Abstract
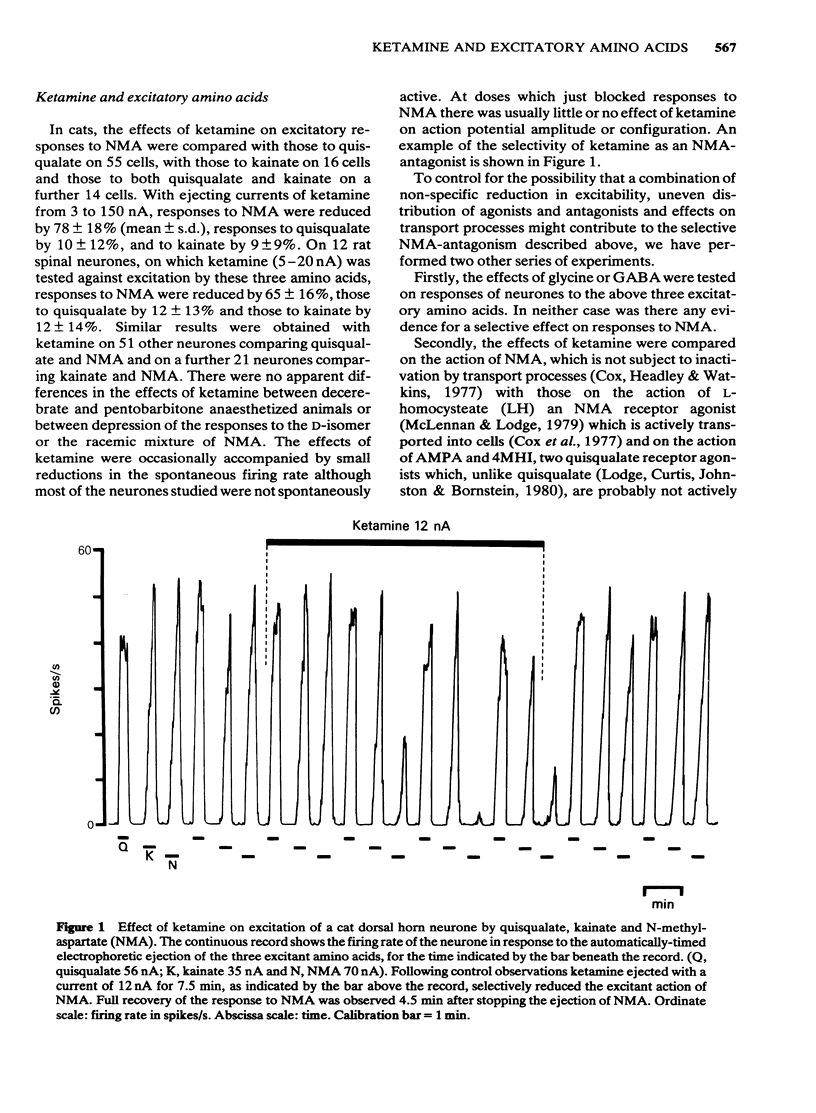
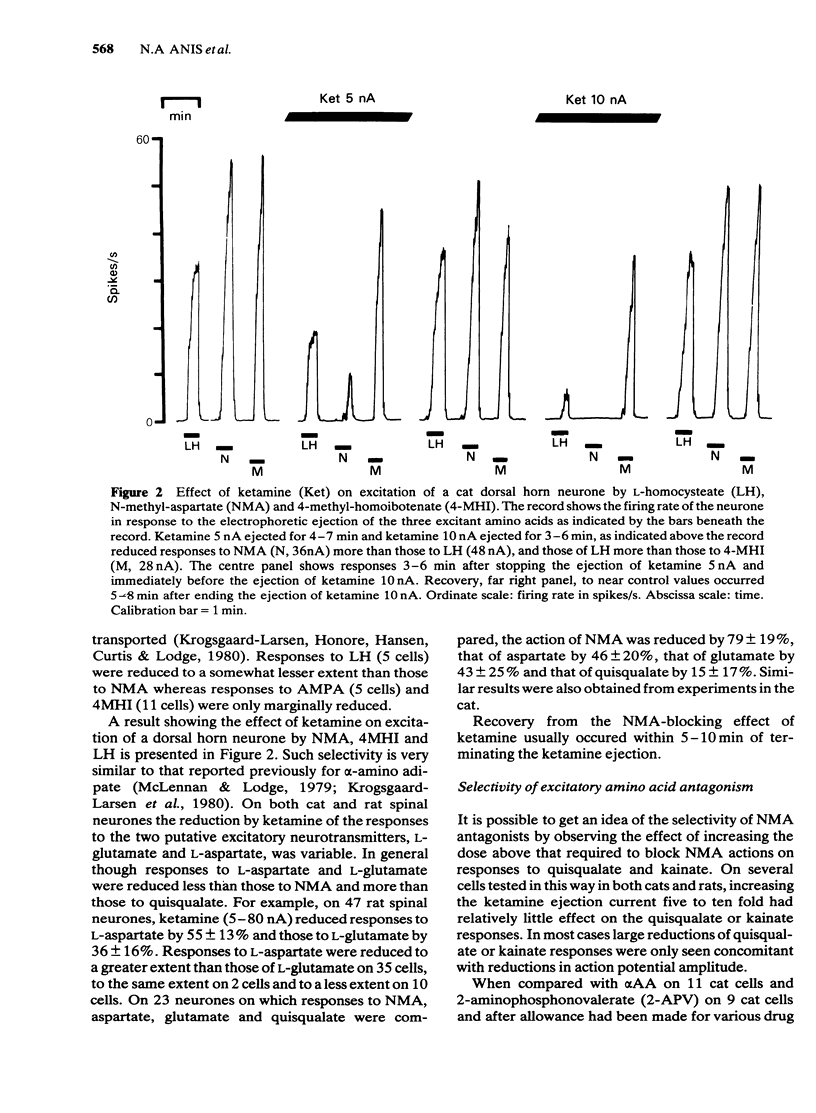
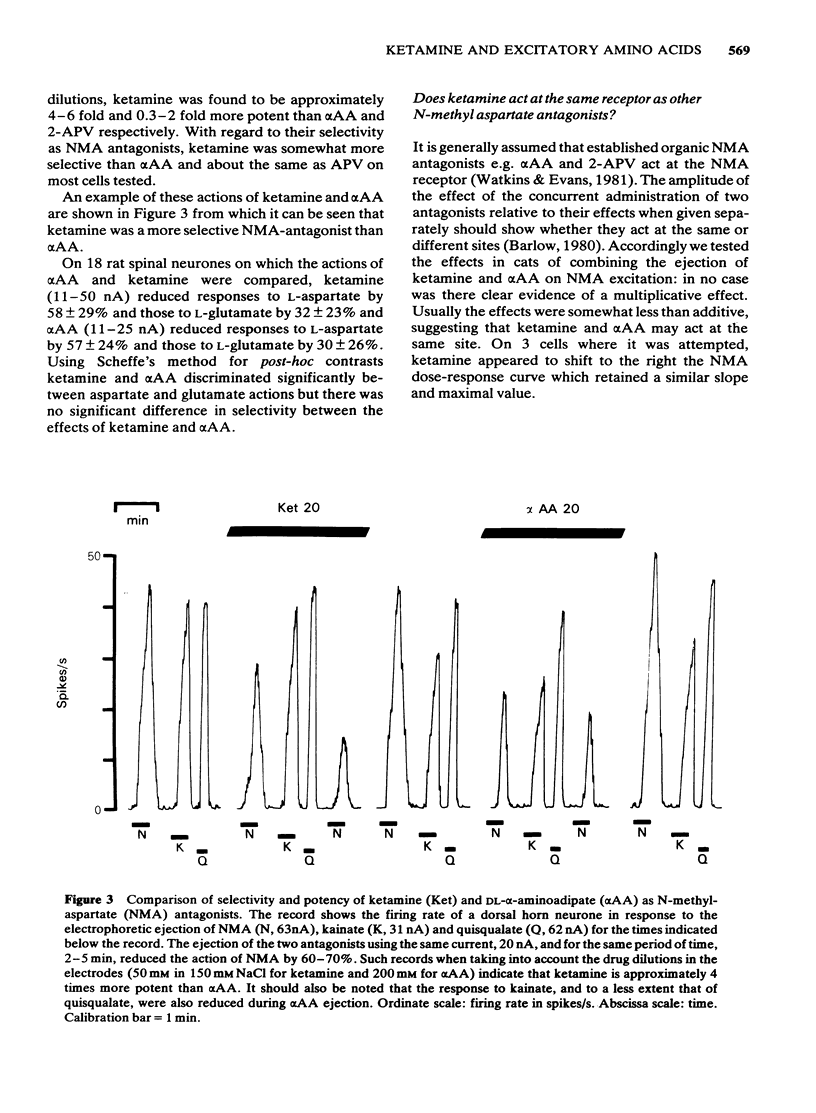
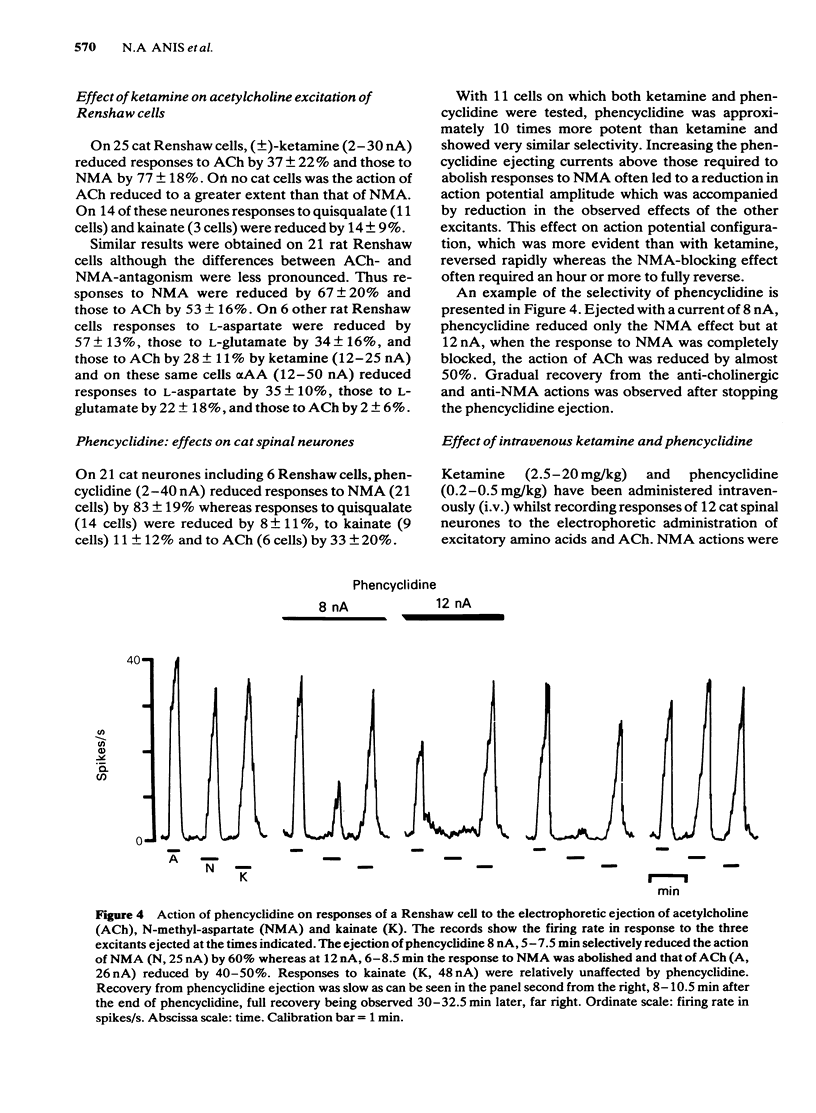
The interaction of two dissociative anaesthetics, ketamine and phencyclidine, with the responses of spinal neurones to the electrophoretic administration of amino acids and acetylcholine was studied in decerebrate or pentobarbitone-anaesthetized cats and rats. Both ketamine and phencyclidine selectively blocked excitation by N-methyl-aspartate (NMA) with little effect on excitation by quisqualate and kainate. Ketamine reduced responses to L-aspartate somewhat more than those of L-glutamate; the sensitivity of responses to these two putative transmitters was between that to NMA on one hand and that to quisqualate or kainate on the other. On Renshaw cells, ketamine and phencyclidine reduced responses to acetylcholine less than those to NMA but more than those to quisqualate or kainate. Dorsal root-evoked synaptic excitation of Renshaw cells was reduced to a greater extent than that following ventral root excitation. Intravenous ketamine, 2.5-20 mg/kg, and phencyclidine, 0.2-0.5 mg/kg, also selectively blocked excitation of neurones by NMA. Ketamine showed no consistent or selective effect on inhibition of spinal neurones by electrophoretically administered glycine or gamma-aminobutyricacid (GABA). The results suggest that reduction of synaptic excitation mediated via NMA receptors contributes to the anaesthetic/analgesic properties of these two dissociative anaesthetics.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel A., Gratton D. A. The effect of anaesthetic agents on cerebral cortical responses in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Aug;76(4):541–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09252.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronstam R. S., Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T., Albuquerque E. X., Jim K. F., Triggle D. J. Sites of action of phencyclidine. III. Interactions with muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Sep;18(2):179–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Davies J., Dray A., Evans R. H., Martin M. R., Watkins J. C. D-alpha-aminoadipate, alpha, epsilon-diominopimelic acid and HA-966 as antagonists of amino acid-induced and synpatic excitation of mammalian spinal neurones in vivo. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 16;148(2):543–548. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90745-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonta I. L., De Vos C. J., Grijsen H., Hillen F. C., Noach E. L., Sim A. W. 1-Hydroxy-3-amino-pyrrolidone-2(HA-966): a new GABA-like compound, with potential use in extrapyramidal diseases. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Nov;43(3):514–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conseiller C., Benoist J. M., Hamann K. F., Maillard M. C., Besson J. M. Effects of ketamine (CI 581) on cell responses to cutaneous stimulations in laminae IV and V in the cat's dorsal horn. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 May;18(3):346–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corssen G., Domino E. F. Dissociative anesthesia: further pharmacologic studies and first clinical experience with the phencyclidine derivative CI-581. Anesth Analg. 1966 Jan-Feb;45(1):29–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W., Headley M. H., Watkins J. C. Actions of L- and D-homocysteate in rat CNS: a correlation between low-affinity uptake and the time courses of excitation by microelectrophoretically applied L-glutamate analogues. J Neurochem. 1977 Sep;29(3):579–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Johnston G. A. Amino acid transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Ergeb Physiol. 1974;69(0):97–188. doi: 10.1007/3-540-06498-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Ryall R. W. The synaptic excitation of Renshaw cells. Exp Brain Res. 1966;2(1):81–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00234362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOMINO E. F. NEUROBIOLOGY OF PHENCYCLIDINE (SERNYL), A DRUG WITH AN UNUSUAL SPECTRUM OF PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIVITY. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1964;6:303–347. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60772-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dafny N., Rigor B. M. Neurophysiological approach as a tool to study effects of drugs on the central nervous system: dose-effect of ketamine. Exp Neurol. 1978 Apr;59(2):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(78)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. Selective antagonism of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation in the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):621–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Watkins J. C. Mg2+-like selective antagonism of excitatory amino acid-induced responses by alpha, epsilon-diaminopimelic acid, D-alpha-aminoadipate and HA-966 in isolated spinal cord of frog and immature rat. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 16;148(2):536–542. