Abstract
We compared plasma viral load values obtained with COBAS AMPLICOR human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) MONITOR version 1.5 and with COBAS TaqMan HIV-1 assays. Mean values were 4.2 and 2.9 log10 copies/ml, respectively, showing the lack of agreement between the two assays.
Plasma RNA viral load quantification is a clinically validated tool for monitoring human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection (5). There are several commercially available PCR assays for HIV-1 RNA quantification. Most of them were recently automated for sample preparation and were coupled to a real-time PCR-based method, giving a broader range of HIV-1 quantification and fewer time-consuming manipulations (2, 4, 6). Since June 2006, the 4,000 HIV-1-infected patients managed in the Department of Infectious Diseases of Bichat Claude Bernard Hospital (Paris, France), whose viral loads had previously been assayed with the COBAS AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR version 1.5 method (Roche Diagnostics Systems, Inc., Branchburg, NJ) and by automated extraction with the Magnapure large-volume kit (Roche Diagnostics, Meylan, France), have been monitored with the new RealTime COBAS TaqMan HIV-1 system assay, as recommended by the manufacturer. However, we were puzzled by significant discrepancies (more than 0.5 log10 copies/ml) between the two assays of serial plasma samples from patients not taking antiretroviral therapy.
We therefore compared HIV-1 RNA values obtained with the COBAS AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR version 1.5 with those of the COBAS TaqMan HIV-1 assay in the routine clinical setting.
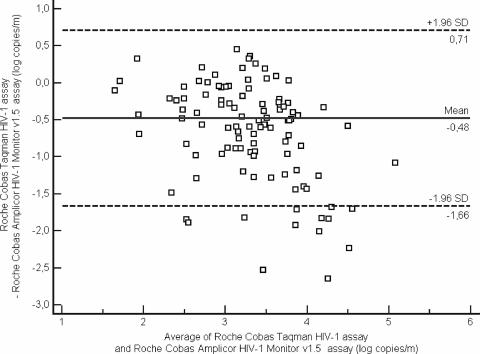
Plasma EDTA samples stored at −80°C were tested in parallel with the COBAS AMPLICOR MONITOR 1.5 assay (still available in our laboratory) and the COBAS TaqMan HIV system. Moreover, samples from all untreated patients with HIV-1 RNA values below 5,000 copies/ml with the COBAS TaqMan HIV system were also tested with the COBAS AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR 1.5 assay. The HIV-1 subtypes were determined in all the patients by examining the relatedness of the pol sequences with reference sequences of HIV-1 genetic subtypes and circulating recombinant forms obtained from the Los Alamos database (http://hiv-web.lanl.gov). Mean values (log10 copies/ml) obtained with the two assays were compared with a t test for paired data. Discrepancies between the two assays were examined individually for each HIV-1 subtype by using the Kruskal-Wallis test. Statistical analyses were done with SAS version 8.2 software (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC), and P values of less than 0.05 were considered to indicate significant differences. Bland and Altman curves were used to represent the degree of agreement between the two techniques (Fig. 1).
FIG. 1.
Degree of agreement in log10 copies/ml between the COBAS MONITOR 1.5 and the COBAS TaqMan assays for the 160 plasma specimens. The x axis of the Bland and Altman curves bears the mean values for each sample obtained by the two techniques. The y axis bears the differences between the values obtained by the two techniques. The solid lines represent the mean differences between the values, and the dotted lines represent the mean difference plus or minus 1.96 SD (95% limit of agreement).
The HIV-1 plasma viral load was determined with both assays, using 160 plasma specimens obtained from 140 patients. The mean values (± standard deviation [SD]) were 2.99 log copies/ml (±1.13) and 2.51 log copies/ml (±0.80), respectively, with the COBAS AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR 1.5 assay and the COBAS TaqMan HIV system (Fig. 1). Among the 140 patients in whom viral load was determined with both assays, discrepancies of more than 0.5 log copies/ml were observed for 34 cases (24%). These patients were infected by subtypes A (n = 4), B (n = 9), D (n = 1), CRF_02 (n = 15), CRF_13cpx (n = 1), F (n = 1), and G (n = 3). The viral loads obtained with the 54 plasma samples from these 34 patients are summarized in Table 1. The mean values obtained with the COBAS TaqMan System and the COBAS AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR 1.5 assay were 2.9 (±0.54) and 4.2 log10 (±0.82) copies/ml, respectively. The mean values obtained with the two assays differed by 1.3 log10 copies/ml (P < 0.0001). The viral load distributions obtained for B versus non-B subtypes did not differ significantly between the two assays (P = 0.32).
TABLE 1.
