Abstract
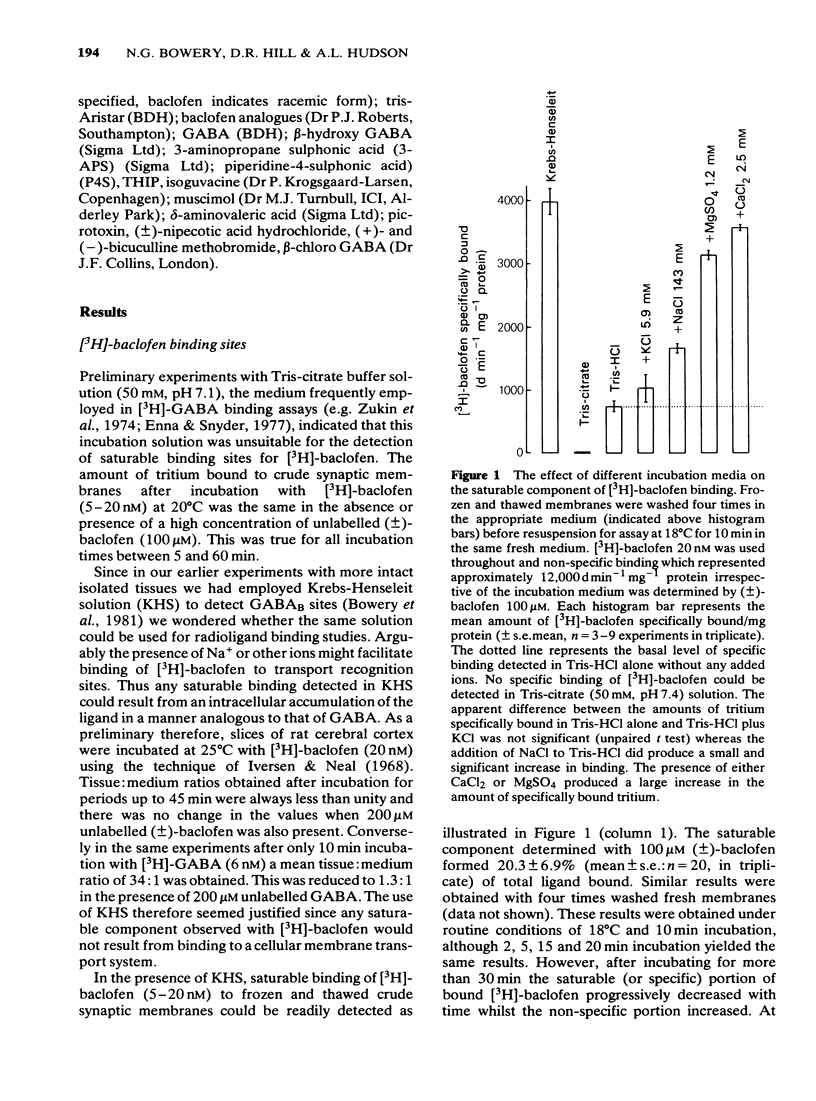
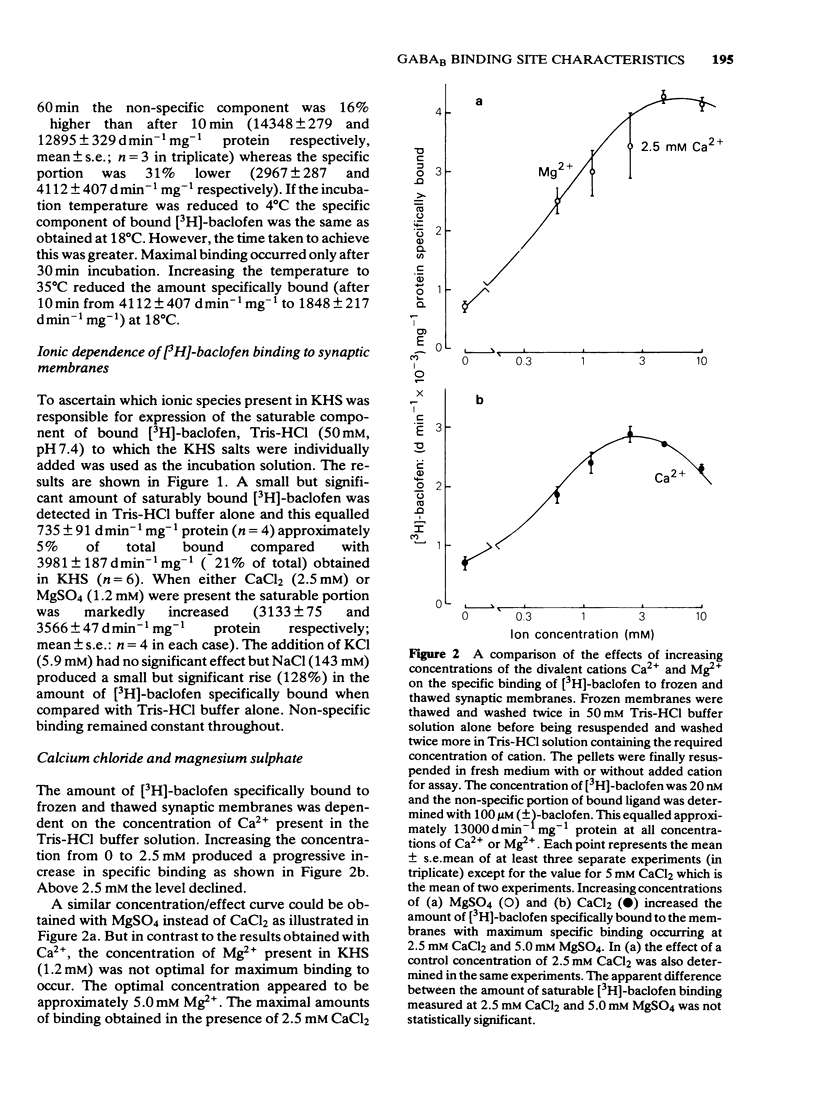
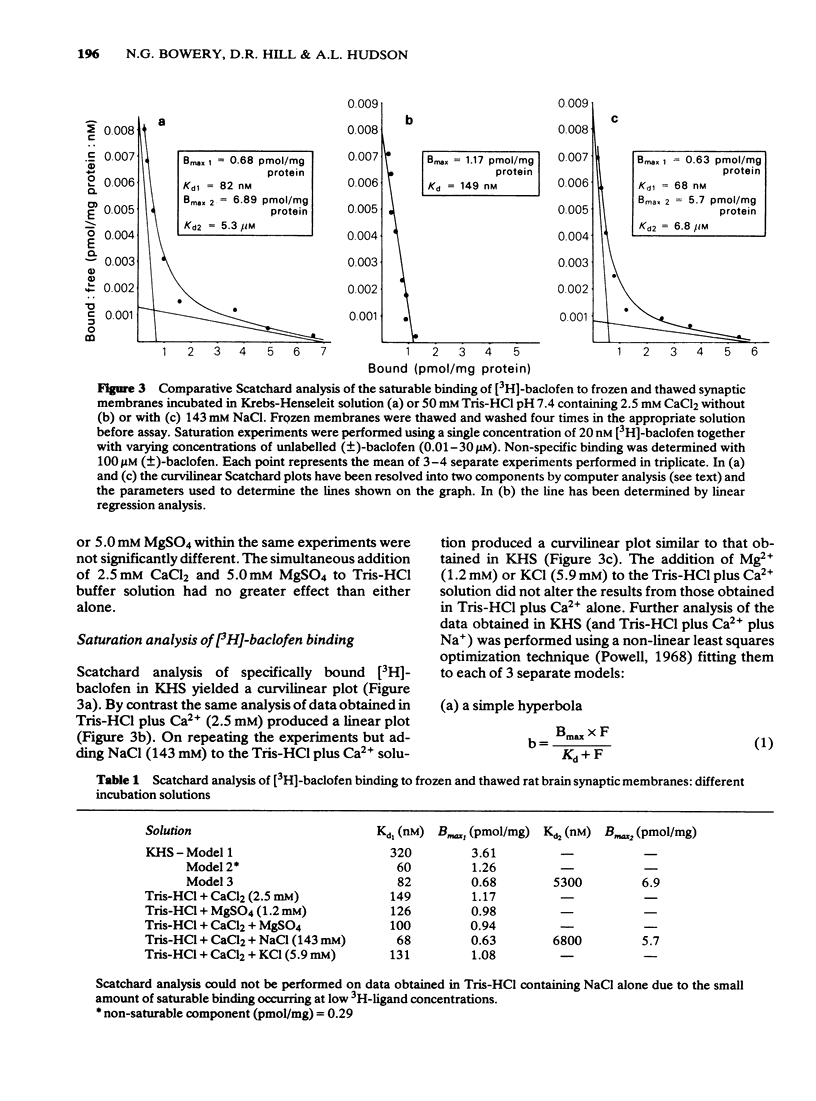
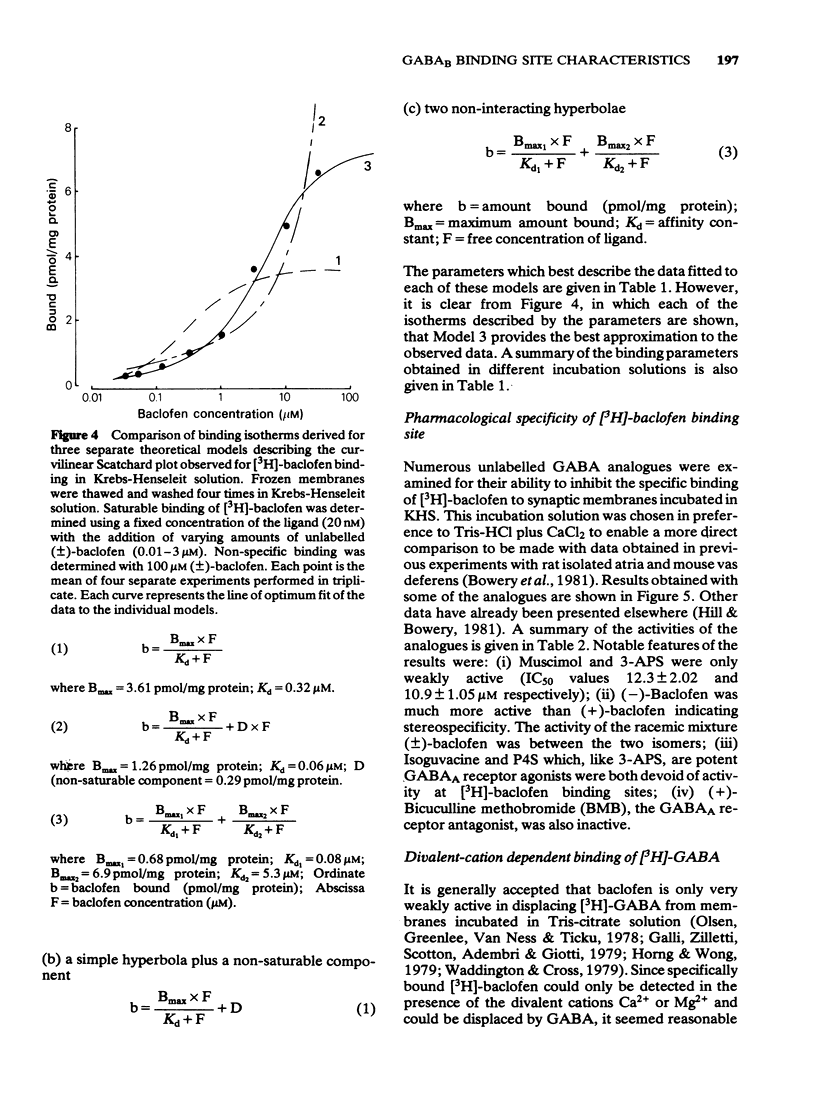
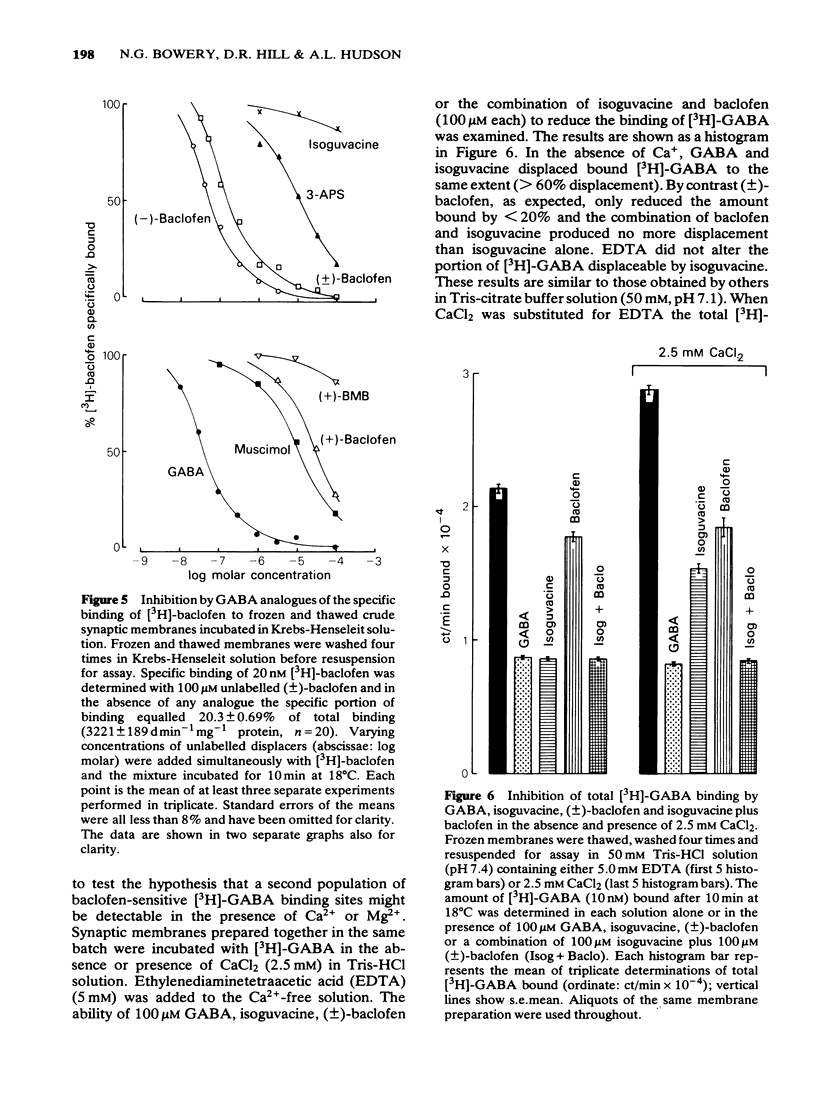
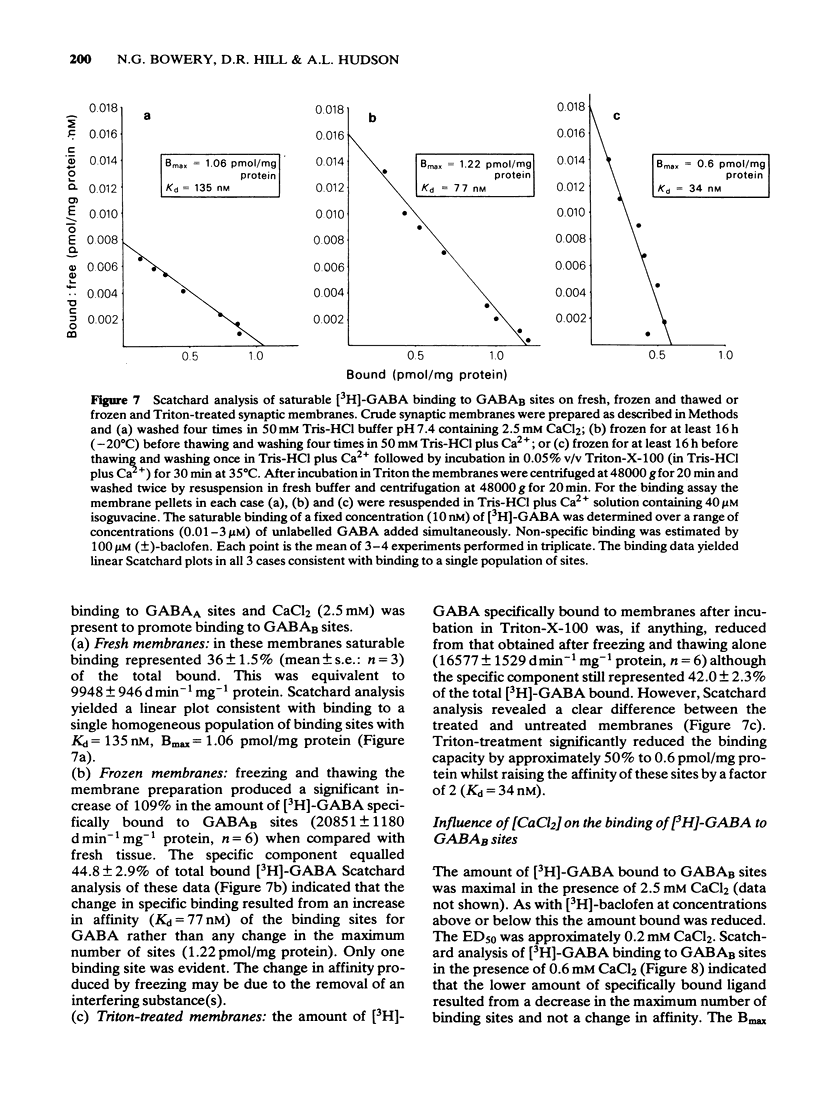
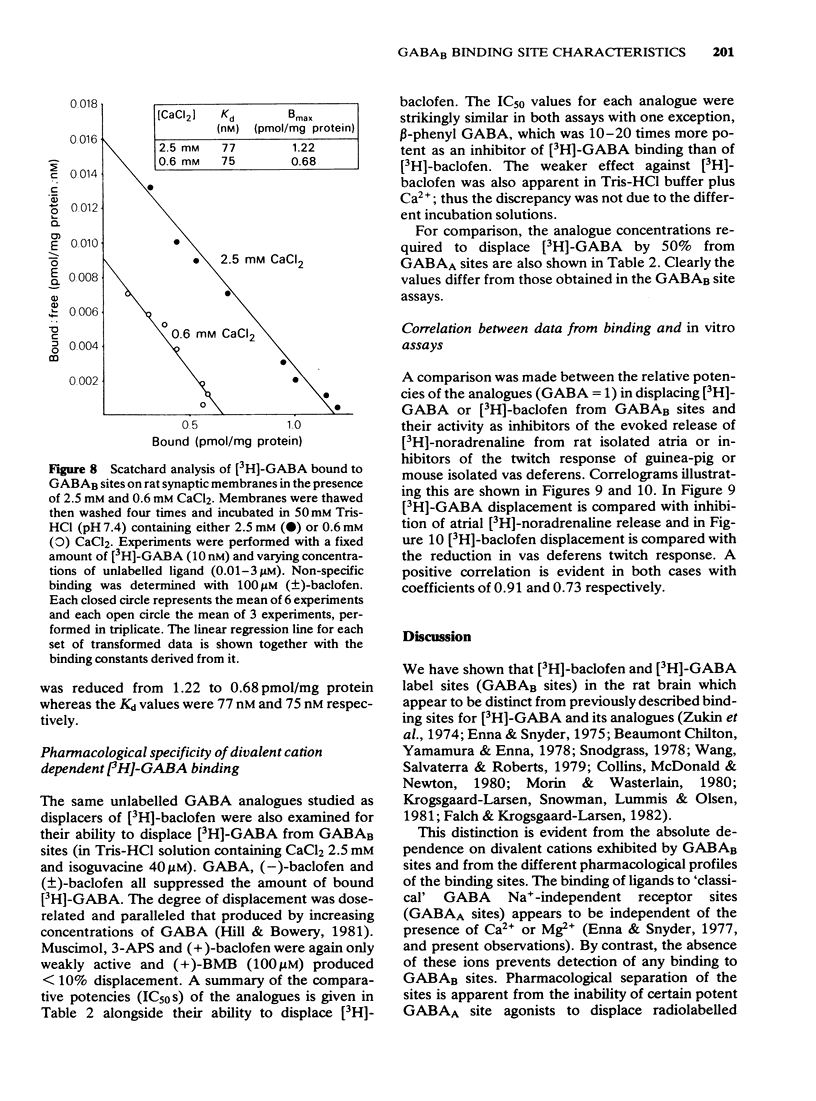
1 Saturable binding of (+/-)-[3H]-baclofen and [3H]-gamma- aminobutyric acid ([3H]-GABA) to rat brain crude synaptic membranes has been examined by means of a centrifugation assay. 