Abstract
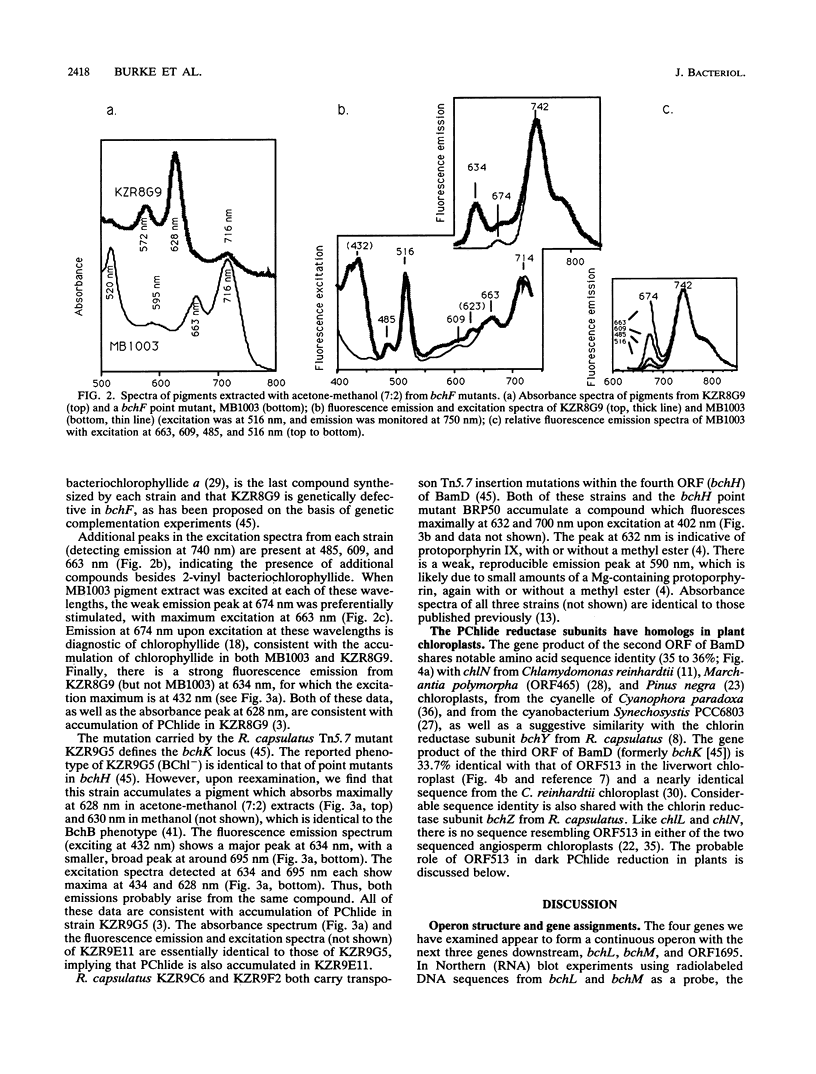
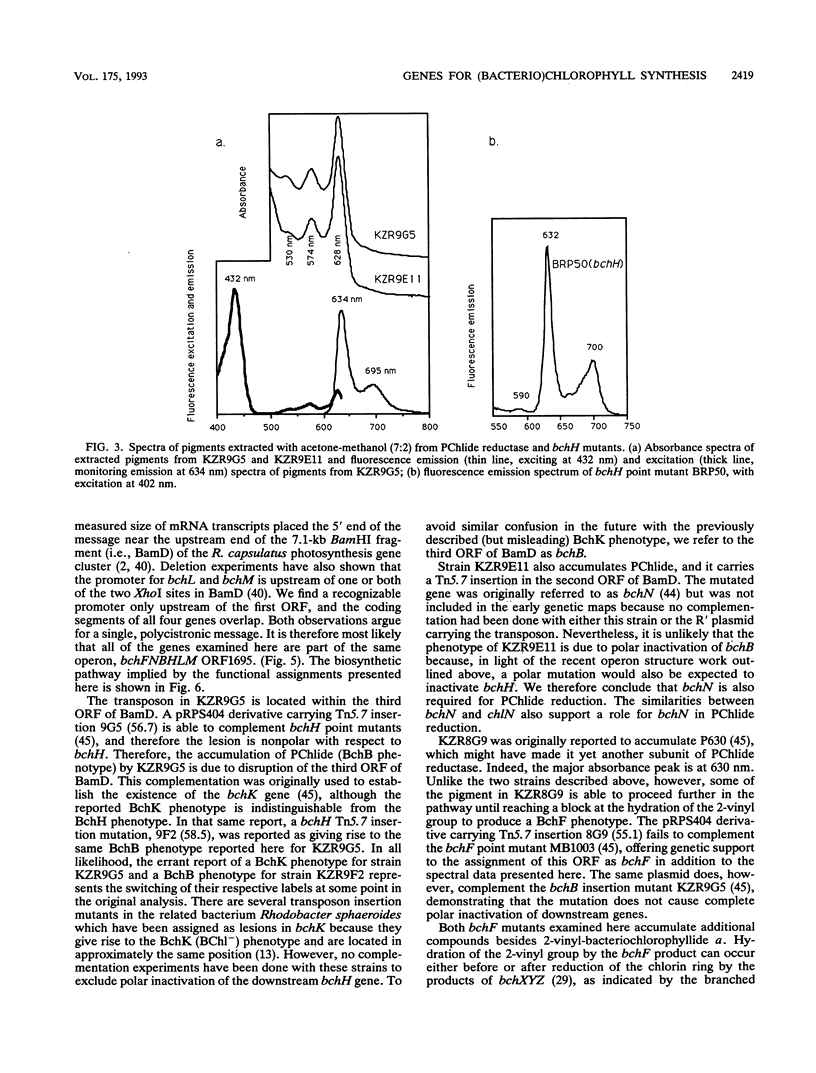
We present the nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of four contiguous bacteriochlorophyll synthesis genes from Rhodobacter capsulatus. Three of these genes code for enzymes which catalyze reactions common to the chlorophyll synthesis pathway and therefore are likely to be found in plants and cyanobacteria as well. The pigments accumulated in strains with physically mapped transposon insertion mutations are analyzed by absorbance and fluorescence spectroscopy, allowing us to assign the genes as bchF, bchN, bchB, and bchH, in that order. bchF encodes a bacteriochlorophyll alpha-specific enzyme that adds water across the 2-vinyl group. The other three genes are required for portions of the pathway that are shared with chlorophyll synthesis, and they were expected to be common to both pathways. bchN and bchB are required for protochlorophyllide reduction in the dark (along with bchL), a reaction that has been observed in all major groups of photosynthetic organisms except angiosperms, where only the light-dependent reaction has been clearly established. The purple bacterial and plant enzymes show 35% identity between the amino acids coded by bchN and chlN (gidA) and 49% identity between the amino acids coded by bchL and chlL (frxC). Furthermore, bchB is 33% identical to ORF513 from the Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast. We present arguments in favor of the probable role of ORF513 (chlB) in protochlorophyllide reduction in the dark. The further similarities of all three subunits of protochlorophyllide reductase and the three subunits of chlorin reductase in bacteriochlorophyll synthesis suggest that the two reductase systems are derived from a common ancestor.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong G. A., Alberti M., Leach F., Hearst J. E. Nucleotide sequence, organization, and nature of the protein products of the carotenoid biosynthesis gene cluster of Rhodobacter capsulatus. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Apr;216(2-3):254–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00334364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C. E., Buggy J. J., Yang Z. M., Marrs B. L. The superoperonal organization of genes for pigment biosynthesis and reaction center proteins is a conserved feature in Rhodobacter capsulatus: analysis of overlapping bchB and puhA transcripts. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Sep;228(3):433–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00260637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belanger F. C., Rebeiz C. A. Chloroplast biogenesis. Detection of divinyl protochlorophyllide in higher plants. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1266–1272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biel A. J., Marrs B. L. Transcriptional regulation of several genes for bacteriochlorophyll biosynthesis in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata in response to oxygen. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):686–694. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.686-694.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L., Dautricourt J. P., Maulik S., Relph J. Improved sensitivity of biological sequence database searches. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Jul;6(3):237–245. