Abstract
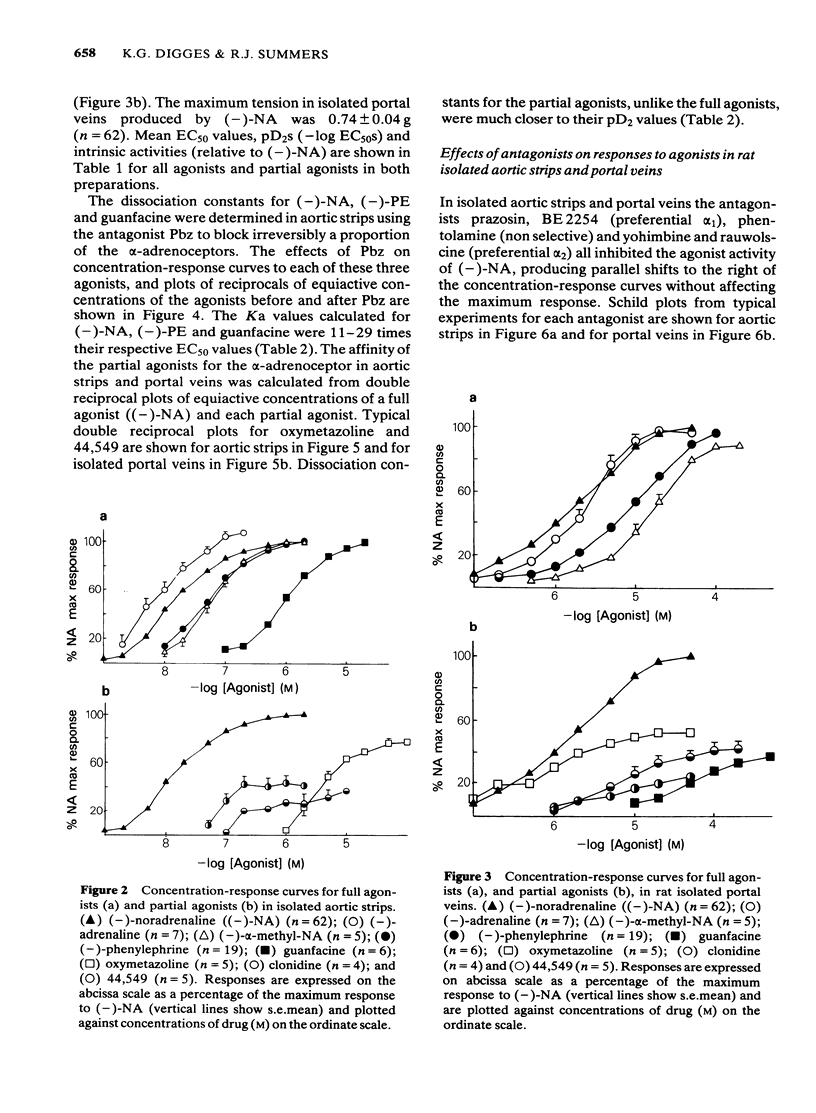
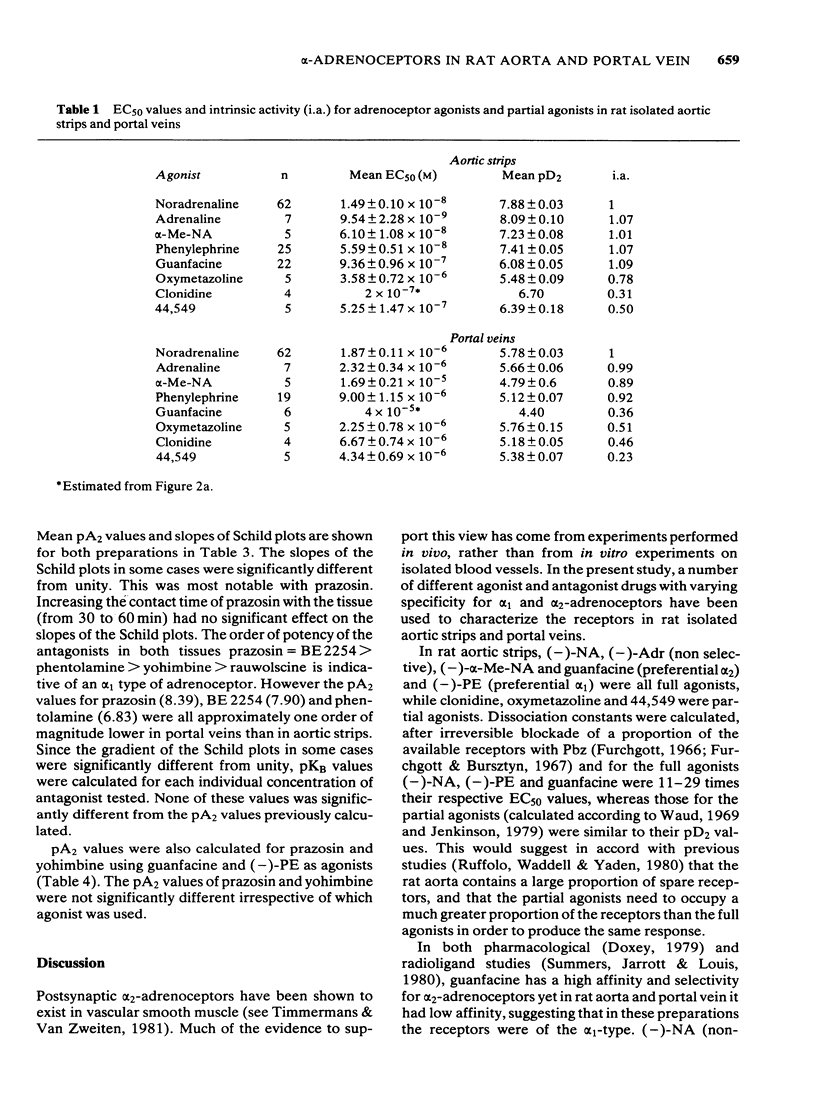
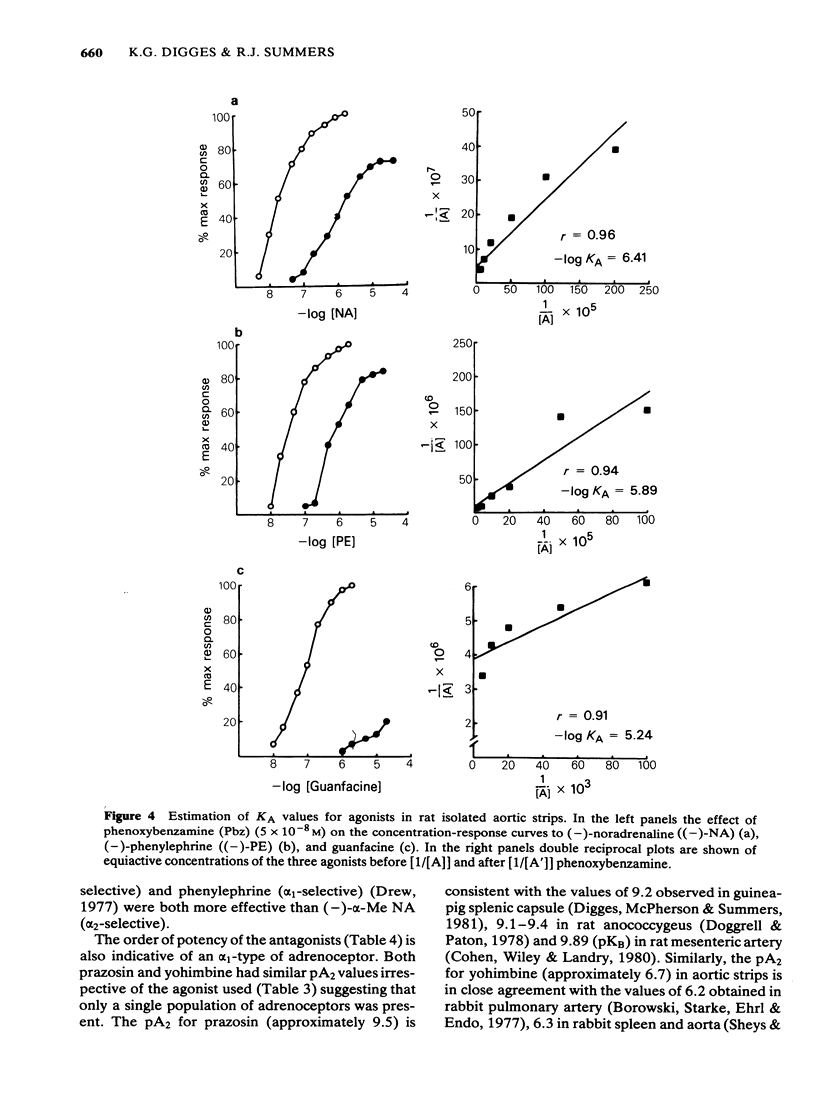
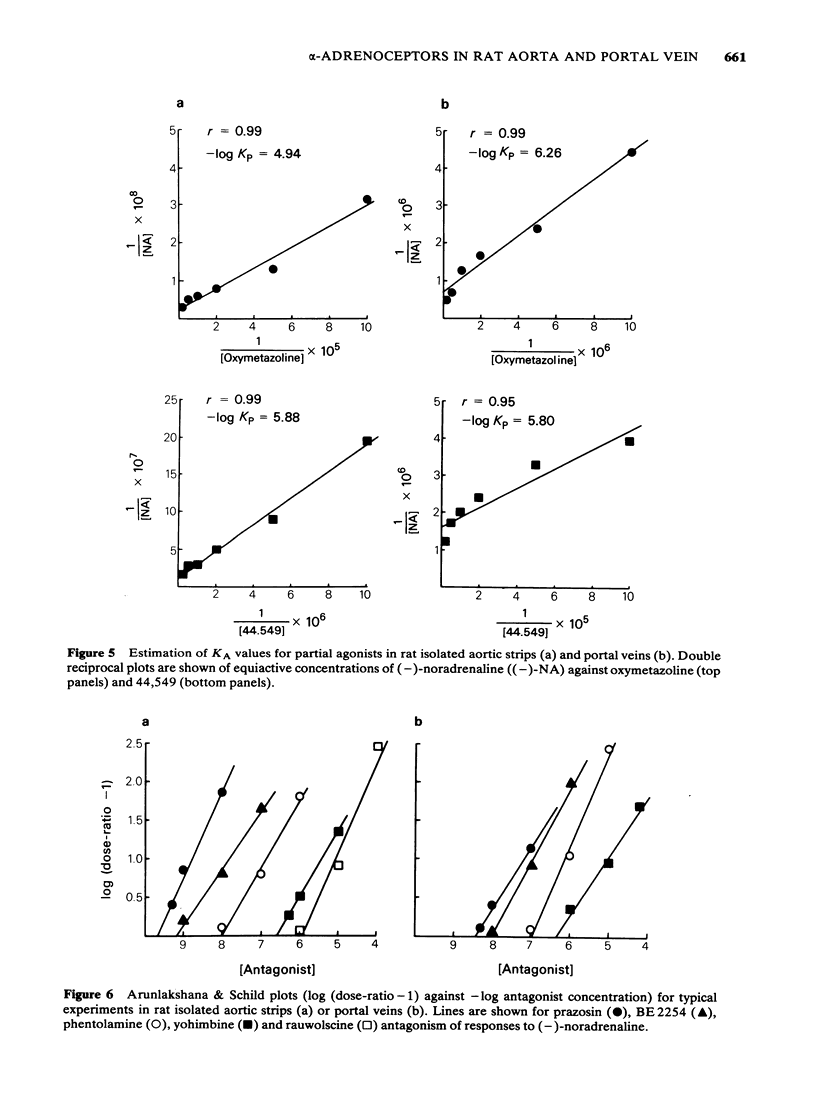
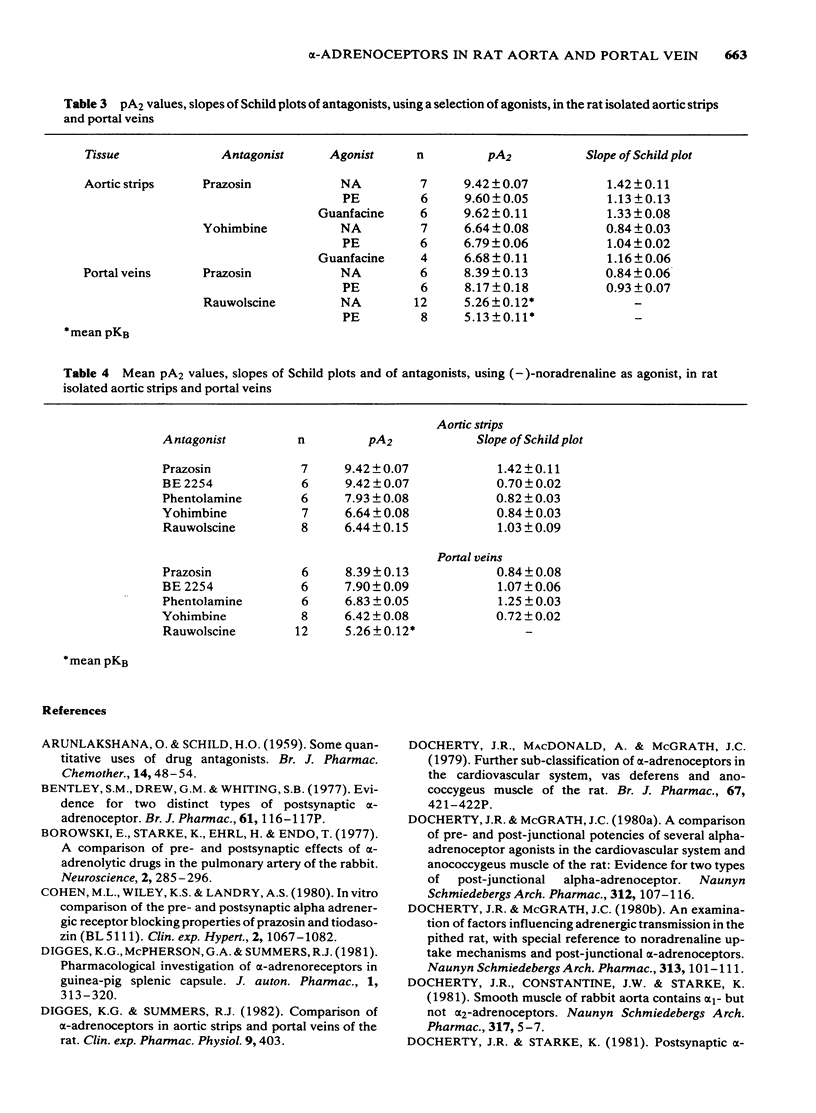
Postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors in rat isolated aortic strips and portal veins have been examined using a number of agonist and antagonist drugs which have varying selectivity for alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptors. In both tissues (-)-noradrenaline [-)-NA), (-)-adrenaline [-) Adr) (-)-alpha-methyl noradrenaline [-)-alpha-Me-NA) and (-)-phenylephrine [-)-PE) were full agonists, while clonidine, oxymetazoline and (2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5,6-dihydroimidazo(2,1,b) thiazole (44,549) were partial agonists. Guanfacine was a full agonist in aortic strips but only a partial agonist in portal veins. In aortic strips, pA2 values for prazosin and yohimbine were not significantly different using (-)-NA, (-)-PE or guanfacine as the agonist, suggesting a single population of alpha-adrenoceptors. The order of potency of the antagonists, prazosin = 2-(beta-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-ethylaminomethyl)-tetralone (BE2254) greater than phentolamine greater than yohimbine greater than rauwolscine, is indicative of an alpha 1-type of receptor. In portal veins, the order of potency of the antagonists was prazosin greater than BE2254 greater than phentolamine greater than yohimbine greater than rauwolscine, again indicating an alpha 1-type of receptor. The mean pA2 value for yohimbine was not significantly different in either tissue. However, mean pA2 values for prazosin, BE-2254 and phentolamine were approximately one order of magnitude lower in portal veins than in aortic strips, suggesting that the receptors in the two tissues may not be identical.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley S. M., Drew G. M., Whiting S. B. Evidence for two distinct types of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;61(1):116P–117P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowski E., Starke K., Ehrl H., Endo T. A comparison of pre- and postsynaptic effects of alpha-adrenolytic drugs in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. Neuroscience. 