Abstract
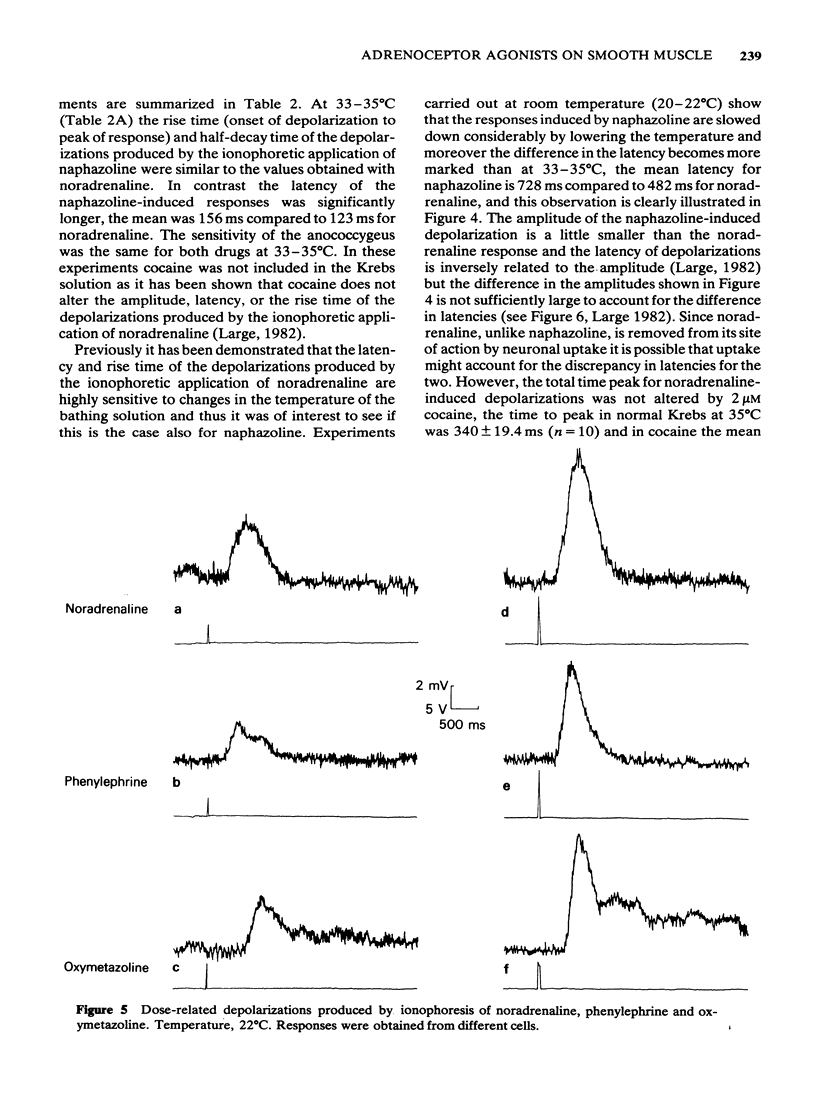
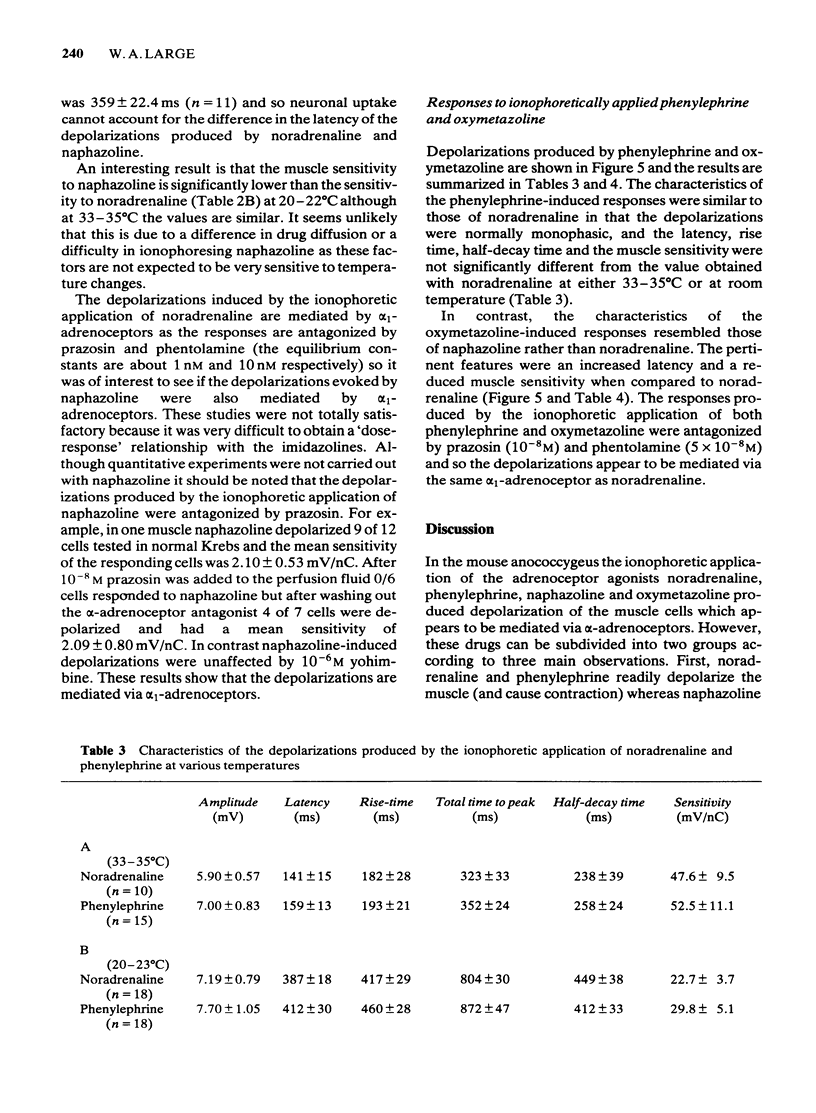
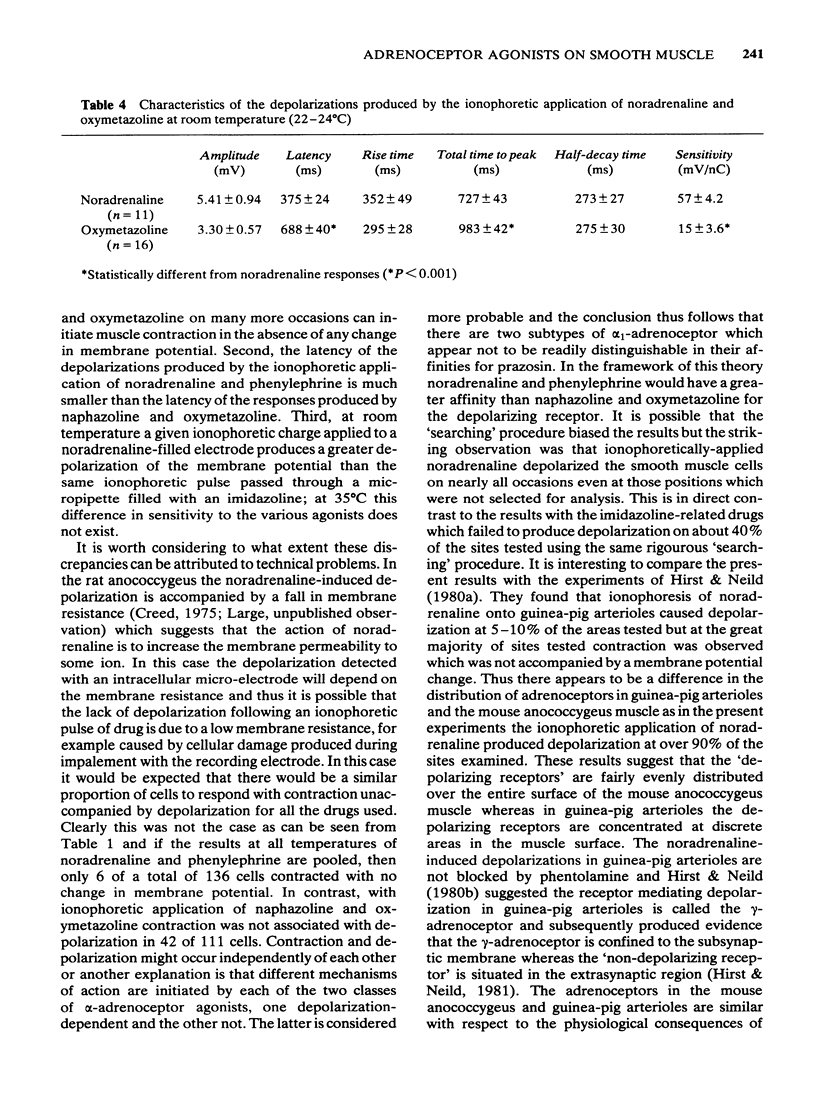
1 Noradrenaline phenylephrine, naphazoline and oxymetazoline were applied by ionophoresis to the mouse anococcygeus muscle and the membrane potential was recorded with an intracellular microelectrode. 2 The ionophoretic application of noradrenaline and phenylephrine produced dose-related depolarizations in 96% of the cells tested; in contrast, naphazoline and oxymetazoline depolarized only 62% of the cells although contraction was always seen. 3 The depolarizations produced by all four drugs had similar characteristics in shape and time course except that the latency of responses induced by the imidazoline-related drugs was significantly longer than the value obtained with the phenylethanolamines. This discrepancy was not due to the difference in susceptibility to neuronal uptake of the two groups of drugs. 4 The time to peak depolarization for naphazoline and oxymetazoline was longer than that for noradrenaline and phenylephrine but was not sufficient to account for the considerably slower contraction produced by the former drugs. 