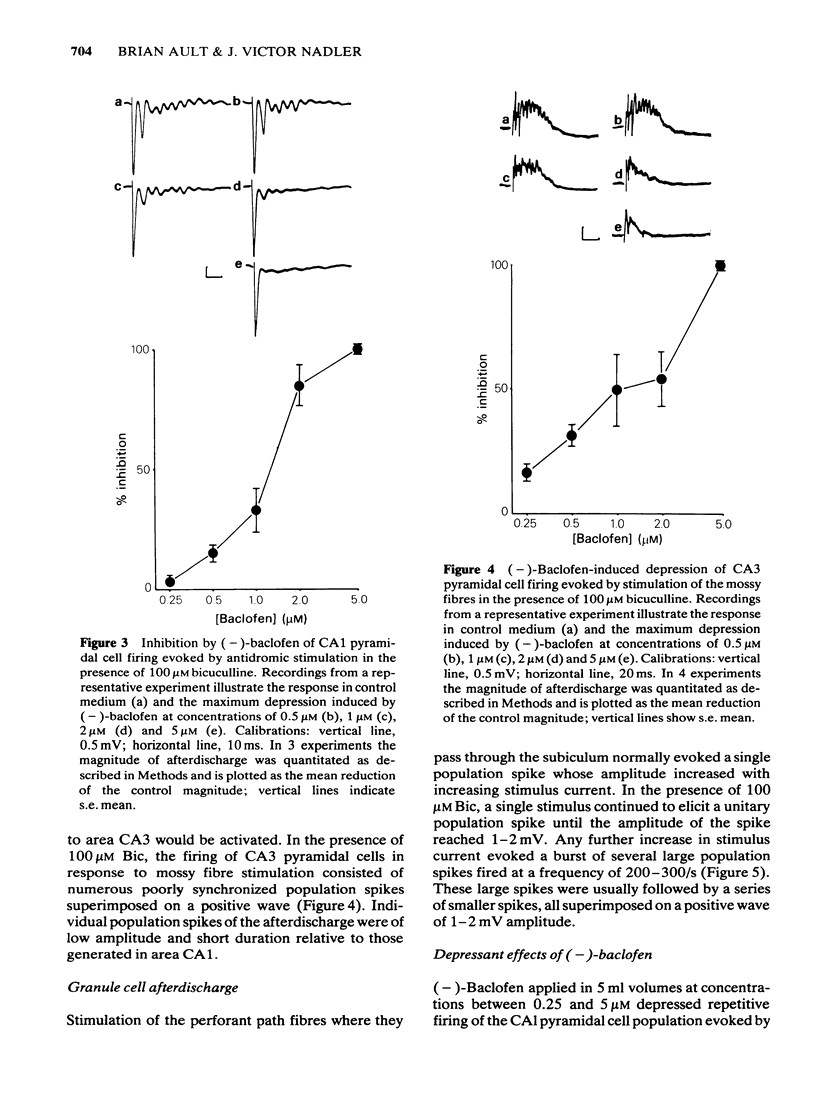
1 The effects of baclofen were tested on epileptiform discharge in the rat hippocampal slice. Slices were superfused with bicuculline methiodide (100 microM) and maximal periods of afterdischarge were evoked by stimulating the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway in area CA1, mossy fibres in area CA3 or perforant path fibres in the fascia dentata or by antidromic stimulation of CA1 pyramidal cells. 2 (-)-Baclofen attenuated the afterdischarge evoked by stimulating all three sets of fibres in areas CA1 and CA3. In each case, a threshold effect was observed at a concentration of 0.25 or 0.5 microM, and complete suppression was usually attained with a concentration of 5 microM. EC50 values ranged between 1 and 2 microM. (-)-Baclofen attenuated hippocampal afterdischarge with 120 times the potency of (+)-baclofen. It did not, however, affect the repetitive firing of dentate granule cells in response to stimulation of perforant path fibres. 3 (-)-Baclofen also reduced the amplitude of the initial population spike evoked by stimulation of Schaffer collateral-commissural fibres, but did not affect the antidromic population spike nor the initial population spike evoked by stimulation of the mossy fibres. 4 Recurrent inhibition in area CA1 was abolished by 1 microM (-)-baclofen. Thus baclofen, unlike many anticonvulsants, does not suppress afterdischarge by potentiating GABAergic inhibition. 5 These results suggest that baclofen attenuates hippocampal afterdischarge by a combination of pre- and postsynaptic mechanisms.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alger B. E., Nicoll R. A. Epileptiform burst afterhyperolarization: calcium-dependent potassium potential in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. Science. 1980 Dec 5;210(4474):1122–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.7444438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Bliss T. V., Skrede K. K. Unit analysis of hippocampal polulation spikes. Exp Brain Res. 1971;13(2):208–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00234086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Evans R. H. The depressant action of baclofen on the isolated spinal cord of the neonatal rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 May 22;71(4):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Nadler J. V. Baclofen selectively inhibits transmission at synapses made by axons of CA3 pyramidal cells in the hippocampal slice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):291–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedito M. A., Leite J. R. Baclofen as an anticonvulsant in experimental models of convulsions. Exp Neurol. 1981 May;72(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(81)90228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Doble A., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L., Shaw J. S., Turnbull M. J., Warrington R. Bicuculline-insensitive GABA receptors on peripheral autonomic nerve terminals. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 24;71(1):53–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L., Doble A., Middlemiss D. N., Shaw J., Turnbull M. (-)Baclofen decreases neurotransmitter release in the mammalian CNS by an action at a novel GABA receptor. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):92–94. doi: 10.1038/283092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins G. G., Anson J., Kelly E. P. Baclofen: effects on evoked field potentials and amino acid neurotransmitter release in the rat olfactory cortex slice. Brain Res. 1982 Apr 29;238(2):371–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Lodge D., Bornstein J. C., Peet M. J. Selective effects of (-)-baclofen on spinal synaptic transmission in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1981;42(2):158–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00236902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A., Sears E. S. The effects of Lioresal on synaptic activity in the isolated spinal cord. Neurology. 1974 Oct;24(10):957–963. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.10.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R. Possible mechanisms of enkephalin action on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 1981 Sep;1(9):1022–1035. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-09-01022.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K. Two types of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor on embryonic sensory neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;74(3):579–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox S., Krnjević K., Morris M. E., Puil E., Werman R. Action of baclofen on mammalian synaptic transmission. Neuroscience. 1978;3(6):495–515. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjerstad L., Andersen P., Langmoen I. A., Lundervold A., Hablitz J. Synaptic triggering of epileptiform discharges in Ca2 pyramidal cells in vitro. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Oct;113(2):245–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hablitz J. J., Johnston D. Endogenous nature of spontaneous bursting in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1981 Dec;1(4):325–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00716267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Bowery N. G. 3H-baclofen and 3H-GABA bind to bicuculline-insensitive GABA B sites in rat brain. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):149–152. doi: 10.1038/290149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. A., Hailstone M. H., Freeman C. G. Baclofen: stereoselective inhibition of excitant amino acid release. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;32(3):230–231. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1980.tb12902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles W. D., Schwartzkroin P. A. Local circuit synaptic interactions in hippocampal brain slices. J Neurosci. 1981 Mar;1(3):318–322. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-03-00318.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutsson E., Lindblom U., Mårtensson A. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid levels of baclofen (Lioresal) at optimal therapeutic responses in spastic paresis. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Nov;23(3):473–484. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo Y., Kurachi M., Fukuda H. An apparent excitatory action of baclofen on the isolated perfused spinal cord of the frog. Gen Pharmacol. 1981;12(3):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(81)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanthorn T. H., Cotman C. W. Baclofen selectively inhibits excitatory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 23;225(1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90326-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacVicar B. A., Dudek F. E. Electrotonic coupling between granule cells of rat dentate gyrus: physiological and anatomical evidence. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Apr;47(4):579–592. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.47.4.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olpe H. R., Baudry M., Fagni L., Lynch G. The blocking action of baclofen on excitatory transmission in the rat hippocampal slice. J Neurosci. 1982 Jun;2(6):698–703. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-06-00698.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Leeb-Lundberg F. Convulsant and anticonvulsant drug binding sites related to GABA-regulated chloride ion channels. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1981;26:93–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potashner S. J. Baclofen: effects on amino acid release and metabolism in slices of guinea pig cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1979 Jan;32(1):103–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince D. A. Neurophysiology of epilepsy. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:395–415. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Prince D. A. Cellular and field potential properties of epileptogenic hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1978 May 19;147(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90776-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Prince D. A. Changes in excitatory and inhibitory synaptic potentials leading to epileptogenic activity. Brain Res. 1980 Feb 3;183(1):61–76. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm-Mathisen J. Localization of transmitter candidates in the brain: the hippocampal formation as a model. Prog Neurobiol. 1977;8(2):119–181. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(77)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. P., Dudek F. E. A physiological test for electrotonic coupling between CA1 pyramidal cells in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1982 Mar 11;235(2):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub R. D., Wong R. K. Cellular mechanism of neuronal synchronization in epilepsy. Science. 1982 May 14;216(4547):745–747. doi: 10.1126/science.7079735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub R. D., Wong R. K. Penicillin-induced epileptiform activity in the hippocampal slice: a model of synchronization of CA3 pyramidal cell bursting. Neuroscience. 1981;6(2):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White W. F., Nadler J. V., Cotman C. W. A perfusion chamber for the study of CNS physiology and pharmacology in vitro. Brain Res. 1978 Sep 8;152(3):591–596. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A. Afterpotential generation in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jan;45(1):86–97. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto C. Intracellular study of seizure-like afterdischarges elicited in thin hippocampal sections in vitro. Exp Neurol. 1972 Apr;35(1):154–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(72)90066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto C., Kawai N. Generation of the seizure discharge in thin sections from the guinea pig brain in chloride-free medium in vitro. Jpn J Physiol. 1968 Oct 15;18(5):620–631. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.18.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