1977;2(2):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Wiley K. S., Landry A. S. In vitro comparison of the pre- and postsynaptic alpha adrenergic receptor blocking properties of prazosin and tiodazosin (BL5111). Clin Exp Hypertens. 1980;2(6):1067–1082. doi: 10.3109/10641968009037161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J. G., Vanhoutte P. M. Differences in pharmacological properties of postjunctional alpha-adrenergic receptors among arteries and veins. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1980 Apr;244(2):328–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J., Vanhoutte P. M. Uneven distribution of postjunctional alpha 1-and alpha 2-like adrenoceptors in canine arterial and venous smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1981 Jun;48(6 Pt 1):875–884. doi: 10.1161/01.res.48.6.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digges K. G., McPherson G. A., Summers R. J. Pharmacological investigation of alpha-adrenoreceptors in guinea-pig splenic capsule. J Auton Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;1(4):313–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1981.tb00461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., Constantine J. W., Starke K. Smooth muscle of rabbit aorta contains alpha 1-but not alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;317(1):5–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00506248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., MacDonald A., McGrath J. C. Further sub-classification of alpha-adrenoceptors in the cardiovascular system, vas deferens and anococcygeus of the rat [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;67(3):421P–422P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. A comparison of pre- and post-junctional potencies of several alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the cardiovascular system and anococcygeus muscle of the rat. Evidence for two types