Abstract
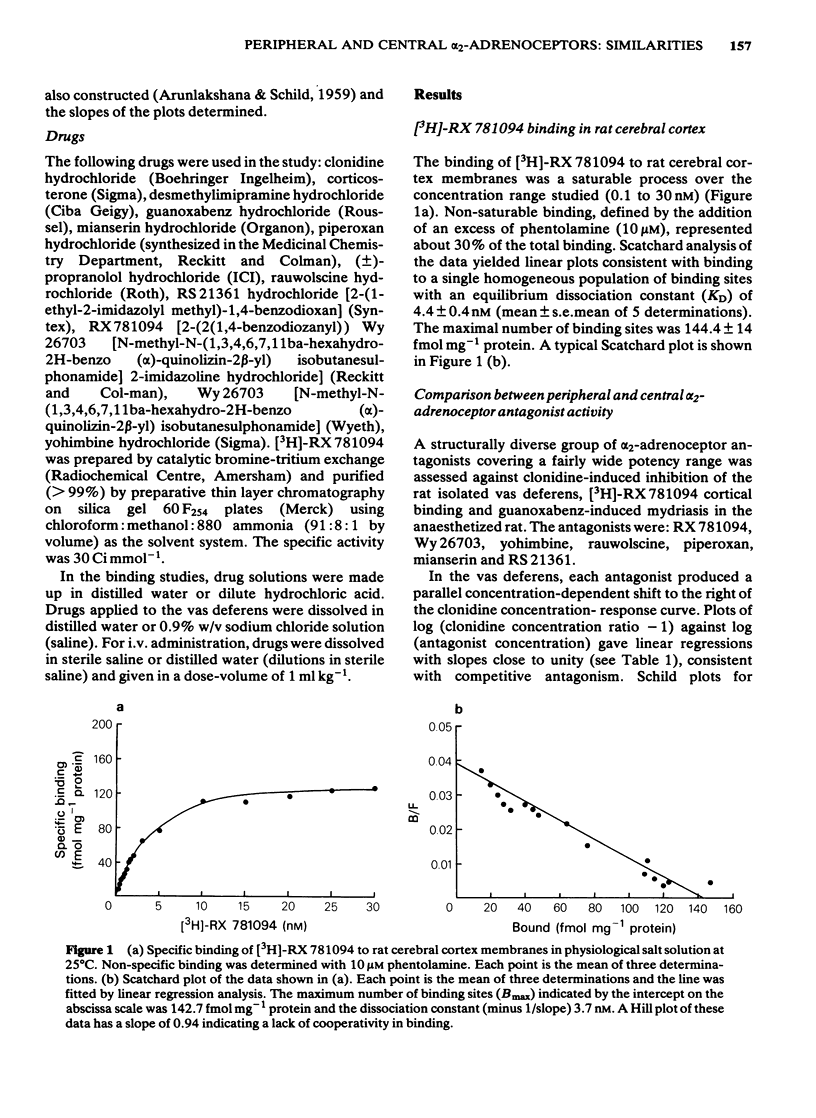
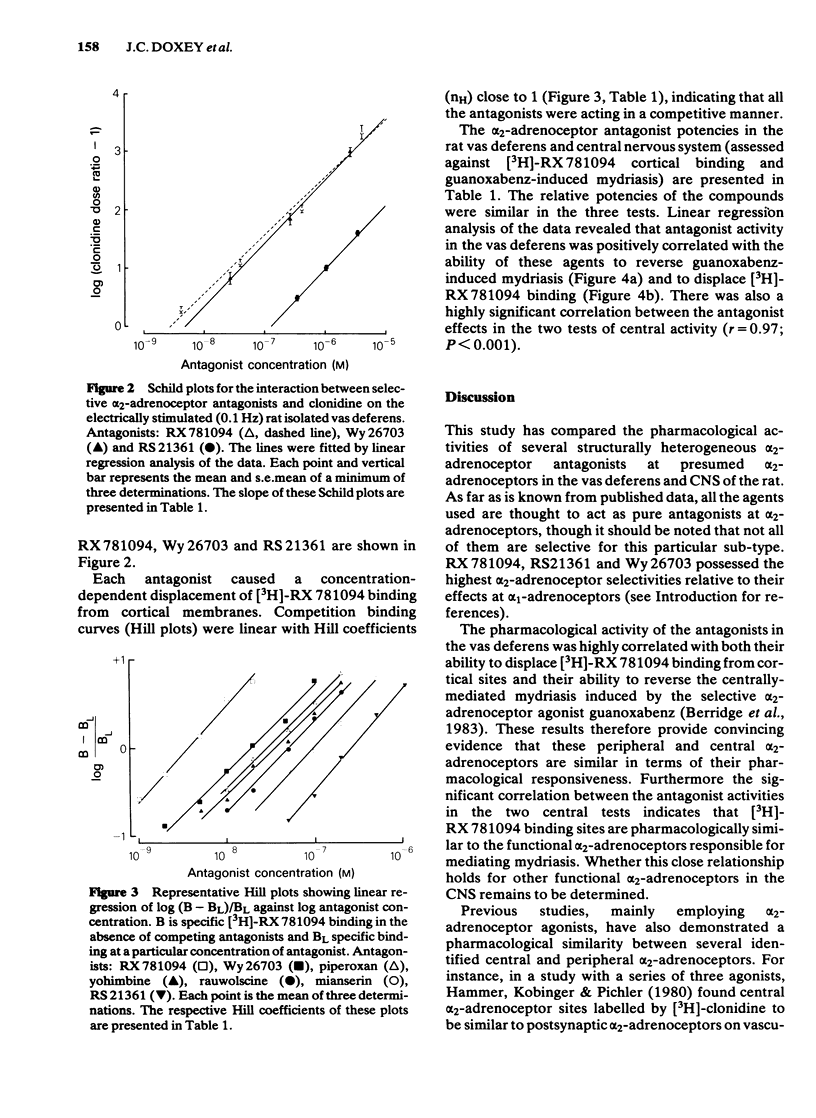
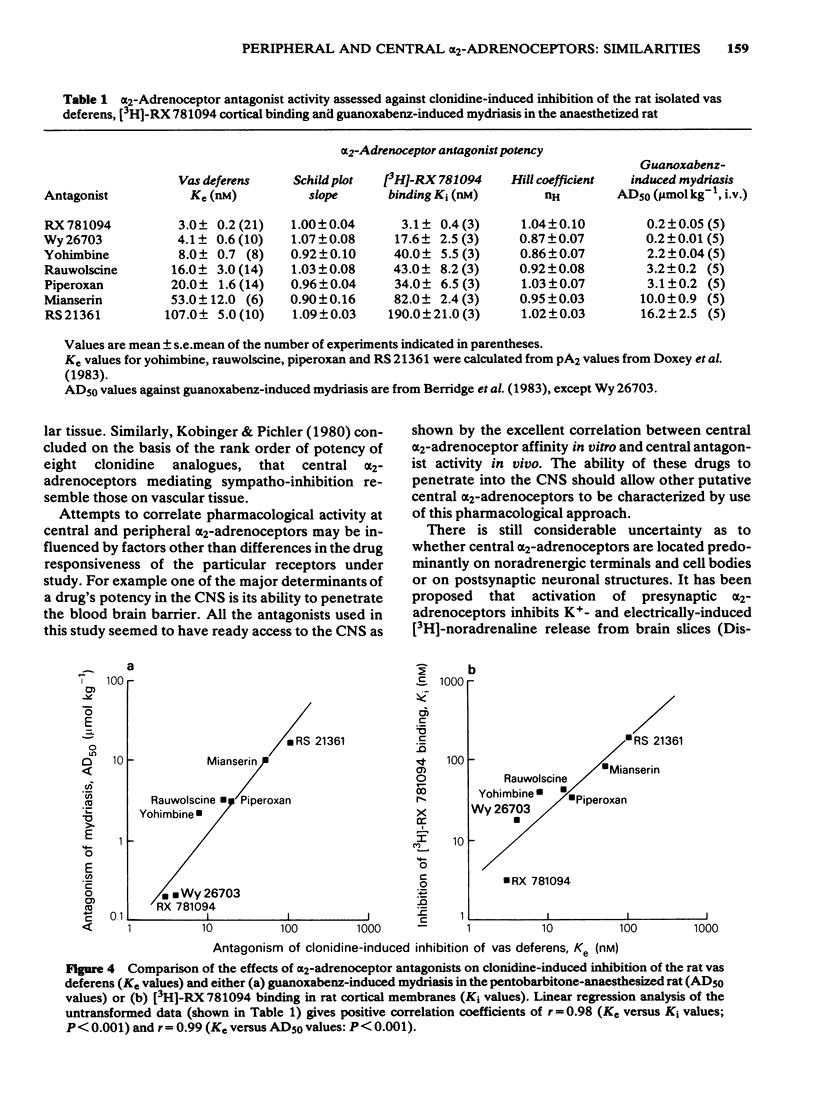
Seven alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists with diverse chemical structures have been examined for their effects at alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the vas deferens and central nervous system of the rat. Antagonist potency assessed against the presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist action of clonidine in the isolated vas deferens (RX 781094 greater than Wy 26703 greater than yohimbine greater than rauwolscine greater than piperoxan greater than mianserin greater than RS 21361) was highly correlated with the ability of these drugs to displace saturable [3H]-RX 781094 binding from cerebral cortex membranes. Similarly, antagonist potency in the vas deferens was highly correlated with antagonist activity in reversing the centrally-mediated mydriasis induced by the selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist, guanoxabenz, in pentobarbitone-anaesthetized rats. The results indicate that the presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the vas deferens are pharmacologically similar to characterized these alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the central nervous system of the rat.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge T. L., Gadie B., Roach A. G., Tulloch I. F. alpha 2-Adrenoceptor agonists induced mydriasis in the rat by an action within the central nervous system. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):507–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dismukes K., de Boer A. A., Mulder A. H. On the mechanism of alpha-receptor mediated modulation of 3H-noradrenaline release from slices of rat brain neocortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;299(2):115–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00498553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Roach A. G. Presynaptic alpha-adrenoreceptors; in vitro methods and preparations utilised in the evaluation of agonists and antagonists. J Auton Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;1(1):73–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1980.tb00444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Roach A. G., Smith