Abstract
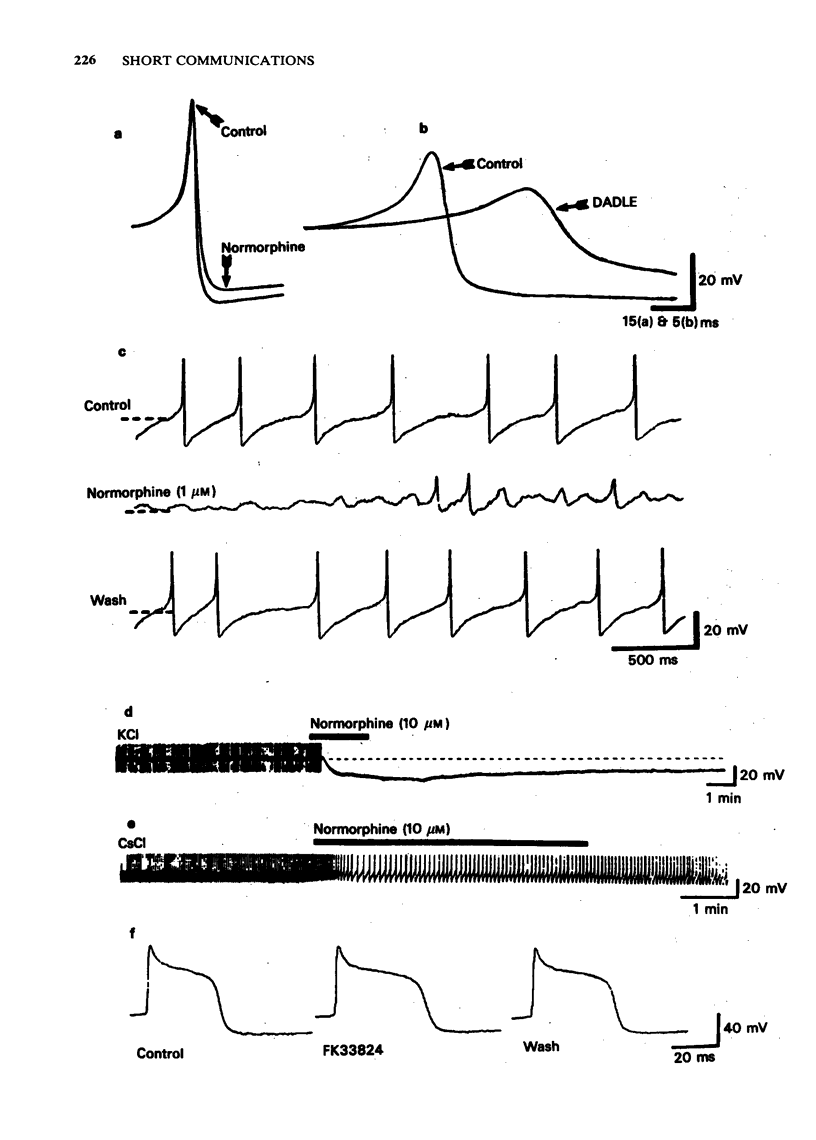
Opiates act on mu-receptors to increase the potassium conductance of rat locus coeruleus neurones. Opiates also depress the rate of rise and peak amplitude of calcium action potentials in these cells. The action of opiates on calcium action potentials was prevented by two procedures which blocked the opiate-induced potassium current, intracellular caesium and extracellular barium. This indicates that the opiate reduction in calcium entry is secondary to an increased potassium current.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bixby J. L., Spitzer N. C. Enkephalin reduces calcium action potentials in Rohon-Beard neurons in vivo. J Neurosci. 1983 May;3(5):1014–1018. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-05-01014.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G., Pepper C. M., Shefner S. A. Electrophysiological properties of neurons contained in the locus coeruleus and mesencephalic nucleus of the trigeminal nerve in vitro. Exp Brain Res. 1982;45(1-2):29–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00235760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Waterfield A. A. In vitro models in the study of structure-activity relationships of narcotic analgesics. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1975;15:29–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.15.040175.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montel H., Starke K., Weber F. Influence of morphine and naloxone on the release of noradrenaline from rat brain cortex slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;283(4):357–369. doi: 10.1007/BF00501109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A. Opiates and enkephalin reduce the excitability of neuronal processes. Neuroscience. 1981;6(10):1943–1951. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudge A. W., Leeman S. E., Fischbach G. D. Enkephalin inhibits release of substance P from sensory neurons in culture and decreases action potential duration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):526–530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Tepper J. M., Young S. J., Ling N., Groves P. M. Noradrenergic terminal excitability: effects of opioids. Neurosci Lett. 1982 May 17;30(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werz M. A., Macdonald R. L. Opioid peptides decrease calcium-dependent action potential duration of mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons in cell culture. Brain Res. 1982 May 6;239(1):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90859-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Egan T. M., North R. A. Enkephalin opens potassium channels on mammalian central neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):74–77. doi: 10.1038/299074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J., Zieglgänsberger W. Mature spinal ganglion cells are not sensitive to opiate receptor mediated actions. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Jan 20;21(2):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Jessell T. M., Gamse R., Mudge A. W., Leeman S. E. Intrathecal morphine inhibits substance P release from mammalian spinal cord in vivo. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):155–157. doi: 10.1038/286155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