of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;312(2):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00569718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. An examination of factors influencing adrenergic transmission in the pithed rat, with special reference to noradrenaline uptake mechanisms and post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;313(2):101–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00498564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., Starke K. Postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes in rabbit blood vessels and rat anococcygeus muscle studied in vitro. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1981 Jul-Aug;3(4):854–866. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198107000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggrell S. A., Paton D. M. Effects of prazosin and phentolamine on responses to field stimulation and to noradrenaline in vas deferens and anococcygeus muscle of the rat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1978 Jun;233(2):209–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C. Pre- and postsynaptic effects of alpha-agonists in the anococcygeus muscle of the pithed rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb 15;54(1-2):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90423-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Smith C. F., Walker J. M. Selectivity of blocking agents for pre-and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 May;60(1):91–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb16752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Pharmacological characterisation of the presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in the rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar 21;42(2):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M., Whiting S. B. Evidence for two distinct types of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in vascular smooth muscle in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;67(2):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eltze M. Investigations on the mode of action of a new antihypertensive drug, urapidil, in the isolated rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct 26;59(1-2):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauernig R. A., Moulds R. F., Shaw J. The action of prazosin in human vascular preparations. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1978 Jan;231(1):81–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Presynaptic regulation of catecholamine release. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Jul 1;23(13):1793–1800. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madjar H., Docherty J. R., Starke K. An examination of pre- and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors in the autoperfused rabbit hindlimb. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1980 Sep-Oct;2(5):619–627. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198009000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulds R. J., Jauernig R. A. Mechanism of prazosin collapse. Lancet. 1977 Jan 22;1(8004):200–201. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91808-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdy R. E., Krueger C. G., Young S. Evidence for nonclassical alpha adrenoceptor blockade by prazosin in isolated rabbit blood vessels. Life Sci. 1980 Dec 8;27(23):2187–2195. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90383-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Waddell J. E., Yaden E. L. Heterogeneity of postsynaptic Alpha adrenergic receptors in mammalian aortas. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 May;221(2):309–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Waddell J. E., Yaden E. L. Receptor interactions of imidazolines. IV. Structural requirements for alpha adrenergic receptor occupation and receptor activation by clonidine and a series of structural analogs in rat aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 May;213(2):267–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Yaden E. L., Waddell J. E. Receptor interactions of imidazolines. V. clonidine differentiates postsynaptic alpha adrenergic receptor subtypes in tissues from the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Jun;213(3):557–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepperson N. B., Langer S. Z. The effects of the 2-amino-tetrahydronaphthalene derivative M7, a selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1981 Dec;318(1):10–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00503305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheys E. M., Green R. D. A quantitative study of alpha adrenergic receptors in the spleen and aorta of the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Feb;180(2):317–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha-adrenoceptor subclassification. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;88:199–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan A. T., Drew G. M. Pharmacological characterisation of pre- and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors in dog saphenous vein. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;314(3):249–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00498546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. J., Jarrott B., Louis W. J. Selectivity of a series of clonidine-like drugs for alpha 1 and alpha 2 adrenoceptors in rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Dec;20(3):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., Kwa H. Y., van Zwieten P. A. Possible subdivision of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors mediating pressor responses in the pithed rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;310(2):189–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00500284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., van Zwieten P. A. Mini-review. The postsynaptic alpha 2-adrenoreceptor. J Auton Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;1(2):171–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1981.tb00509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E. Pharmacological classification of adrenergic alpha receptors in the guinea pig. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):164–166. doi: 10.1038/273164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