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90744-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glen J. B. The use of ketamine (CI-581) in feline anaesthetic practice. Vet Rec. 1973 Jan 20;92(3):65–68. doi: 10.1136/vr.92.3.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Headley P. M., Lodge D., Biscoe T. J. Acetylcholine receptors on Renshaw cells of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;30(2):252–259. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(75)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janis K. M., Wright W. Failure to produce analgesia with ketamine in two patients with cortical disease. Anesthesiology. 1972 Apr;36(4):405–406. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197204000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahata L. M., Taub A., Kosada Y. Lamina-specific suppression of dorsal-horn unit activity by detamine hydrochloride. Anesthesiology. 1973 Jan;38(1):4–11. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197301000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Honoré T., Hansen J. J., Curtis D. R., Lodge D. New class of glutamate agonist structurally related to ibotenic acid. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):64–66. doi: 10.1038/284064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge D., Anis N. A., Burton N. R. Effects of optical isomers of ketamine on excitation of cat and rat spinal neurones by amino acids and acetylcholine. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Apr 26;29(3):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90330-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge D., Curtis D. R., Johnston G. A., Bornstein J. C. In vivo inactivation of quisqualate: studies in the cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1980 Jan 27;182(2):491–495. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91211-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge D., Headley P. M., Curtis D. R. Selective antagonism by D-alpha-aminoadipate of amino acid and synaptic excitation of cat spinal neurons. Brain Res. 1978 Sep 8;152(3):603–608. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTHY D. A., CHEN G., KAUMP D. H., ENSOR C. GENERAL ANESTHETIC AND OTHER PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF 2-(O-CHLOROPHENYL)-2-METHYLAMINO CYCLOHEXANONE HCL (CI-58L). J New Drugs. 