2 The binding of [3H]-baclofen could be detected in fresh or previously frozen tissue and was dependent on the presence of physiological concentrations of Ca2+ or Mg2+ although a lower affinity Na+ -dependent component could also be observed. Both components probably reflect binding to receptor recognition sites. 3 The saturable portion of bound [3H]-baclofen formed 20.3 +/- 6.9% of total bound ligand. This could be displaced by GABA (IC50 = 0.04 microM), (-)-baclofen (0.04 microM) and to a much lesser extent by (+)-baclofen (33 microM). Isoguvacine, piperidine-4-sulphonic acid and bicuculline methobromide were inactive (up to 100 microM) and muscimol was only weakly active (IC50 = 12.3 microM). 4 Saturable binding of [3H]-GABA increased on adding CaCl2 or MgSO4 (up to 2.5 mM and 5.0 mM respectively) to the Tris-HCl incubation solution. This binding (GABAB site binding) was additional to the bicuculline-sensitive binding of GABA (GABAA site binding) and could be completely displaced by (-)-baclofen (IC50 = 0.13 microM). 5 Increasing the Ca2+ concentration (0 to 2.5 mM) increased the binding capacity of the membranes without changing their affinity for the ligand. 6 The binding of [3H]-GABA to GABAB sites could be demonstrated in fresh as well as previously frozen membranes with a doubling of the affinity being produced by freezing. Further incubation with the non-ionic detergent Triton-X-100 (0.05% v/v) reduced the binding capacity by 50%. 7 The pharmacological profile of displacers of [3H]-GABA from GABAB sites correlated well with that for [3H]-baclofen displacement. A correlation with data previously obtained in isolated preparations of rat atria and mouse vas deferens was also apparent. 8 It is concluded that [3H]-baclofen or [3H]-GABA are both ligands for the same bicuculline-insensitive, divalent cation-dependent binding sites in the rat brain.
