Abstract
Dinucleotide AppppA (5',5'''-P1,P4-diadenosine tetraphosphate) is rapidly synthesized in Escherichia coli cells during heat shock. apaH mutants lack AppppN hydrolase activity and, therefore, contain constitutively levels of AppppA, which affect several cellular processes. However, the precise role of AppppA remains undetermined. Photo-crosslinking experiments with radioactively labelled azido-AppppA have shown that a number of proteins, including heat shock proteins DnaK and GroEL, specifically bind to AppppA. Several other unidentified proteins (C40, C45, and E89) also bind strongly to AppppA. In this work, we have identified the AppppA-binding protein E89 as heat shock protein ClpB. In addition, since ClpB belongs to a family of proteins implicated in proteolysis, we have examined the effects of apaH mutants on protein degradation. Constitutively elevated levels of AppppA stimulate lon-independent proteolysis only in heat-shocked cells. We also show that overproduction of ClpB from a plasmid rescues apaH mutants from sensitivity to killing by heat.
Full text
PDF


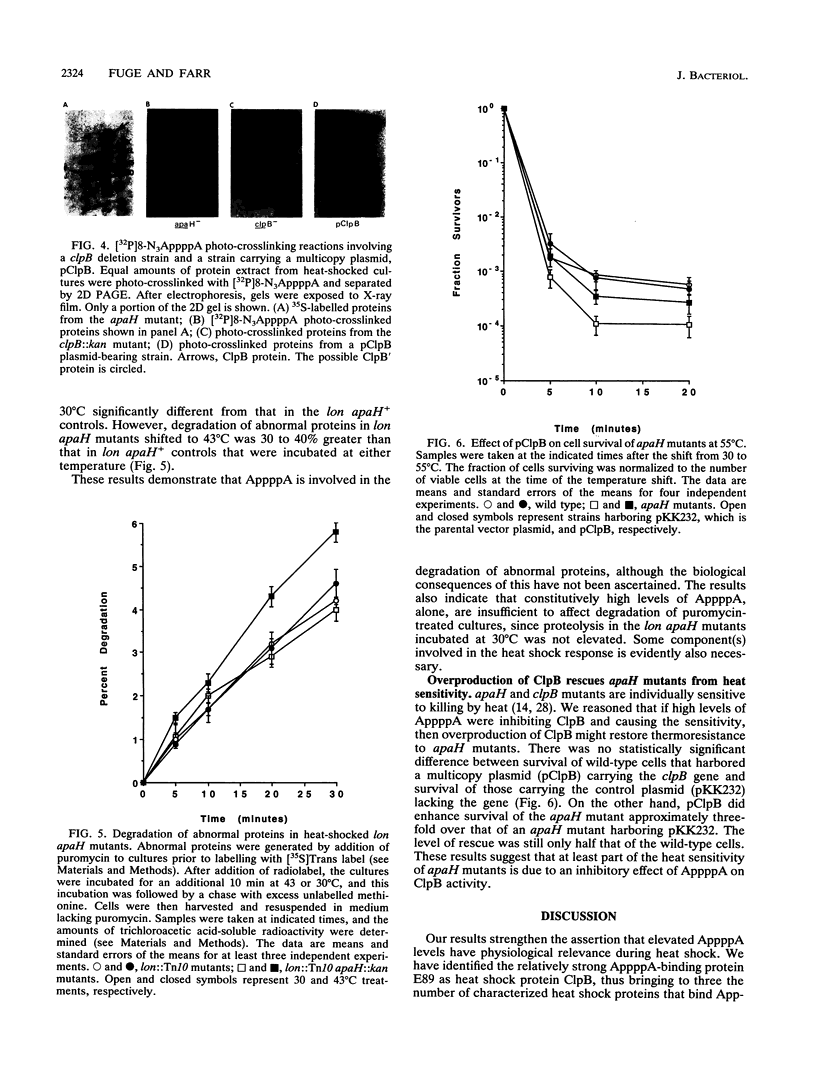


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. C., Jacobson M. K. Alteration of adenyl dinucleotide metabolism by environmental stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2350–2352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. ZTP (5-amino 4-imidazole carboxamide riboside 5'-triphosphate): a proposed alarmone for 10-formyl-tetrahydrofolate deficiency. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90455-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Lee P. C., Wilson S. W., Cutler C. W., Ames B. N. AppppA and related adenylylated nucleotides are synthesized as a consequence of oxidation stress. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. Escherichia coli DnaK protein possesses a 5'-nucleotidase activity that is inhibited by AppppA. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):931–935. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.931-935.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brevet A., Chen J., Lévêque F., Plateau P., Blanquet S. In vivo synthesis of adenylylated bis(5'-nucleosidyl) tetraphosphates (Ap4N) by Escherichia coli aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8275–8279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlier J., Sanchez R. Lysyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli K12. Chromatographic heterogeneity and the lysU-gene product. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):43–51. doi: 10.1042/bj2480043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. H., Goldberg A. L. The product of the lon (capR) gene in Escherichia coli is the ATP-dependent protease, protease La. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4931–4935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr S. B., Arnosti D. N., Chamberlin M. J., Ames B. N. An apaH mutation causes AppppA to accumulate and affects motility and catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5010–5014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Goldberg A. L. Production of abnormal proteins in E. coli stimulates transcription of lon and other heat shock genes. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):587–595. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S. Genetics of proteolysis in Escherichia coli*. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:163–198. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Squires C., Pichersky E., Carrington M., Hobbs M., Mattick J. S., Dalrymple B., Kuramitsu H., Shiroza T., Foster T. Conservation of the regulatory subunit for the Clp ATP-dependent protease in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3513–3517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang B. J., Park W. J., Chung C. H., Goldberg A. L. Escherichia coli contains a soluble ATP-dependent protease (Ti) distinct from protease La. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5550–5554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang B. J., Woo K. M., Goldberg A. L., Chung C. H. Protease Ti, a new ATP-dependent protease in Escherichia coli, contains protein-activated ATPase and proteolytic functions in distinct subunits. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8727–8734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama-Fujimura Y., Gottesman S., Maurizi M. R. A multiple-component, ATP-dependent protease from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4477–4485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., Gottesman S., Pumphrey J., Rudikoff S., Clark W. P., Maurizi M. R. The two-component, ATP-dependent Clp protease of Escherichia coli. Purification, cloning, and mutational analysis of the ATP-binding component. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15226–15236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa M., Wada C., Yoshioka S., Yura T. Expression of ClpB, an analog of the ATP-dependent protease regulatory subunit in Escherichia coli, is controlled by a heat shock sigma factor (sigma 32). J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4247–4253. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4247-4253.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroh H. E., Simon L. D. The ClpP component of Clp protease is the sigma 32-dependent heat shock protein F21.5. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):6026–6034. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.6026-6034.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. C., Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. AppppA, heat-shock stress, and cell oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7496–7500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léveque F., Blanchin-Roland S., Fayat G., Plateau P., Blanquet S. Design and characterization of Escherichia coli mutants devoid of Ap4N-hydrolase activity. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 20;212(2):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurizi M. R., Trisler P., Gottesman S. Insertional mutagenesis of the lon gene in Escherichia coli: lon is dispensable. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1124–1135. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1124-1135.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S., Bloch P. L., Reeh S., Neidhardt F. C. Patterns of protein synthesis in E. coli: a catalog of the amount of 140 individual proteins at different growth rates. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plateau P., Fromant M., Blanquet S. Heat shock and hydrogen peroxide responses of Escherichia coli are not changed by dinucleoside tetraphosphate hydrolase overproduction. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3817–3820. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3817-3820.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez Y., Lindquist S. L. HSP104 required for induced thermotolerance. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1112–1115. doi: 10.1126/science.2188365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez Y., Taulien J., Borkovich K. A., Lindquist S. Hsp104 is required for tolerance to many forms of stress. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2357–2364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires C. L., Pedersen S., Ross B. M., Squires C. ClpB is the Escherichia coli heat shock protein F84.1. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4254–4262. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4254-4262.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires C., Squires C. L. The Clp proteins: proteolysis regulators or molecular chaperones? J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1081–1085. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1081-1085.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., McKittrick N., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. The dnaK protein modulates the heat-shock response of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Kelley P. M., Neidhardt F. C. Differential induction of heat shock, SOS, and oxidation stress regulons and accumulation of nucleotides in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):26–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.26-32.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]