Abstract
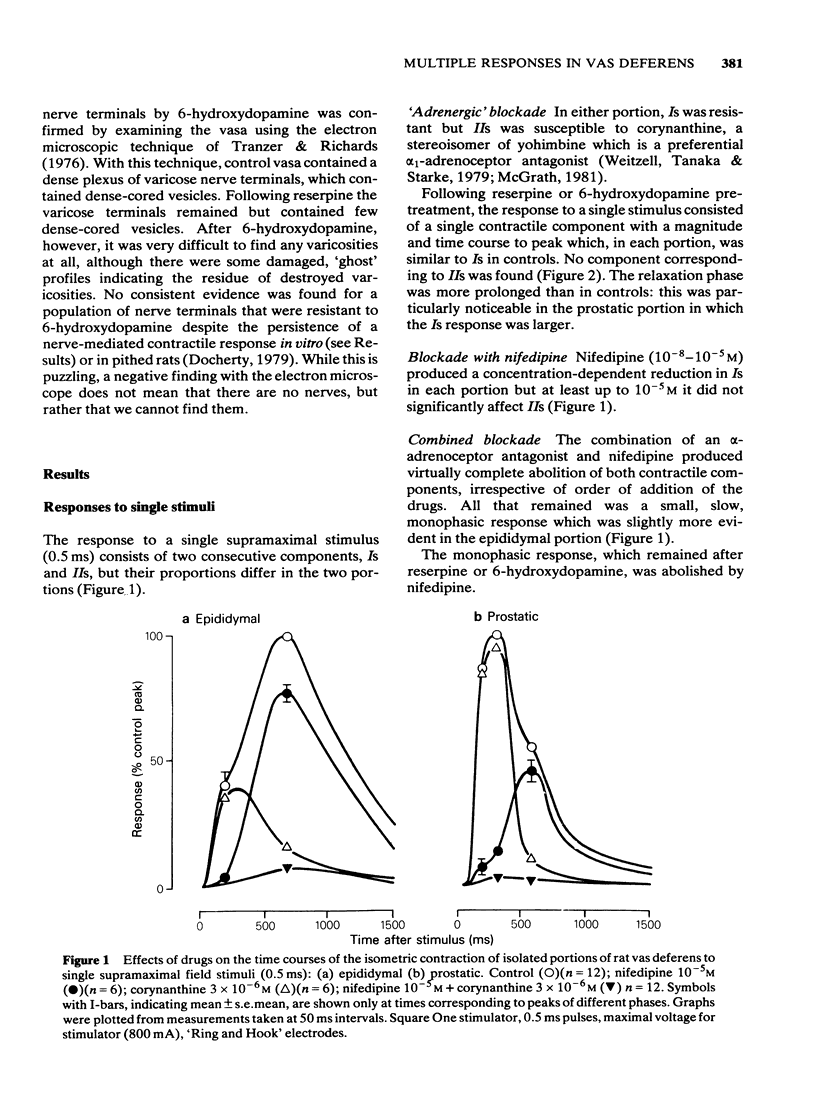
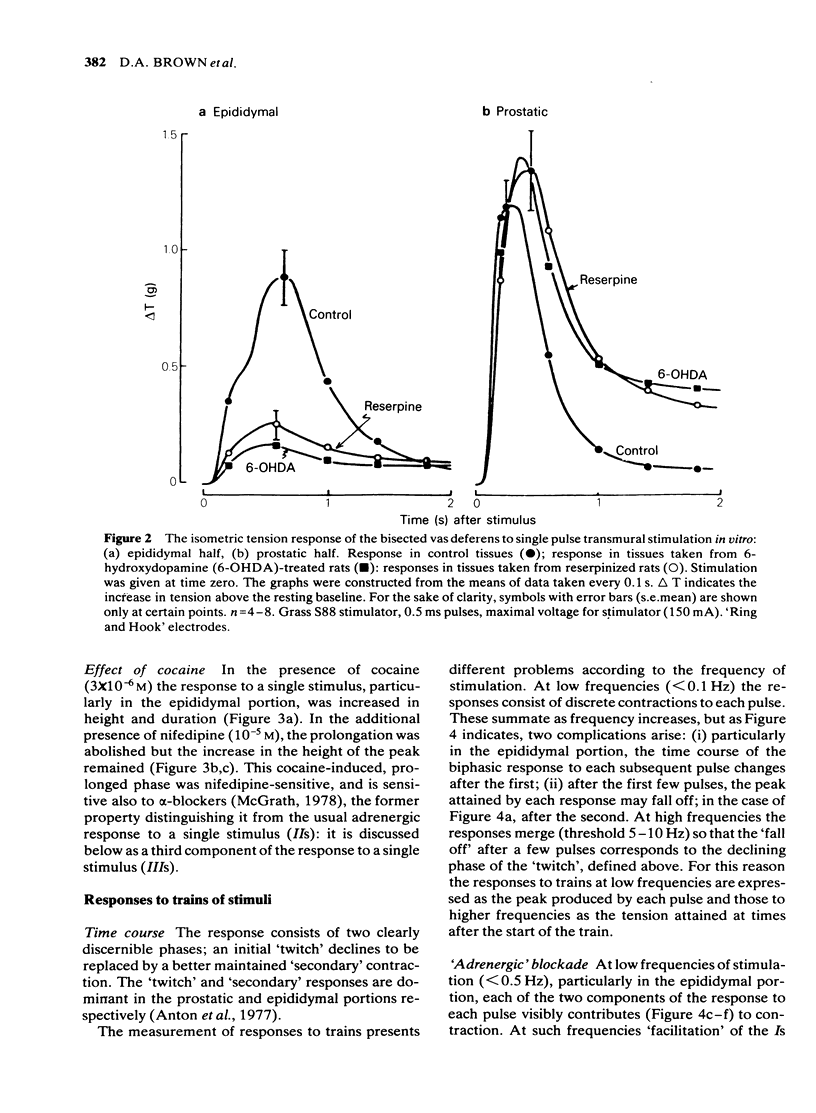
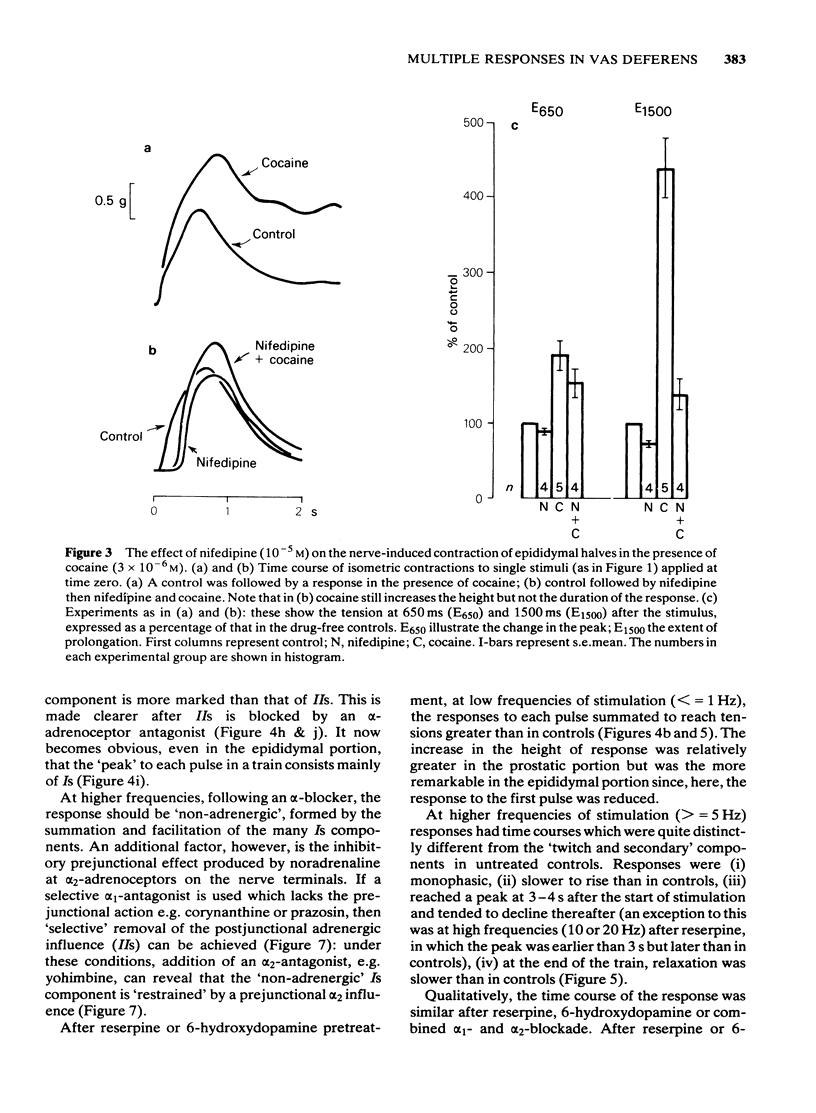
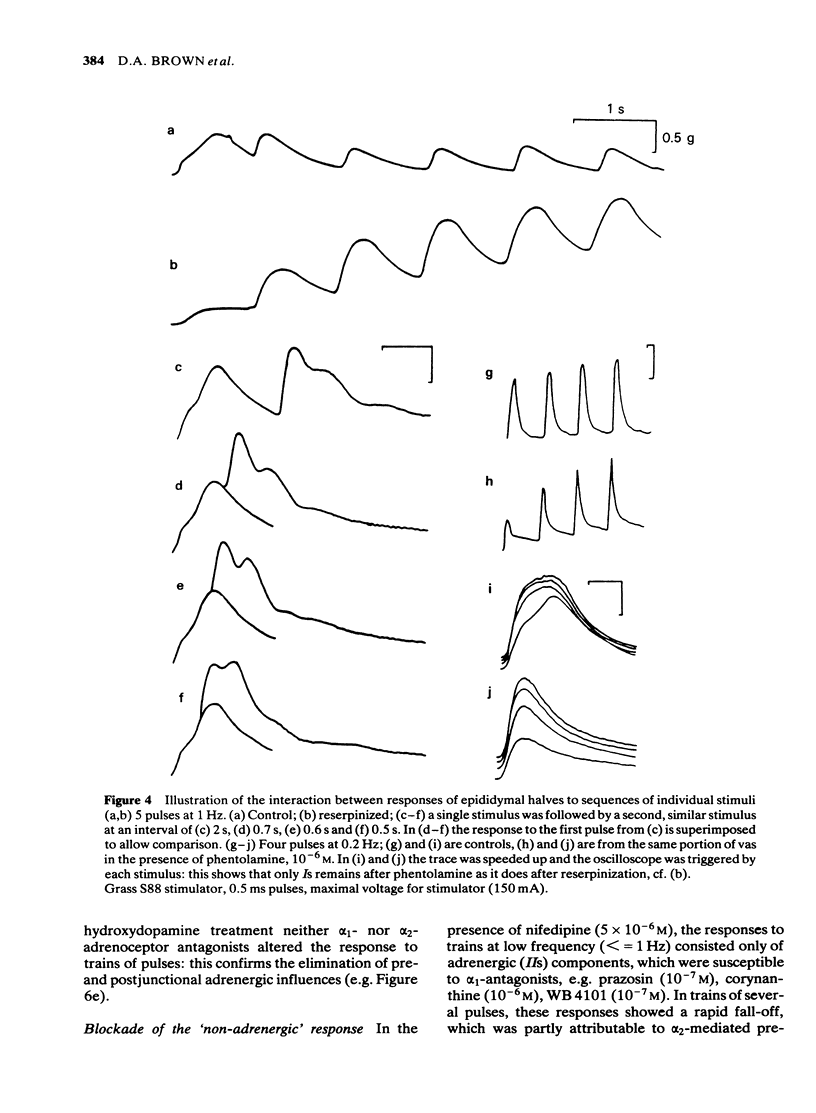
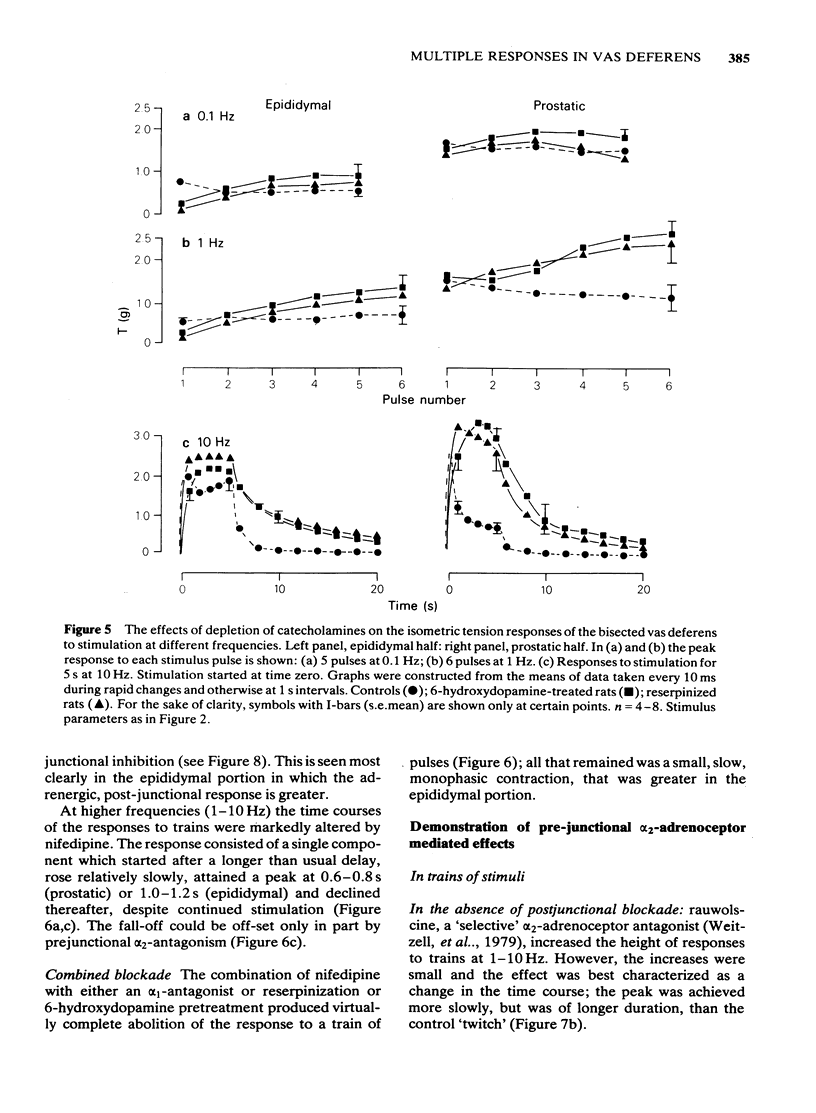
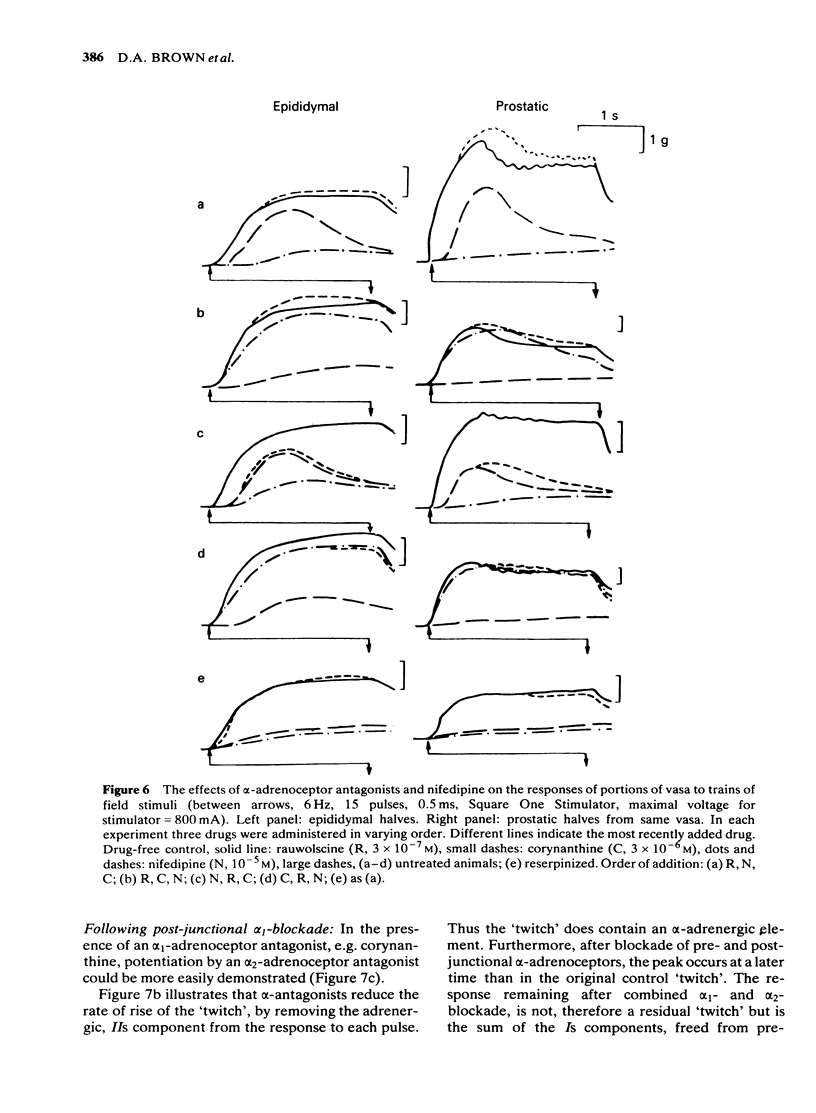
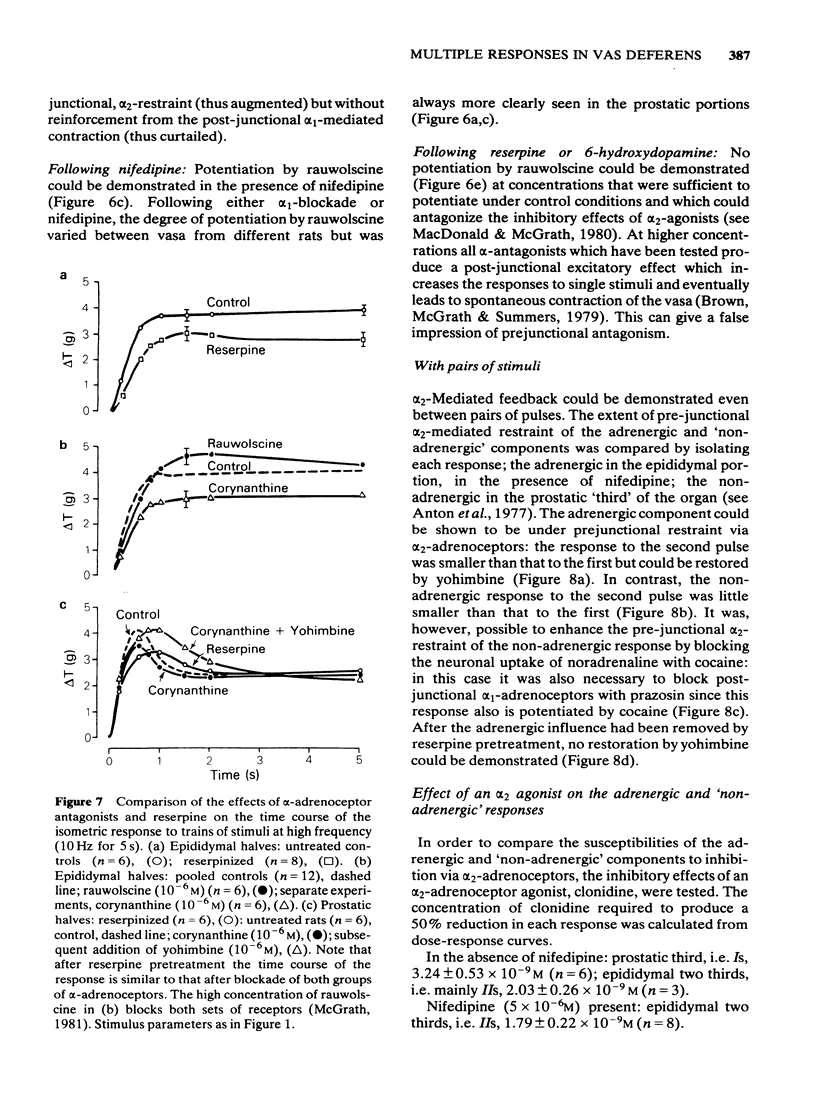
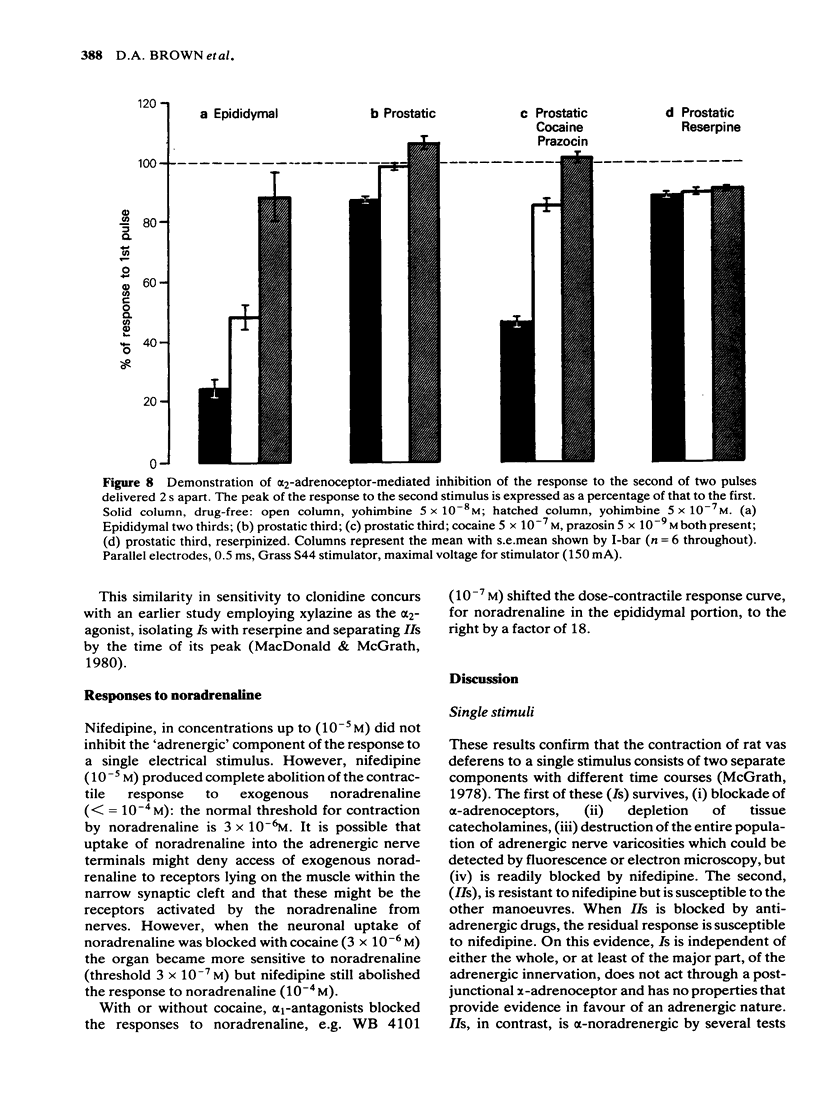
Adrenergic and 'non-adrenergic' nerve-induced contractions in rat vas deferens were separated pharmacologically. Responses to single stimuli comprised two components, an alpha-noradrenergic component (IIs), dominant in the epididymal portion, and a 'non-adrenergic' component (Is), dominant in the prostatic portion. Is but not IIs was blocked by nifedipine. A combination of adrenergic blockade and nifedipine virtually abolished all components. After cocaine, a third component (IIIs) emerged which was abolished by either adrenergic blockade or nifedipine. The response to trains of stimuli consisted of 'twitch' and 'secondary' components. This biphasic time course was modified by adrenergic blockade or