Abstract
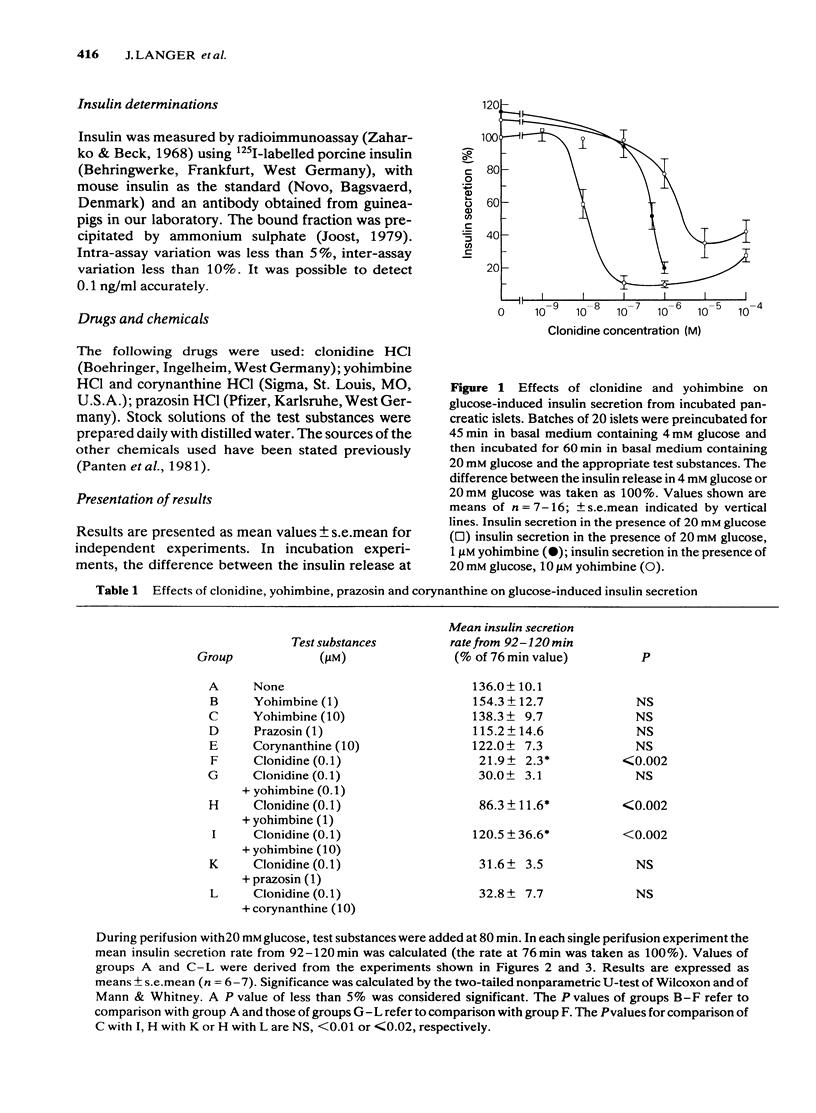
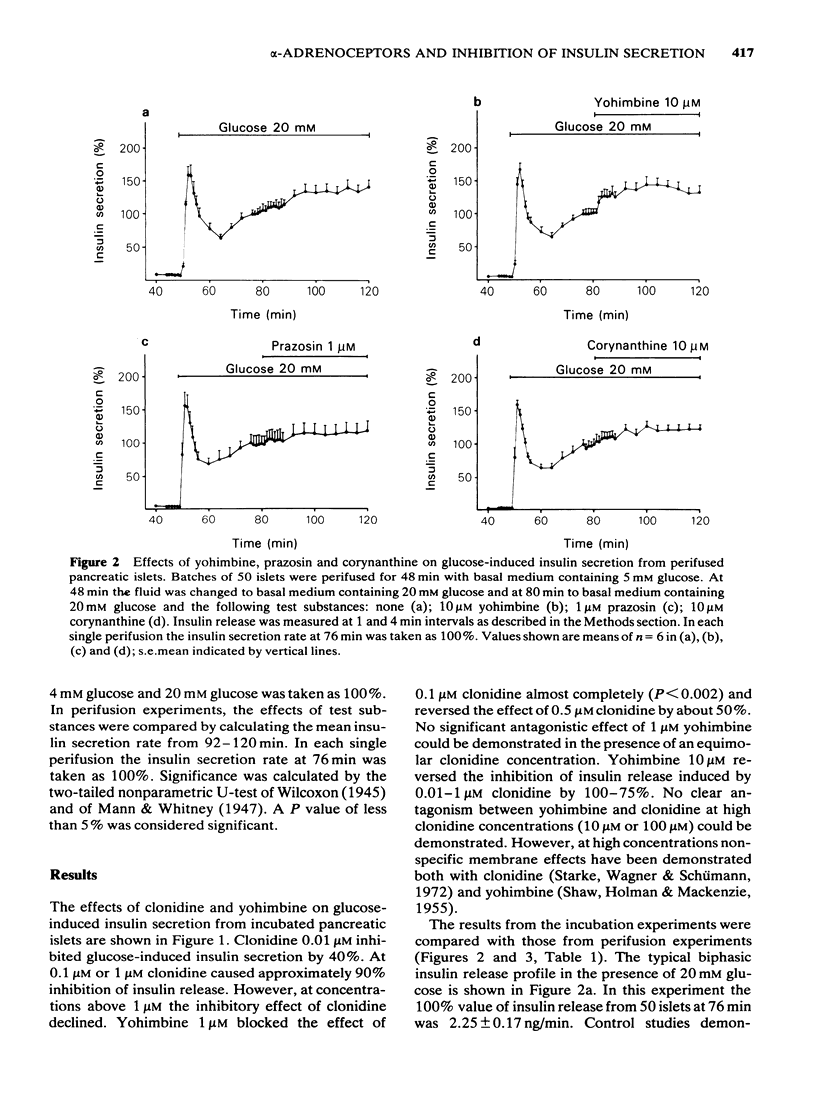
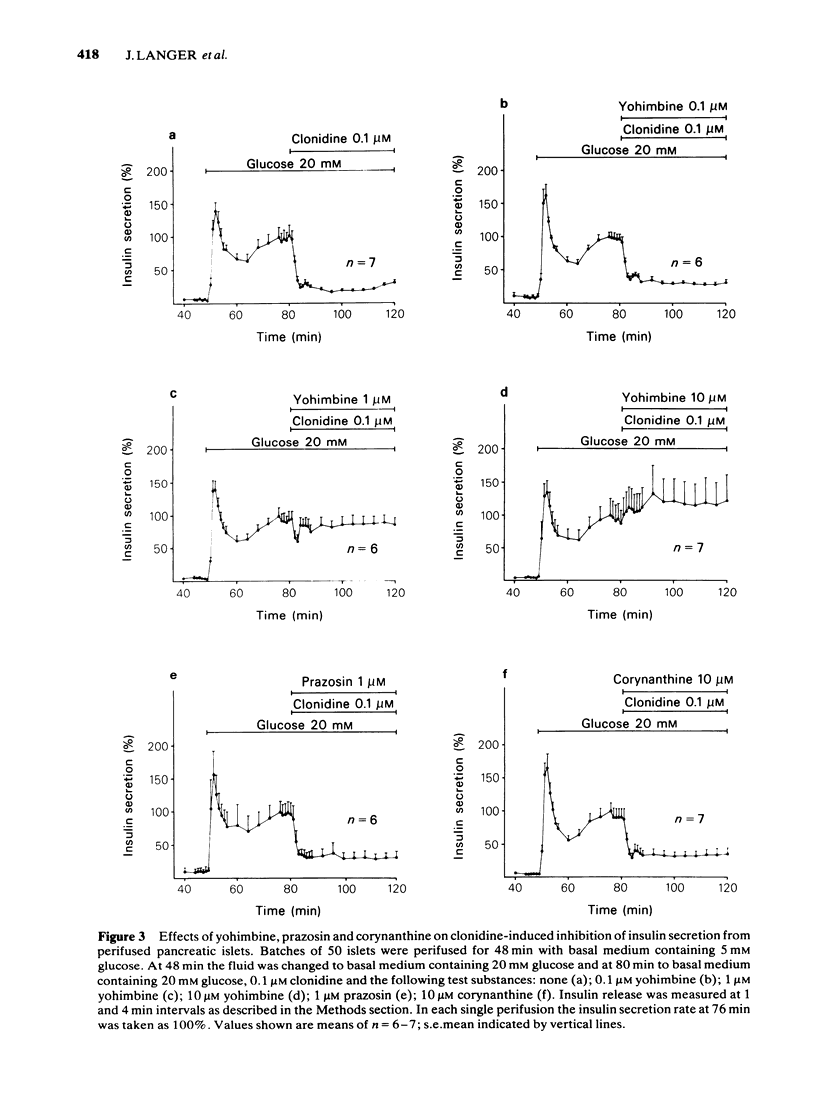
The effects of clonidine, yohimbine, corynanthine and prazosin on glucose-induced insulin secretion by incubated or perifused mouse pancreatic islets were investigated. Clonidine (0.1 microM) inhibited glucose-induced insulin secretion alone and in the presence of yohimbine (0.1 microM), corynanthine (10 microM) or prazosin (1 microM). In higher concentrations, yohimbine (1-10 microM) antagonized the inhibitory effect of clonidine (0.1 microM) upon glucose-induced insulin secretion by incubated islets and by perifused islets. The results support the view that adrenergic inhibition of insulin secretion is mediated by alpha 2-adrenoceptors on pancreatic beta-cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borowski E., Starke K., Ehrl H., Endo T. A comparison of pre- and postsynaptic effects of alpha-adrenolytic drugs in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. Neuroscience. 1977;2(2):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambridge D., Davey M. J., Massingham R. Prazosin, a selective antagonist of post-synaptic alpha-adrenoceptors [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;59(3):514P–515P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll-Garcia E., Gill J. R. Insulin release by isolated pancreatic islets of the mouse incubated in vitro. Diabetologia. 1969 Apr;5(2):61–66. doi: 10.1007/BF01211999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M. Ultrastructural morphometry of the pancreatic -cell. Diabetologia. 1973 Apr;9(2):115–119. doi: 10.1007/BF01230690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoftiezer V., Carpenter A. M. Comparison of streptozotocin and alloxan-induced diabetes in the rat, including volumetric quantitation of the pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1973 Jun;9(3):178–184. doi: 10.1007/BF01219780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joost H. G. Effects of possible beta-cell membrane label, metahexamide-isothiocyanate, on insulin release. Horm Metab Res. 1979 Feb;11(2):104–106. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1092689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Presynaptic regulation of catecholamine release. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Jul 1;23(13):1793–1800. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq-Meyer V., Herchuelz A., Valverde I., Couturier E., Marchand J., Malaisse W. J. Mode of action of clonidine upon islet function: dissociated effects upon the time course and magnitude of insulin release. Diabetes. 1980 Mar;29(3):193–200. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.3.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A. The preparation of, and studies on, free cell suspensions from mouse pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1974 Oct;10(5):431–438. doi: 10.1007/BF01221634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loubatières A., Mariani M. M., Sorel G., Savi L. The action of beta-adrenergic blocking and stimulating agents on insulin secretion. Characterization of the type of beta receptor. Diabetologia. 1971 Jun;7(3):127–132. doi: 10.1007/BF01212541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A., Halter J. B., Robertson R. P. Induction of defective insulin secretion and impaired glucose tolerance by clonidine. Selective stimulation of metabolic alpha-adrenergic pathways. Diabetes. 1978 May;27(5):554–562. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.5.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague W., Howell S. L. Cyclic AMP and the physiology of the islets of Langerhans. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;6:201–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Nakadate T., Ishii K., Kato R. Postsynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in isolated rat islets of Langerhans: inhibition of insulin release and cyclic 3':5'-adenosine monophosphate accumulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Mar;216(3):607–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Nakadate T., Kato R. Alpha 2-adrenoceptors modulating insulin release from isolated pancreatic islets. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;313(2):151–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00498572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S., Tarvin J. T. Somatostatin: mechanism of action in pancreatic islet beta-cells. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):836–842. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panten U., Biermann J., Graen W. Recognition of insulin-releasing fuels by pancreatic B-cells: alpha-ketoisocaproic acid is an appropriate model compound to study the role of B-cell metabolism. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;20(1):76–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panten U., Ishida H., Schauder P., Frerichs H., Hasselblatt A. A versatile microperifusion system. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr Beta adrenergic stimulation of insulin release in man. Diabetes. 1967 Mar;16(3):150–155. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.3.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Graber A. L., Kuzuya T., Williams R. H. The effect of epinephrine on immunoreactive insulin levels in man. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):228–236. doi: 10.1172/JCI105335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW F. H., HOLMAN M., MACKENZIE J. G. The action of yohimbine on nerve and muscle of amphibia. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1955 Aug;33(4):497–505. doi: 10.1038/icb.1955.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W. The adenylate cyclase-cyclic AMP system in islets of Langerhans and its role in the control of insulin release. Diabetologia. 1979 May;16(5):287–296. doi: 10.1007/BF01223617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha-adrenoceptor subclassification. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;88:199–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Borowski E., Endo T. Preferential blockade of presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors by yohimbine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1975 Dec;34(2):385–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(75)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Wagner J., Schümann H. J. Adrenergic neuron blockade by clonidine: comparison with guanethidine and local anesthetics. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1972 Feb;195(2):291–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Orci L. Possible roles of the pancreatic D-cell in the normal and diabetic states. Diabetes. 1977 Mar;26(3):241–244. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.3.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzell R., Tanaka T., Starke K. Pre- and postsynaptic effects of yohimbine stereoisomers on noradrenergic transmission in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;308(2):127–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00499054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenkeller D. E., Sharp G. W. Insulin release. Demonstration of a priming effect of 3-isobutyl-1-methyl-xanthine (IBMX) on islets of Langerhans. Diabetes. 1981 Sep;30(9):754–756. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.9.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki S., Katada T., Ui M. Alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of insulin secretion via interference with cyclic AMP generation in rat pancreatic islets. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 May;21(3):648–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaharko D. S., Beck L. V. Studies of a simplified plasma insulin immunoassaay using cellulose powder. Diabetes. 1968 Jul;17(7):444–459. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.7.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