Comparative plasma viral load values
| Patient | HIV-1 subtype | HIV-1 RNA viral load
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MONITOR 1.5 (copies/ml) | MONITOR 1.5 (log10 copies/ml) | COBAS TaqMan (copies/ml) | COBAS TaqMan (log10 copies/ml) | ||
| 1a | CRF02 | 13,700 | 4.14 | 207 | 2.32 |
| 1b | 66,400 | 4.82 | 787 | 2.90 | |
| 2 | CRF02 | 254,000 | 5.40 | 4,980 | 3.70 |
| 3a | CRF02 | 38,300 | 4.58 | 1,393 | 3.14 |
| 3b | 142,000 | 5.15 | 1,396 | 3.14 | |
| 4 | A | 122,000 | 5.09 | 1,824 | 3.26 |
| 5a | CRF02 | 5,960 | 3.78 | 692 | 2.84 |
| 5b | 4,250 | 3.63 | 555 | 2.74 | |
| 6a | B | 22,500 | 4.35 | 1,291 | 3.11 |
| 6b | 150,000 | 5.18 | 2,192 | 3.34 | |
| 7a | CRF02 | 2,840 | 3.45 | <40 | <1.6 |
| 7b | 54,200 | 4.73 | 159 | 2.20 | |
| 8 | CRF02 | 416,000 | 5.62 | 34,300 | 4.54 |
| 9a | B | 139,000 | 5.14 | 2,894 | 2.38 |
| 9b | 51,200 | 4.71 | 1,889 | 3.28 | |
| 10a | CRF02 | 58,300 | 4.77 | 3,271 | 3.51 |
| 10b | 29,000 | 4.46 | 1,914 | 3.28 | |
| 11a | CRF02 | 1,340 | 3.13 | 140 | 2.15 |
| 11b | 1,000 | 3.00 | 272 | 2.43 | |
| 12a | CRF02 | 17,300 | 4.24 | 1,887 | 3.28 |
| 12b | 15,800 | 4.20 | 835 | 2.92 | |
| 13a | CRF13cpx | 1,964 | 3.29 | 100 | 2.00 |
| 13b | 3,080 | 3.49 | 671 | 2.83 | |
| 14 | G | 3,090 | 3.49 | <40 | <1.6 |
| 15 | CRF02 | 46,200 | 4.66 | 1,840 | 3.26 |
| 16 | CRF02 | 1,210 | 3.08 | <40 | <1.6 |
| 17 | B | 5,800 | 3.76 | 1,535 | 3.19 |
| 18a | A | 6,540 | 3.82 | 418 | 2.62 |
| 18b | 3,900 | 3.59 | 989 | 3.00 | |
| 19 | B | 13,500 | 4.13 | 2,650 | 3.42 |
| 20 | B | 2,750 | 3.44 | 301 | 2.48 |
| 21 | CRF02 | 3,720 | 3.57 | 476 | 2.68 |
| 22a | CRF02 | 2,880 | 3.46 | 705 | 2.85 |
| 22b | 2,930 | 3.47 | 388 | 2.59 | |
| 23a | CRF02 | 7,220 | 3.86 | 1,780 | 3.25 |
| 23b | 5,910 | 3.77 | 1,590 | 3.20 | |
| 24a | G | 9,600 | 3.98 | 512 | 2.71 |
| 24b | 13,600 | 4.13 | 2,188 | 3.34 | |
| 25 | B | 6,810 | 3.83 | 802 | 2.90 |
| 26a | F | 22,200 | 4.35 | 3,175 | 3.50 |
| 26b | 10,400 | 4.02 | 3201 | 3.51 | |
| 27 | D | 61,500 | 4.79 | 16,379 | 4.21 |
| 28a | A | 3,440 | 3.54 | 611 | 2.79 |
| 28b | 2,680 | 3.43 | 697 | 2.84 | |
| 29a | CRF02 | 4,890 | 3.69 | 1,010 | 3.00 |
| 29b | 5,320 | 3.73 | 1,340 | 3.13 | |
| 30a | A | 5,700 | 3.73 | 869 | 2.94 |
| 30b | 6,920 | 3.84 | 700 | 2.85 | |
| 31a | B | 430,000 | 5.63 | 2,507 | 3.40 |
| 31b | 53,900 | 4.73 | 1,040 | 3.00 | |
| 32 | B | 381,000 | 5.58 | 846 | 2.93 |
| 33 | B | 11,000 | 4.04 | 3,353 | 3.53 |
| 34a | G | 35,900 | 4.54 | 136 | 2.13 |
| 34b | 14,400 | 4.16 | <40 | <1.6 | |
Significant differences in viral load quantification, therefore, exist between these commercial assays from the same manufacturer. It has previously been shown that HIV genetic diversity can influence plasma HIV-1 RNA quantification in patients infected by non-B subtypes, and several authors have reported the failure of commercial assays for viral load monitoring in patients infected by non-B subtypes (1, 3, 4). This finding led the manufacturer to adapt the COBAS MONITOR version 1.0 assay to accept a broader range of viral diversity. Our results show that the COBAS TaqMan HIV-1 system underquantifies not only divergent subtypes like CRF_02 but also HIV-1 subtype B. Recently, Gueudin et al. reported that viral load values obtained with the COBAS TaqMan system were 0.28 log10 lower on average than those obtained with the COBAS MONITOR version 1.5 assay: 23 (26%) of 88 patients had more than a 0.5 log10 difference between the values of the two methods, and nine had a difference exceeding 1 log10 copies/ml (4). It is noteworthy that the primers designed for the COBAS TaqMan system are located in the same highly conserved gag region of the HIV-1 genome as in the COBAS MONITOR 1.5 assay (6) (7). The most likely explanation for