Abstract
1 Tetraethylammonium (TEA, 1-8 mmol/l) evoked spasm of guinea-pig trachealis which was unaffected by atropine (1 mumol/l), mepyramine (1 mumol/l) or tetrodotoxin (3 mumol/l). 2 The spasm evoked by TEA was markedly suppressed in Ca2+-free Krebs solution while that evoked by acetylcholine was much less affected. 3 Extracellular electrical recording showed that exposure to Ca2+-free Krebs solution suppressed both spontaneous electrical slow wave activity of the trachea and the spasm and slow waves induced by TEA. These effects were reversible. 4 TEA (2 and 8 mmol/l) increased the lanthanum-resistant calcium fraction of trachea. 5 It is concluded that TEA acts directly on the smooth muscle of guinea-pig trachea, that the spasm and electrical slow waves evoked are Ca2+-dependent and that the cellular influx of Ca2+ is increased.
Full text
PDF

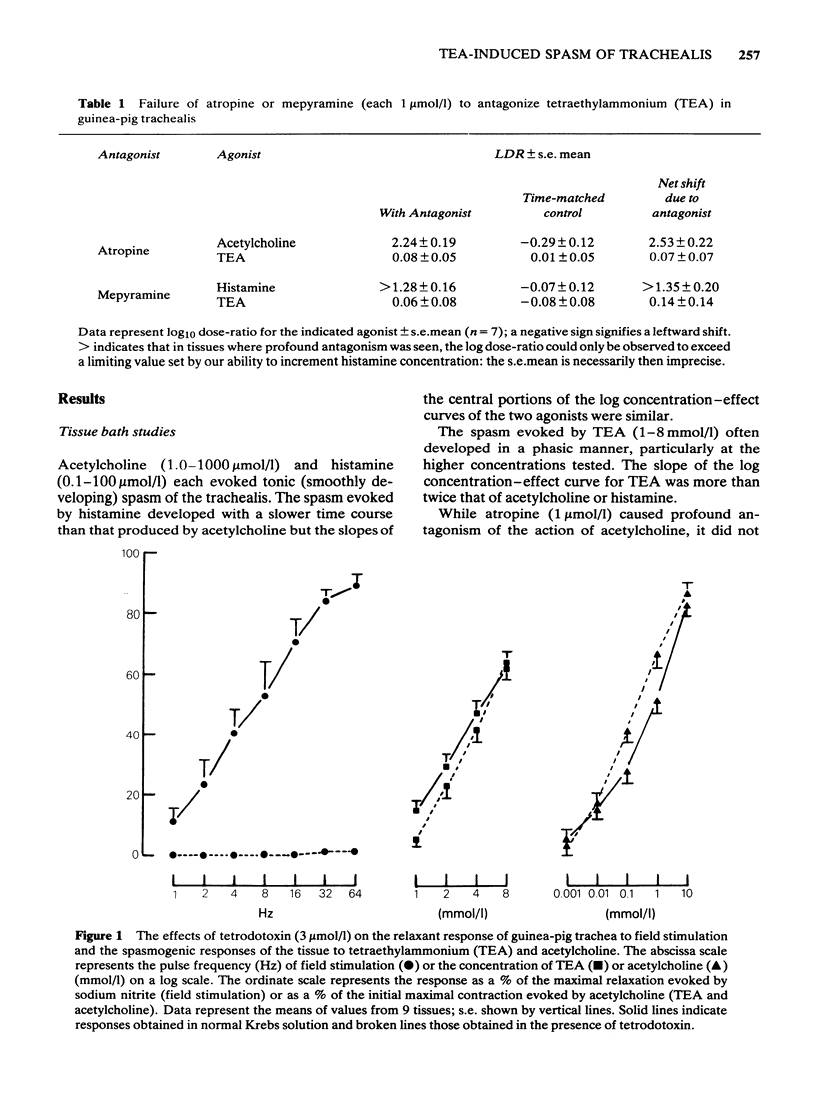
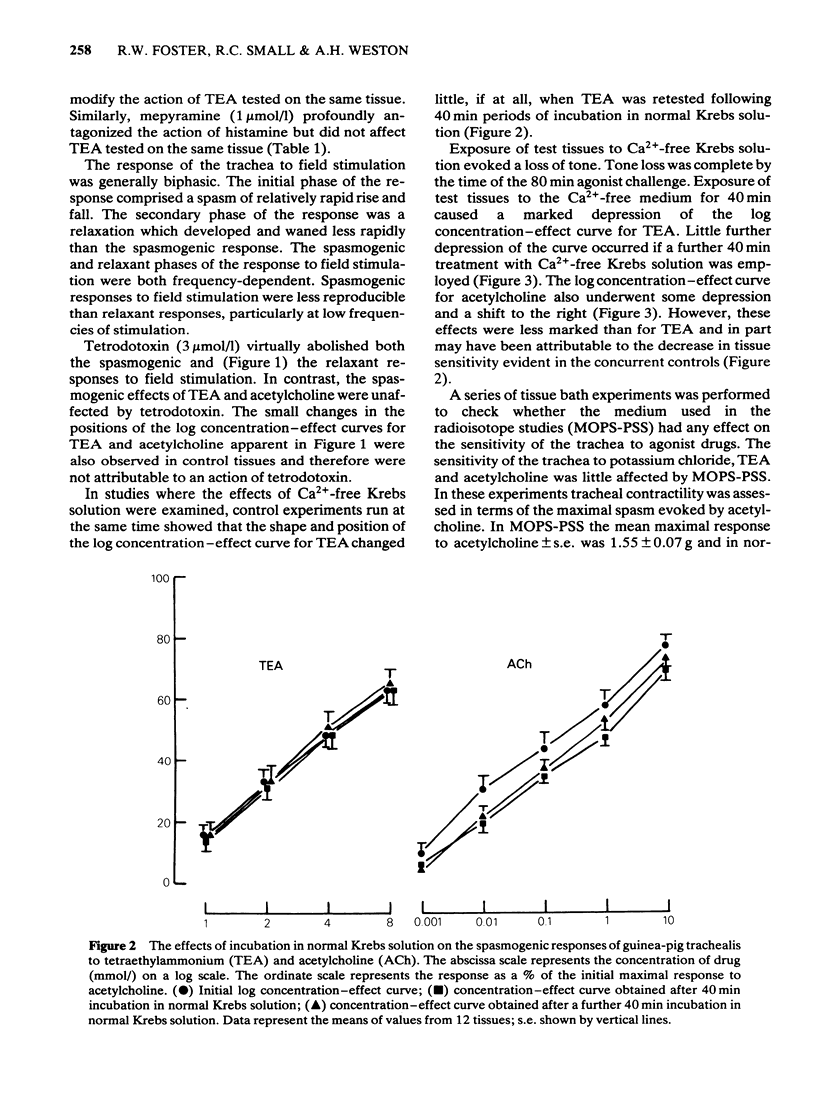