5 At room temperature the sensitivity of the mouse anococcygeus to ionophoretically applied naphazoline and oxymetazoline was significantly lower than that to noradrenaline and phenylephrine but at 35 degrees C the sensitivity was similar for all drugs. 6 These results suggest that there might be two subclasses of alpha 1-adrenoceptor in the mouse anococcygeus; stimulation of one type leads to depolarization and contraction and activation of the other class produces contraction with no change in membrane potential.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coates J., Jahn U., Weetman D. F. The existence of a new subtype of alpha-adrenoceptor on the rat anococcygeus is revealed by SGD 101/75 and phenoxybenzamine. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;75(3):549–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Large W. A., Rang H. P. An analysis of the action of a false transmitter at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(2):361–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creed K. E. Membrane properties of the smooth muscle cells of the rat anococcygeus muscle. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(1):49–62. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer F., Peper K. Iontophoretic application of acetylcholine: advantages of high resistance micropipettes in connection with an electronic current pump. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Apr 22;348(3):263–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00587417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson A., Wedmore C. V. Responses of the isolated anococcygeus muscle of the mouse to drugs and to field stimulation. J Auton Pharmacol. 1981 Jun;1(3):225–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1981.tb00451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. Evidence for two populations of excitatory receptors for noradrenaline on arteriolar smooth muscle. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):767–768. doi: 10.1038/283767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. Localization of specialized noradrenaline receptors at neuromuscular junctions on arterioles of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1981;313:343–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Large W. A. Membrane potential responses of the mouse anococcygeus muscle to ionophoretically applied noradrenaline. J Physiol. 1982 May;326:385–400. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Evidence for more than one type of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):467–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