nifedipine to reveal the time course of the 'non-adrenergic' and adrenergic components, respectively: these did not correspond to the 'twitch' and 'secondary' components. A combination of adrenergic blockade and nifedipine virtually abolished the whole response. Prejunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of the contractile responses could be blocked by selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists. The adrenergic contractile response demonstrated this 'feed-back' even on the second pulse at 0.5 Hz. Endogenous inhibition of the 'non-adrenergic' contraction required higher frequencies or enhancement of the extracellular concentration of noradrenaline by blockade of its neuronal uptake. Contractile responses to exogenous noradrenaline were abolished by nifedipine, at a concentration that did not affect the adrenergic (IIs) neurotransmission. These results reinforce the view that part of the motor transmission in rat vas deferens is non-adrenergic and allow the disentanglement of the various postjunctional and prejunctional elements contributing to the complex response to a train of stimuli.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambache N., Dunk L. P., Verney J., Zar M. A. Inhibition of post-ganglionic motor transmission in vas deferens by indirectly acting sympathomimetic drugs. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):433–456. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambache N., Zar M. A. Evidence against adrenergic motor transmission in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):359–389. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anton P. G., Duncan M. E., McGrath J. C. An analysis of the anatomical basis for the mechanical response to motor nerve stimulation of the rat vas deferens. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):23–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeley A. G., Brown D. A., Cunnane T. C., French A. M., McGrath J. C., Scott N. C. Effects of nifedipine on electrical and mechanical responses of rat and guinea pig vas deferens. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):759–761. doi: 10.1038/294759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth F. J., Connell G. J., Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. Isolation of the 'non-adrenergic' motor nerve response in rat vas deferens by elimination of the adrenergic motor component [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:19P–20P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., McGrath J. C., Summers R. J. The effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on responses of transmurally stimulated prostatic and epididymal portions of the isolated vas deferens of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;66(4):553–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb13694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Pharmacological characterisation of the presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in the rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar 21;42(2):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedan J. S., Hogaboom G. K., O'Donnell J. P., Colby J., Westfall D. P. Contribution by purines to the neurogenic response of the vas deferens of the guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 5;69(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90600-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French A. M., Scott N. C. A comparison of the effects of nifedipine and verapamil on rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Jun;73(2):321–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10424.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McGrath J. C. The effect of pithing and of nerve stimulation on the depletion of noradrenaline by reserpine in the rat anococcygeus muscle and vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Dec;52(4):585–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. A new example of a morphine-sensitive neuro-effector junction: adrenergic transmission in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Dec;46(4):764–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb06901.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. S. The kinetics of uptake of 5-fluorouracil by rat liver. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;77(3):413–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09313.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald A., McGrath J. C. The distribution of adrenoceptors and other drug receptors between the two ends of the rat vas deferens as revealed by selective agonists and antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):445–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Adrenergic and 'non-adrenergic' components in the contractile response of the vas deferens to a single indirect stimulus. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:23–39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Evidence for more than one type of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):467–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L. Differences in secretory excitability between short and long adrenergic neurons: comparison of 3H-noradrenaline secretion evoked by field stimulation of guinea-pig vas deferens and human blood vessels. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Jun;100(2):264–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb05947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranzer J. P., Richards J. G. Ultrastructural cytochemistry of biogenic amines in nervous tissue: methodologic improvements. J Histochem Cytochem. 1976 Nov;24(11):1178–1193. doi: 10.1177/24.11.63507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzell R., Tanaka T., Starke K. Pre- and postsynaptic effects of yohimbine stereoisomers on noradrenergic transmission in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;308(2):127–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00499054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Euler U. S. Acute neuromuscular transmission failure in vas deferens after reserpine. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 May-Jun;76(1):255–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