1965 Jan-Feb;5(1):21–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1965.tb00219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marietta M. P., WAY W. L., Castagnoli N., Jr, Trevor A. J. On the pharmacology of the ketamine enantiomorphs in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Jul;202(1):157–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R. Multiple opioid receptors: a little about their history and some implications related to evolution. Life Sci. 1981 Apr 6;28(14):1547–1554. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwaha J., Palmer M. R., Woodward D. J., Hoffer B. J., Freedman R. Electrophysiological evidence for presynaptic actions of phencyclidine on noradrenergic transmission in rat cerebellum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Dec;215(3):606–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H., Lodge D. The antagonism of amino acid-induced excitation of spinal neurones in the cat. Brain Res. 1979 Jun 15;169(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90375-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchin M. C. The effect of anaesthetics on the uptake and release of gamma-aminobutyrate and D-aspartate in rat brain slices. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;73(3):681–689. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb16803.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M., Loh L., Singer L., Moore P. H. Ketamine as the sole anaesthetic agent for minor surgical procedures. Anaesthesia. 1971 Apr;26(2):158–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1971.tb04756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani M., Kikuchi H., Kitahata L. M., Taub A., Toyooka H., Hanaoka K., Dohi S. Effects of ketamine on nociceptive cells in the medial medullary reticular formation of the cat. Anesthesiology. 1979 Nov;51(5):414–417. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197911000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padjen A. L., Smith P. A. Specific effects of alpha-D,L-aminoadipic acid on synaptic transmission in frog spinal cord. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;58(6):692–698. doi: 10.1139/y80-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekoe G. M., Smith D. J. The involvement of opiate and monoaminergic neuronal systems in the analgesic effects of ketamine. Pain. 1982 Jan;12(1):57–73. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(82)90170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Hammer R. P., Jr, Herkenham M., Pert C. B. Phencyclidine (angel dust)/sigma "opiate" receptor: visualization by tritium-sensitive film. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5881–5885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raja S. N., Guyenet P. G. Action of phencyclidine on synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1982 Mar 25;236(2):289–304. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90715-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. G., Tien A. F. Neuronal responses to ketamine administered microiontophoretically or intraperitoneally in the rat. Gen Pharmacol. 1979;10(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(79)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., Azzaro A. J., Zaldivar S. B., Palmer S., Lee H. S. Properties of the optical isomers and metabolites of ketamine on the high affinity transport and catabolism of monoamines. Neuropharmacology. 1981 Apr;20(4):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(81)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Amino acids as neurotransmitters of corticofugal neurones in the rat: a comparison of glutamate and aspartate. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;67(4):545–551. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Blockade by amino acid antagonists of neuronal excitation mediated by the pyramidal tract. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(1):187–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang A. H., Schroeder L. A. Spinal-cord depressant effects of ketamine and etoxadrol in the cat and the rat. Anesthesiology. 1973 Jul;39(1):37–43. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197307000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Kartalovski B., Geneste P., Kamenka J. M., Lazdunski M. Interaction of phencyclidine ("angel dust") with a specific receptor in rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4678–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten S. M. Dissociation of limbic and neocortical EEG patterns in cats under ketamine anesthesia. J Neurosurg. 1972 Oct;37(4):429–433. doi: 10.3171/jns.1972.37.4.0429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbroth S. H., Fudens J. H. Use of ketamine hybrochloride as an anesthetic in laboratory rabbits, rats, mice, and guinea pigs. Lab Anim Sci. 1972 Dec;22(6):904–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters W. D., Ferrar-Allado T., Guzman-Flores C., Alcaraz M. The cataleptic state induced by ketamine: a review of the neuropharmacology of anesthesia. Neuropharmacology. 1972 May;11(3):303–315. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(72)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Zukin R. S. Specific [3H]phencyclidine binding in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5372–5376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