C. F. Studies on RX 781094: a selective, potent and specific antagonist of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):489–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Smith C. F., Walker J. M. Selectivity of blocking agents for pre-and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 May;60(1):91–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb16752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R., Kobinger W., Pichler L. Binding of an imidazolidine (clonidine), an oxazoloazepin (B-HT 933) and a thiazoloazepin (B-HT 920) to rat brain alpha-adrenoceptors and relation to cardiovascular effects. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Apr 4;62(4):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrott B., Louis W. J., Summers R. J. [3H]-guanfacine: a radioligand that selectively labels high affinity alpha2-adrenoceptor sites in homogenates of rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Feb;75(2):401–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobinger W., Pichler L. Relation between central sympathoinhibitory and peripheral pre- and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors as evaluated by different clonidine-like substances in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980;315(1):21–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00504226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z., Adler-Graschinsky E., Giorgi O. Physiological significance of alpha-adrenoceptor-mediated negative feedback mechanism regulating noradrenaline release during nerve stimulation. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):648–650. doi: 10.1038/265648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Presynaptic regulation of the release of catecholamines. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Dec;32(4):337–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry B. D., U'Prichard D. C. [3H]rauwolscine (alpha-yohimbine): a specific antagonist radioligand for brain alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Dec 17;76(4):461–464. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scatton B., Dedek J., Zivkovic B. Lack of involvement of alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the regulation of striatal dopaminergic transmission. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha-adrenoceptor subclassification. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;88:199–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Montel H. Involvement of alpha-receptors in clonidine-induced inhibition of transmitter release from central monoamine neurones. Neuropharmacology. 1973 Nov;12(11):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(73)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story D. F., McCulloch M. W., Rand M. J., Standford-Starr C. A. Conditions required for the inhibitory feedback loop in noradrenergic transmission. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):62–65. doi: 10.1038/293062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taube H. D., Starke K., Borowski E. Presynaptic receptor systems on the noradrenergic neurones of rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;299(2):123–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00498554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U'Prichard D. C., Greenberg D. A., Snyder S. H. Binding characteristics of a radiolabeled agonist and antagonist at central nervous system alpha noradrenergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 May;13(3):454–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U'Prichard D. C., Reisine T. D., Mason S. T., Fibiger H. C., Yamamura H. I. Modulation of rat brain alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptor populations by lesion of the dorsal noradrenergic bundle. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 7;187(1):143–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90500-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ROSSUM J. M. Cumulative dose-response curves. II. Technique for the making of dose-response curves in isolated organs and the evaluation of drug parameters. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963;143:299–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wemer J., Frankhuyzen A. L., Mulder A. H. Pharmacological characterization of presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors in the nucleus tractus solitarii and the cerebral cortex of the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1982 Jun;21(6):499–506. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(82)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