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.3.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., SISTROM W. R., STANIER R. Y. Kinetic studies of pigment synthesis by non-sulfur purple bacteria. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Feb;49(1):25–68. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030490104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choquet Y., Rahire M., Girard-Bascou J., Erickson J., Rochaix J. D. A chloroplast gene is required for the light-independent accumulation of chlorophyll in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1697–1704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05220.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coomber S. A., Chaudhri M., Connor A., Britton G., Hunter C. N. Localized transposon Tn5 mutagenesis of the photosynthetic gene cluster of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jun;4(6):977–989. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Shochat S., Malkin S., Ohad I. Functional Organization of the Chlorophyll-Containing Complexes of Chlamydomonas reinhardi: A Study of Their Formation and Interconnection with Reaction Centers in the Greening Process of the y-1 Mutant. Plant Physiol. 1982 Sep;70(3):637–644. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorchein A. Control of magnesium-protoporphyrin chelatase activity in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Role of light, oxygen, and electron and energy transfer. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):833–845. doi: 10.1042/bj1340833d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorchein A. Magnesium protoporphyrin chelatase activity in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Studies with whole cells. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):97–106. doi: 10.1042/bj1270097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiratsuka J., Shimada H., Whittier R., Ishibashi T., Sakamoto M., Mori M., Kondo C., Honji Y., Sun C. R., Meng B. Y. The complete sequence of the rice (Oryza sativa) chloroplast genome: intermolecular recombination between distinct tRNA genes accounts for a major plastid DNA inversion during the evolution of the cereals. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):185–194. doi: 10.1007/BF02464880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidholm J., Gustafsson P. Homologues of the green algal gidA gene and the liverwort frxC gene are present on the chloroplast genomes of conifers. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Oct;17(4):787–798. doi: 10.1007/BF00037061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma D., Cook D. N., O'Brien D. A., Hearst J. E. Analysis of the promoter and regulatory sequences of an oxygen-regulated bch operon in Rhodobacter capsulatus by site-directed mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(7):2037–2045. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.7.2037-2045.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madigan M. T., Gest H. Growth of a photosynthetic bacterium anaerobically in darkness, supported by "oxidant-dependent" sugar fermentation. Arch Microbiol. 1978 May 30;117(2):119–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00402298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs B. Mobilization of the genes for photosynthesis from Rhodopseudomonas capsulata by a promiscuous plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1003–1012. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1003-1012.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. M., Miceli S. M., Lechevalier M. P., Roberts R. J. FseI, a new type II restriction endonuclease that recognizes the octanucleotide sequence 5' GGCCGGCC 3'. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2061–2064. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogura Y., Takemura M., Oda K., Yamato K., Ohta E., Fukuzawa H., Ohyama K. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of a frxC-ORF469 gene cluster of Synechocystis PCC6803: conservation with liverwort chloroplast frxC-ORF465 and nif operon. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1992 May;56(5):788–793. doi: 10.1271/bbb.56.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pudek M. R., Richards W. R. A possible alternate pathway of bacteriochlorophyll biosynthesis in a mutant of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3132–3137. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki J. Y., Bauer C. E. Light-independent chlorophyll biosynthesis: involvement of the chloroplast gene chlL (frxC). Plant Cell. 1992 Aug;4(8):929–940. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.8.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. P., Cohen S. N., Clark W. G., Marrs B. L. Alignment of genetic and restriction maps of the photosynthesis region of the Rhodopseudomonas capsulata chromosome by a conjugation-mediated marker rescue technique. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):580–590. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.580-590.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver P. F., Wall J. D., Gest H. Characterization of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Nov 7;105(3):207–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00447139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z. M., Bauer C. E. Rhodobacter capsulatus genes involved in early steps of the bacteriochlorophyll biosynthetic pathway. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5001–5010. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5001-5010.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen H. C., Marrs B. Growth of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata under anaerobic dark conditions with dimethyl sulfoxide. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jun;181(2):411–418. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen H. C., Marrs B. Map of genes for carotenoid and bacteriochlorophyll biosynthesis in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):619–629. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.619-629.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youvan D. C., Bylina E. J., Alberti M., Begusch H., Hearst J. E. Nucleotide and deduced polypeptide sequences of the photosynthetic reaction-center, B870 antenna, and flanking polypeptides from R. capsulata. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):949–957. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90429-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Hearst J. E. Genetic-physical mapping of a photosynthetic gene cluster from R. capsulata. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):937–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90428-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



