Abstract
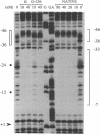
Several activators of sigma 70 holoenzyme whose binding sites lie upstream of the -35 region of promoters require the C-terminal region of the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase to activate transcription. (These are among class I activators, which require the C-terminal region of the alpha subunit for transcription activation.) Because transcription by sigma 54 holoenzyme universally depends upon activators whose binding sites lie well upstream (or downstream) of promoters, we determined whether the C-terminal region of the alpha subunit was also required for transcription from the sigma 54-dependent promoter for the glnA operon. Nitrogen regulatory protein C-dependent activation from the glnA promoter remained good when RNA polymerases containing C-terminal truncations of the alpha subunit were employed. This was also the case for nitrogen fixation protein A-dependent activation if a nitrogen fixation protein A-binding site was appropriately placed upstream of the glnA promoter. These results lead to the working hypothesis (as yet untested) that activators of sigma 54 holoenzyme, which appear to make direct physical contact with the polymerase to catalyze a change in its conformation, activate the sigma 54 holoenzyme by contacting the sigma subunit rather than the alpha subunit of the core enzyme.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buck M., Cannon W. Specific binding of the transcription factor sigma-54 to promoter DNA. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):422–424. doi: 10.1038/358422a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston K., Bell A., Kolb A., Buc H., Busby S. Stringent spacing requirements for transcription activation by CRP. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giladi H., Igarashi K., Ishihama A., Oppenheim A. B. Stimulation of the phage lambda pL promoter by integration host factor requires the carboxy terminus of the alpha-subunit of RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):985–990. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90514-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. Roles of TFIID in transcriptional initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1067–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90027-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Olson C., Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Activation defects caused by mutations in Escherichia coli rpoA are promoter specific. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5156–5160. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5156-5160.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward R. S., Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Functional specialization within the alpha-subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 5;221(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. Structure and function of bacterial sigma factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:839–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert M., Kolb A., Buc H. Overlapping promoters and their control in Escherichia coli: the gal case. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2807–2811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman J., Wong P. K., Sei K., Keener J., Kustu S. Products of nitrogen regulatory genes ntrA and ntrC of enteric bacteria activate glnA transcription in vitro: evidence that the ntrA product is a sigma factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7525–7529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. R., Santero E., Porter S., Kustu S. The integration host factor stimulates interaction of RNA polymerase with NIFA, the transcriptional activator for nitrogen fixation operons. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90284-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Identification of a subunit assembly domain in the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Sequence analysis of two temperature-sensitive mutations in the alpha subunit gene (rpoA) of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):5945–5948. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.5945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Hanamura A., Makino K., Aiba H., Aiba H., Mizuno T., Nakata A., Ishihama A. Functional map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: two modes of transcription activation by positive factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8958–8962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Bipartite functional map of the E. coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit: involvement of the C-terminal region in transcription activation by cAMP-CRP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90553-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Role of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit in transcription activation. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(22):3283–3288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keener J., Kustu S. Protein kinase and phosphoprotein phosphatase activities of nitrogen regulatory proteins NTRB and NTRC of enteric bacteria: roles of the conserved amino-terminal domain of NTRC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):4976–4980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.4976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Igarashi K., Ishihama A., Lavigne M., Buckle M., Buc H. E. coli RNA polymerase, deleted in the C-terminal part of its alpha-subunit, interacts differently with the cAMP-CRP complex at the lacP1 and at the galP1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):319–326. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Santero E., Keener J., Popham D., Weiss D. Expression of sigma 54 (ntrA)-dependent genes is probably united by a common mechanism. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):367–376. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.367-376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malan T. P., Kolb A., Buc H., McClure W. R. Mechanism of CRP-cAMP activation of lac operon transcription initiation activation of the P1 promoter. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):881–909. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M. J., Gibbins J. R. The nucleotide sequence of the nitrogen-regulation gene ntrA of Klebsiella pneumoniae and comparison with conserved features in bacterial RNA polymerase sigma factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7607–7620. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Robertson C. A., Flamm E., Weisberg R. A., Miller H. I. Overproduction of Escherichia coli integration host factor, a protein with nonidentical subunits. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4124–4127. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4124-4127.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ow D. W., Ausubel F. M. Regulation of nitrogen metabolism genes by nifA gene product in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 1983 Jan 27;301(5898):307–313. doi: 10.1038/301307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D. L., Szeto D., Keener J., Kustu S. Function of a bacterial activator protein that binds to transcriptional enhancers. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):629–635. doi: 10.1126/science.2563595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D., Keener J., Kustu S. Purification of the alternative sigma factor, sigma 54, from Salmonella typhimurium and characterization of sigma 54-holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19510–19518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA in E. coli is stimulated by activator bound to sites far from the promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Movsas B., Magasanik B. Activation of glnA transcription by nitrogen regulator I (NRI)-phosphate in Escherichia coli: evidence for a long-range physical interaction between NRI-phosphate and RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5512–5522. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5512-5522.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo F. D., Silhavy T. J. Alpha: the Cinderella subunit of RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14515–14518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santero E., Hoover T. R., North A. K., Berger D. K., Porter S. C., Kustu S. Role of integration host factor in stimulating transcription from the sigma 54-dependent nifH promoter. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):602–620. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santero E., Hoover T., Keener J., Kustu S. In vitro activity of the nitrogen fixation regulatory protein NIFA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7346–7350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. Probing the Escherichia coli glnALG upstream activation mechanism in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8934–8938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Porter S., Kustu S., Echols H. DNA-looping and enhancer activity: association between DNA-bound NtrC activator and RNA polymerase at the bacterial glnA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Carey M., Gralla J. D. Polymerase II promoter activation: closed complex formation and ATP-driven start site opening. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):450–453. doi: 10.1126/science.1310361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedel A., Weiss D. S., Popham D., Dröge P., Kustu S. A bacterial enhancer functions to tether a transcriptional activator near a promoter. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):486–490. doi: 10.1126/science.1970441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss D. S., Batut J., Klose K. E., Keener J., Kustu S. The phosphorylated form of the enhancer-binding protein NTRC has an ATPase activity that is essential for activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):155–167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90579-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yura T., Ishihama A. Genetics of bacterial RNA polymerases. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:59–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.000423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]