these differences in HIV-1 RNA quantification is a COBAS TaqMan system primer or probe mismatch. A problem during the automated nucleic acid extraction procedure on the COBAS AmpliPrep instrument is unlikely, as this would occur at random. Moreover, the discrepancies found here are not due to a problem with a particular lot, as several lots have been used in our laboratory since June 2006. However, we cannot rule out a problem with several lots, as these differences in HIV-1 quantification between the two assays were not observed during the premarketing evaluation of the COBAS TaqMan system (6). Indeed, during the initial evaluation, we tested 112 plasma samples from patients infected by HIV-1 subtype B (n = 54) and by various HIV-1 non-B subtypes (n = 58). We have also observed differences of more than 0.5 log10 copies/ml between the values of the two assays. These differences concerned seven plasma samples (7/112; 6%), as follows: COBAS MONITOR 1.5 > COBAS TaqMan (n = 5) and COBAS TaqMan > COBAS MONITOR 1.5 (n = 2). The frequency of discordant results from the initial evaluation was lower (6%) than that from the study presented here (25%). One possible explanation is that the kit used during the initial evaluation (C-Taq HIV-1 IVD+) was different from the one delivered by Roche after 2006 (CAP CTM HIV-1 IVD+).
These results question the reliability of the RealTime COBAS TaqMan system for viral load quantification in HIV-1-infected patients. They also underline the importance of primer and probe design for real-time PCR quantification of viruses with high genetic diversity. Finally, they stress the need to harmonize viral load assays used in therapeutic trials.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 22 August 2007.
REFERENCES
- 1.Alaeus, A., K. Lidman, A. Sonnerborg, and J. Albert. 1997. Subtype-specific problems with quantification of plasma HIV-1 RNA. AIDS 11:859-865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Berger, A., L. Scherzed, M. Sturmer, W. Preiser, H. W. Doerr, and H. F. Rabenau. 2002. Evaluation of the COBAS AmpliPrep/Cobas Amplicor HIV-1 Monitor Ultrasensitive Test: comparison with the Cobas Amplicor HIV-1 Monitor test (manual specimen preparation). J. Clin. Virol. 25(Suppl. 3):S103-S107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Damond, F., C. Apetrei, D. Descamps, F. Brun-Vezinet, and F. Simon. 1999. HIV-1 subtypes and plasma RNA quantification. AIDS 13:286-288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gueudin, M., J. C. Plantier, V. Lemee, M. P. Schmitt, L. Chartier, T. Bourlet, A. Ruffault, F. Damond, M. Vray, and F. Simon. 2007. Evaluation of the Roche Cobas TaqMan and Abbott RealTime Extraction-Quantification systems for HIV-1 subtypes. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 44:500-505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mellors, J. W., A. Munoz, J. V. Giorgi, J. B. Margolick, C. J. Tassoni, P. Gupta, L. A. Kingsley, J. A. Todd, A. J. Saah, R. Detels, J. P. Phair, and C. R. Rinaldo, Jr. 1997. Plasma viral load and CD4+ lymphocytes as prognostic markers of HIV-1 infection. Ann. Intern. Med. 126:946-954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schumacher, W., E. Frick, M. Kauselmann, V. Maier-Hoyle, R. van der Vliet, and R. Babiel. 2007. Fully automated quantification of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 RNA in human plasma by the COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan system. J. Clin. Virol. 38:304-312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sninsky, J. J., and S. Kwok. 1993. The application of quantitative polymerase chain reaction to therapeutic monitoring. AIDS 7(Suppl. 2):S29-S34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]