Full text
PDF


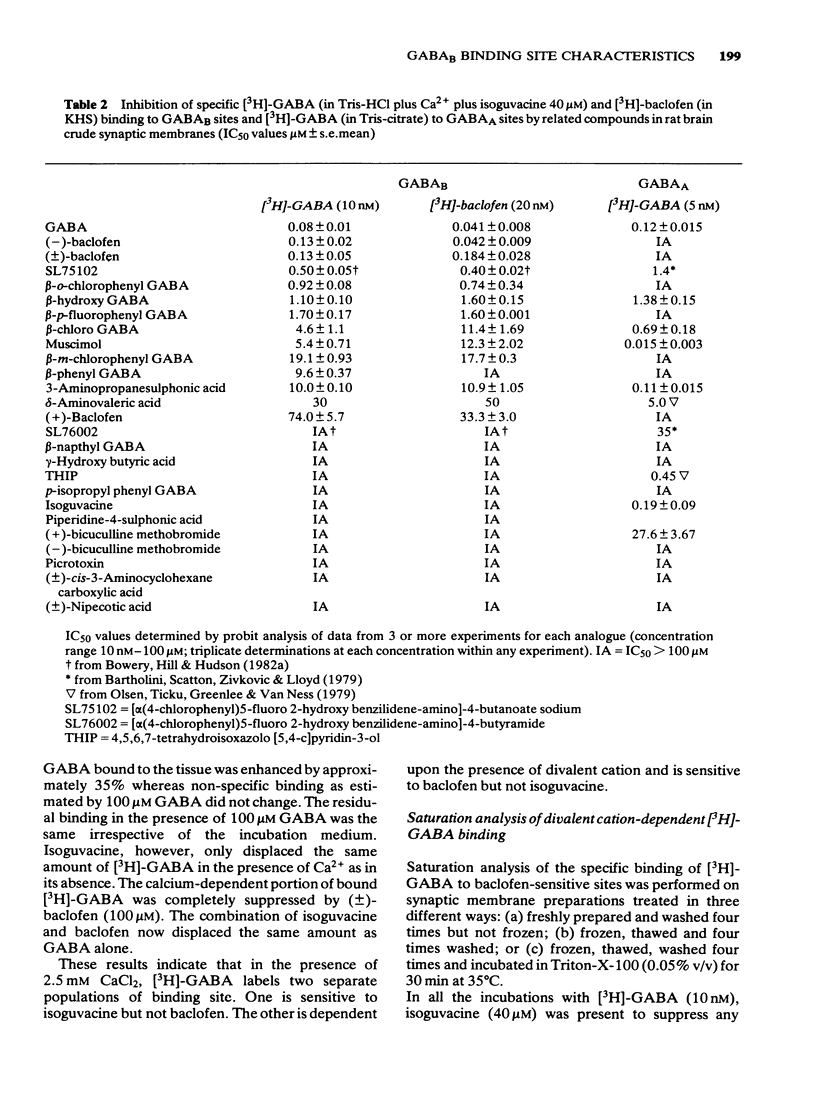




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwar N., Mason D. F. Two actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid on the responses of the isolated basilar artery from the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):177–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08770.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Evans R. H. Central depressant action of baclofen [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:131P–131P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont K., Chilton W. S., Yamamura H. I., Enna S. J. Muscimol binding in rat brain: association with synaptic GABA receptors. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 9;148(1):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Brown D. A. Depolarizing actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid and related compounds on rat superior cervical ganglia in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;50(2):205–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb08563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Doble A., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L., Shaw J. S., Turnbull M. J., Warrington R. Bicuculline-insensitive GABA receptors on peripheral autonomic nerve terminals. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 24;71(1):53–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L., Doble A., Middlemiss D. N., Shaw J., Turnbull M. (-)Baclofen decreases neurotransmitter release in the mammalian CNS by an action at a novel GABA receptor. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):92–94. doi: 10.1038/283092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L. Evidence that SL75102 is an agonist at GABAb as well as GABAa receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1982 May;21(5):391–395. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(82)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hudson A. L. gamma-Aminobutyric acid reduces the evoked release of [3H]-noradrenaline from sympathetic nerve terminals [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 May;66(1):108P–108P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Nielsen M., Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Falch E. Partial agonists for brain GABA/benzodiazepine receptor complex. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):331–333. doi: 10.1038/280331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. J., Cantrill R. C. Delta-aminolaevulinic acid is a potent agonist for GABA autoreceptors. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):514–515. doi: 10.1038/280514a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Felix D., Johnston G. A. GABA, bicuculline and central inhibition. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1222–1224. doi: 10.1038/2261222a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Game C. J., Johnston G. A., McCulloch R. M. Central effects of beta-(para-chlorophenyl)-gamma-aminobutyric acid. Brain Res. 1974 Apr 26;70(3):493–499. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90257-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Johnston G. A. Amino acid transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Ergeb Physiol. 1974;69(0):97–188. doi: 10.1007/3-540-06498-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Lodge D., Bornstein J. C., Peet M. J. Selective effects of (-)-baclofen on spinal synaptic transmission in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1981;42(2):158–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00236902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A., Sears E. S. The effects of Lioresal on synaptic activity in the isolated spinal cord. Neurology. 1974 Oct;24(10):957–963. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.10.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. Selective depression of synaptic excitation in cat spinal neurones by baclofen: an iontophoretic study. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;72(2):373–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. The action of beta-phenyl-GABA derivatives on neurones of the cat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1974 Apr 26;70(3):501–505. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K. Two types of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor on embryonic sensory neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;74(3):579–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J. GABA receptor pharmacology. Functional considerations. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 May 1;30(9):907–913. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Influences ions, enzymes, and detergents on gamma-aminobutyric acid-receptor binding in synaptic membranes of rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 May;13(3):442–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Properties of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor binding in rat brain synaptic membrane fractions. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 12;100(1):81–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falch E., Krogsgaard-Larsen P. The binding of the GABA agonist [3H]THIP to rat brain synaptic membranes. J Neurochem. 1982 Apr;38(4):1123–1129. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb05357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox S., Krnjević K., Morris M. E., Puil E., Werman R. Action of baclofen on mammalian synaptic transmission. Neuroscience. 1978;3(6):495–515. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G., WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli A., Zilletti L., Scotton M., Adembri G., Giotti A. Inhibition of Na+-independent [3H]GABA binding to synaptic membranes of rat brain by beta-substituted GABA derivatives. J Neurochem. 1979 Mar;32(3):1123–1125. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner C. R., Klein J., Grove J. Endogenous GABA determines the characteristics of [3H]GABA-binding. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Oct 22;75(2-3):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Gale K., Suria A., Toffano G. Biochemical evidence for two classes of GABA receptors in rat brain. Brain Res. 1979 Aug 31;172(3):566–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90590-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Bowery N. G. 3H-baclofen and 3H-GABA bind to bicuculline-insensitive GABA B sites in rat brain. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):149–152. doi: 10.1038/290149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horng J. S., Wong D. T. gamma-Aminobutyric acid receptors in cerebellar membranes of rat brain after a treatment with Triton X-100. J Neurochem. 1979 May;32(5):1379–1386. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Neal M. J. The uptake of [3H]GABA by slices of rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1968 Oct;15(10):1141–1149. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb06831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karobath M., Placheta P., Lippitsch M., Krogsgaard-Larsen P. Is stimulation of benzodiazepine receptor binding mediated by a novel GABA receptor? Nature. 1979 Apr 19;278(5706):748–749. doi: 10.1038/278748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Falch E., Schousboe A., Curtis D. R., Lodge D. Piperidine-4-sulphonic acid, a new specific GABA agonist. J Neurochem. 1980 Mar;34(3):756–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Johnston G. A., Lodge D., Curtis D. R. A new class of GABA agonist. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):53–55. doi: 10.1038/268053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Snowman A., Lummis S. C., Olsen R. W. Characterization of the binding of the GABA agonist [3H]piperidine-4-sulphonic acid to bovine brain synaptic membranes. J Neurochem. 1981 Aug;37(2):401–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. G., Arbilla S., Beaumont K., Briley M., De Montis G., Scatton B., Langer S. Z., Bartholini G. gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor stimulation. II. Specificity of progabide (SL 76002) and SL 75102 for the GABA receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Mar;220(3):672–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. R., Martin I. L. Is GABA release modulated by presynaptic receptors? Nature. 1978 Aug 31;274(5674):904–905. doi: 10.1038/274904a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin A. M., Wasterlain C. G. The binding of 3H-isoguvacine to mouse brain synaptic membranes. Life Sci. 1980 Apr 14;26(15):1239–1245. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhyaddin M., Roberts P. J., Woodruff G. N. Presynaptic gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors in the rat anococcygeus muscle and their antagonism by 5-aminovaleric acid. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;77(1):163–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napias C., Bergman M. O., Van Ness P. C., Greenlee D. V., Olsen R. W. GABA binding in mammalian brain: inhibition by endogenous GABA. Life Sci. 1980 Sep 15;27(11):1001–1011. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nistri A., Constanti A. Pharmacological characterization of different types of GABA and glutamate receptors in vertebrates and invertebrates. Prog Neurobiol. 1979;13(2):117–235. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(79)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olpe H. R., Demiéville H., Baltzer V., Bencze W. L., Koella W. P., Wolf P., Haas H. L. The biological activity of d- and l-baclofen (Lioresal). Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Nov 1;52(1):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olpe H. R., Koella W. P., Wolf P., Haas H. L. The action of baclofen on neurons of the substantia nigra and of the ventral tegmental area. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 14;134(3):577–580. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90834-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottaway J. H. Normalization in the fitting of data by iterative methods. Application to tracer kinetics and enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;134(3):729–736. doi: 10.1042/bj1340729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potashner S. J. Baclofen: effects on amino acid release and metabolism in slices of guinea pig cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1979 Jan;32(1):103–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass S. R. Use of 3H-muscimol for GABA receptor studies. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):392–394. doi: 10.1038/273392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Weitzell R. gamma-Aminobutyric acid and postganglionic sympathetic transmission in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. J Auton Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;1(1):45–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1980.tb00440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. The effects of 4-aminopyridine on the isolated vas deferens and its effects on the inhibitory properties of adenosine, morphine, noradrenaline and gamma-aminobutyric acid. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;73(3):791–796. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb16817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallman J. F., Thomas J. W., Gallager D. W. GABAergic modulation of benzodiazepine binding site sensitivity. Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):383–385. doi: 10.1038/274383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardy M., Rolland B., Bardakjian J., Gonnard P. Action of beta-(4-chlorophenyl-GABA) on uptake and metabolism of GABA in different subcellular fractions of rat brain. Experientia. 1978 Sep 15;34(9):1137–1138. doi: 10.1007/BF01922915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toffano G., Guidotti A., Costa E. Purification of an endogenous protein inhibitor of the high affinity binding of gamma-aminobutyric acid to synaptic membranes of rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4024–4028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddington J. L., Cross A. J. Baclofen and muscimol: behavioural and neurochemical sequelae of unilateral intranigral administration and effects on 3H-GABA receptor binding. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;306(3):275–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00507114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. J., Salvaterra P., Roberts E. Characterization of [3H]muscimol binding to mouse brain membranes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Apr 1;28(7):1123–1128. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90316-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkin G. P., Hudson A. L., Hill D. R., Bowery N. G. Autoradiographic localization of GABAB receptors in rat cerebellum. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):584–587. doi: 10.1038/294584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda Y., Kuriyama K. Presence of a low molecular weight endogenous inhibitor on 3H-muscimol binding in synaptic membranes. Nature. 1980 Jun 26;285(5767):670–673. doi: 10.1038/285670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4802–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