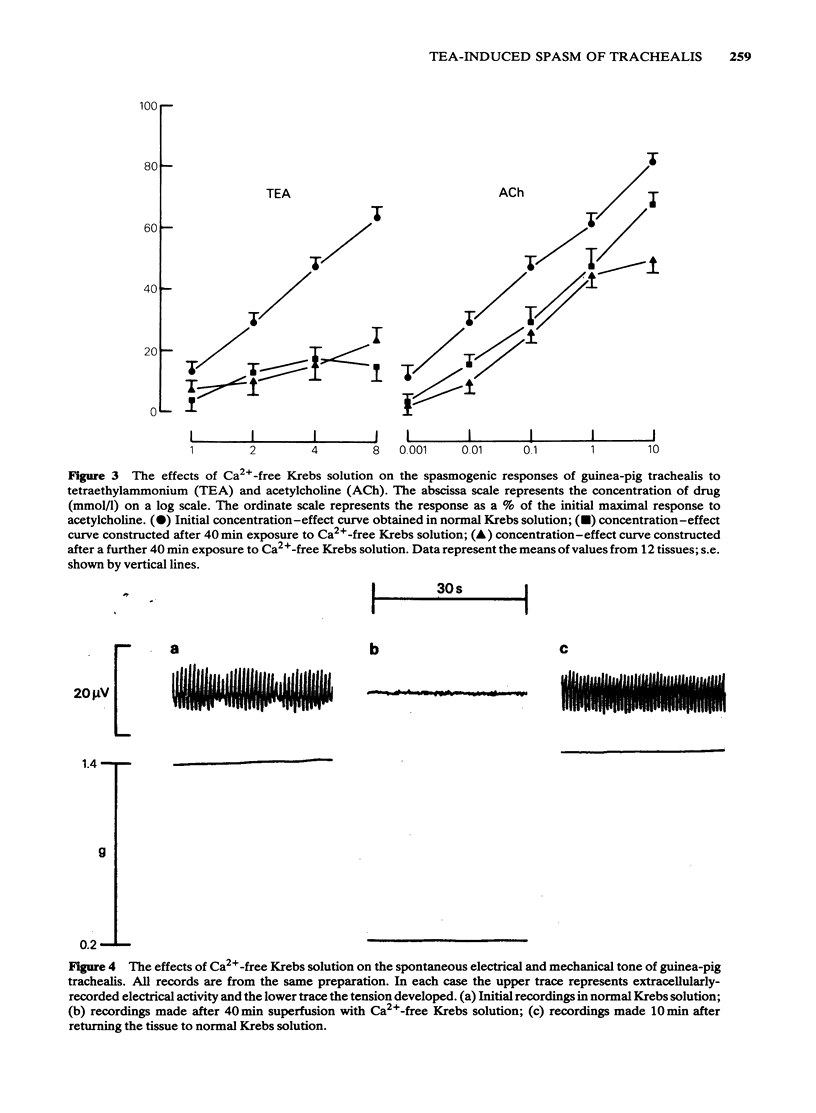
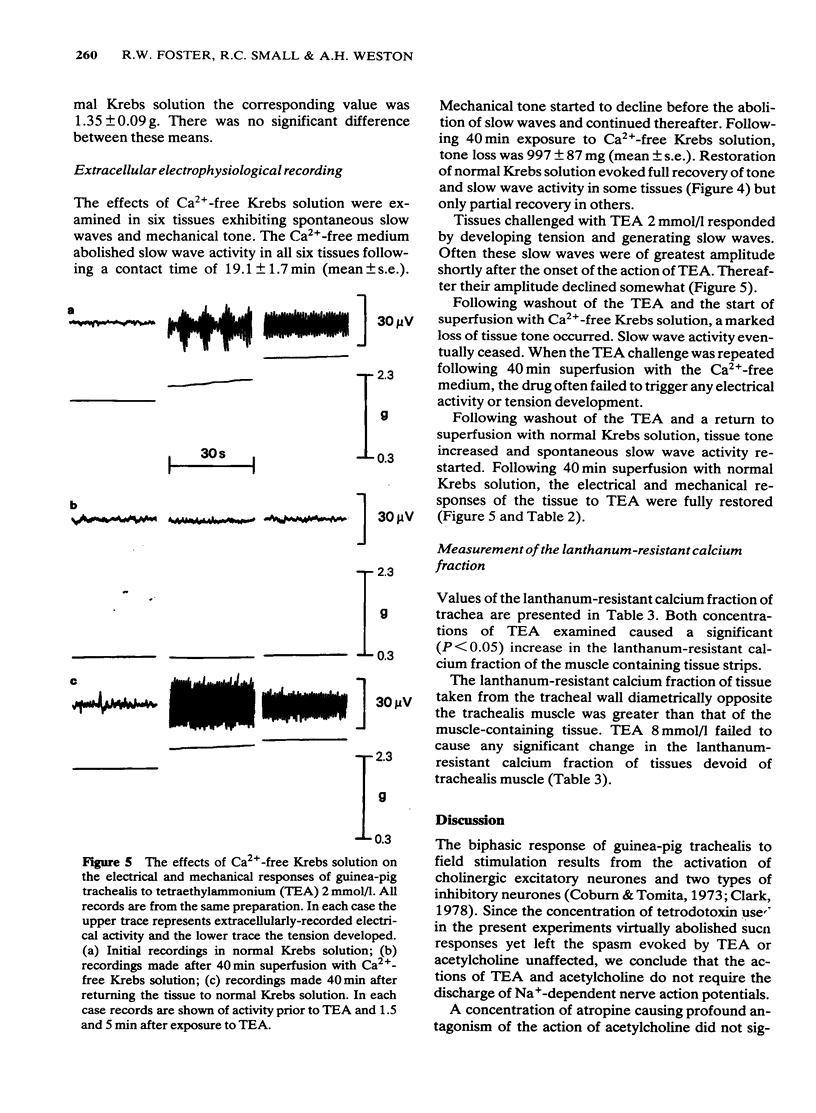


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coburn R. F., Tomita T. Evidence for nonadrenergic inhibitory nerves in the guinea pig trachealis muscle. Am J Physiol. 1973 May;224(5):1072–1080. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.5.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese B. R., Denborough M. A. Sources of calcium for contraction of guinea-pig isolated tracheal smooth muscle. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1981 Mar-Apr;8(2):175–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1981.tb00149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetley M., Weston A. H. Some effects of sodium nitroprusside, methoxyverapamil (D600) and nifedipine on rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;68(2):311–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10420.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannan M. S., Daniel E. E. Formation of gap junctions by treatment in vitro with potassium conductance blockers. J Cell Biol. 1978 Aug;78(2):338–348. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.2.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick C. T. Excitation and contraction in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):263–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroeger E. A., Stephens N. L. Effect of tetraethylammonium on tonic airway smooth muscle: initiation of phasic electrical activity. Am J Physiol. 1975 Feb;228(2):633–636. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.2.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small R. C. Electrical slow waves and tone of guinea-pig isolated trachealis muscle: effects of drugs and temperature changes. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;77(1):45–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


