Abstract
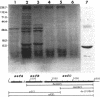
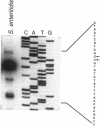
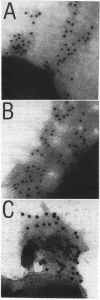
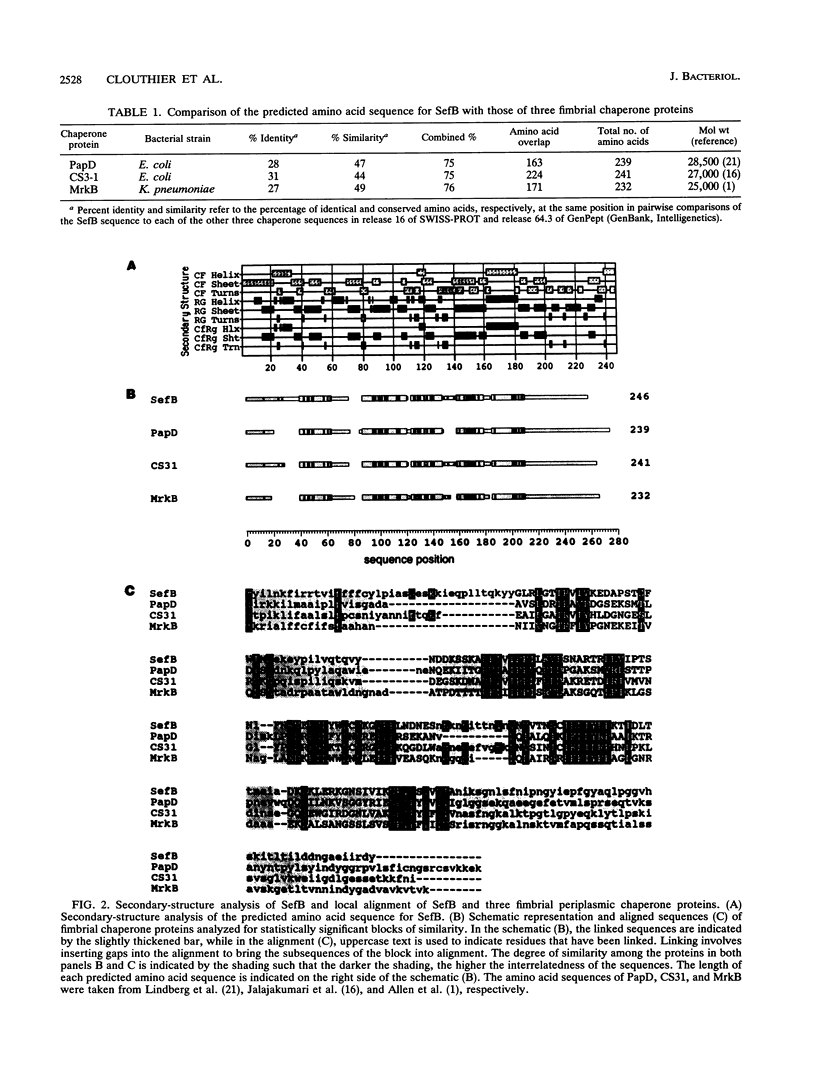
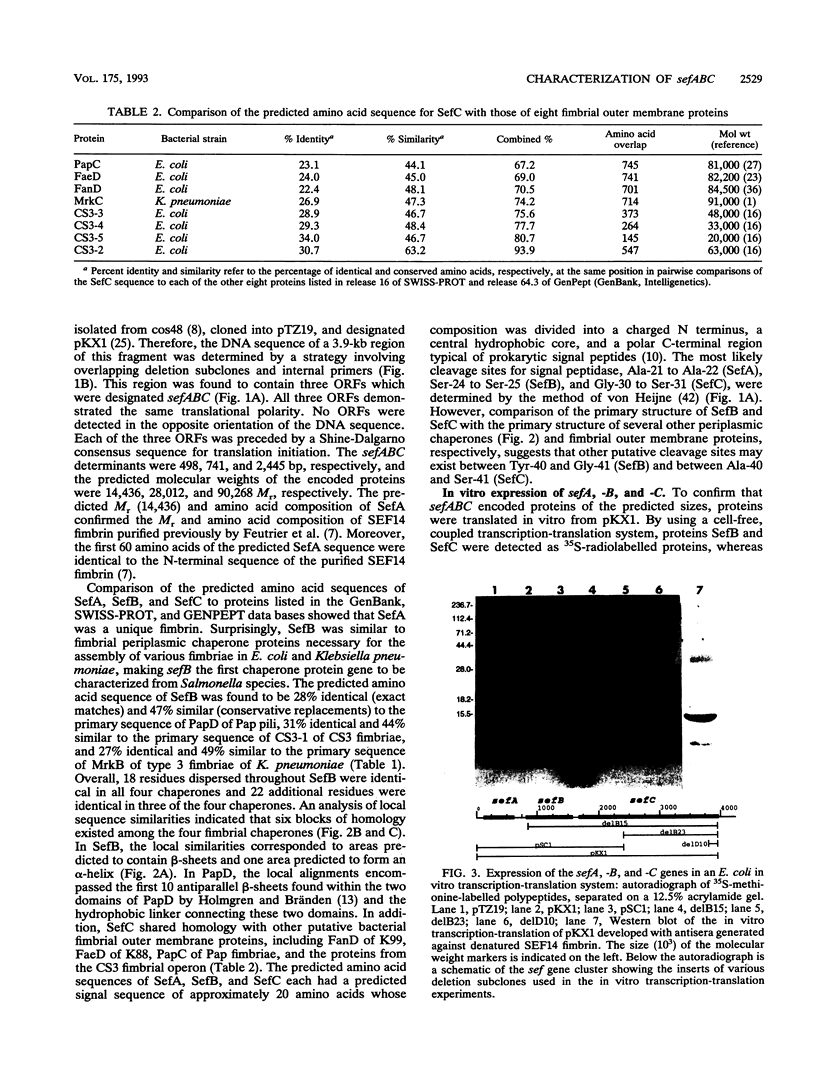
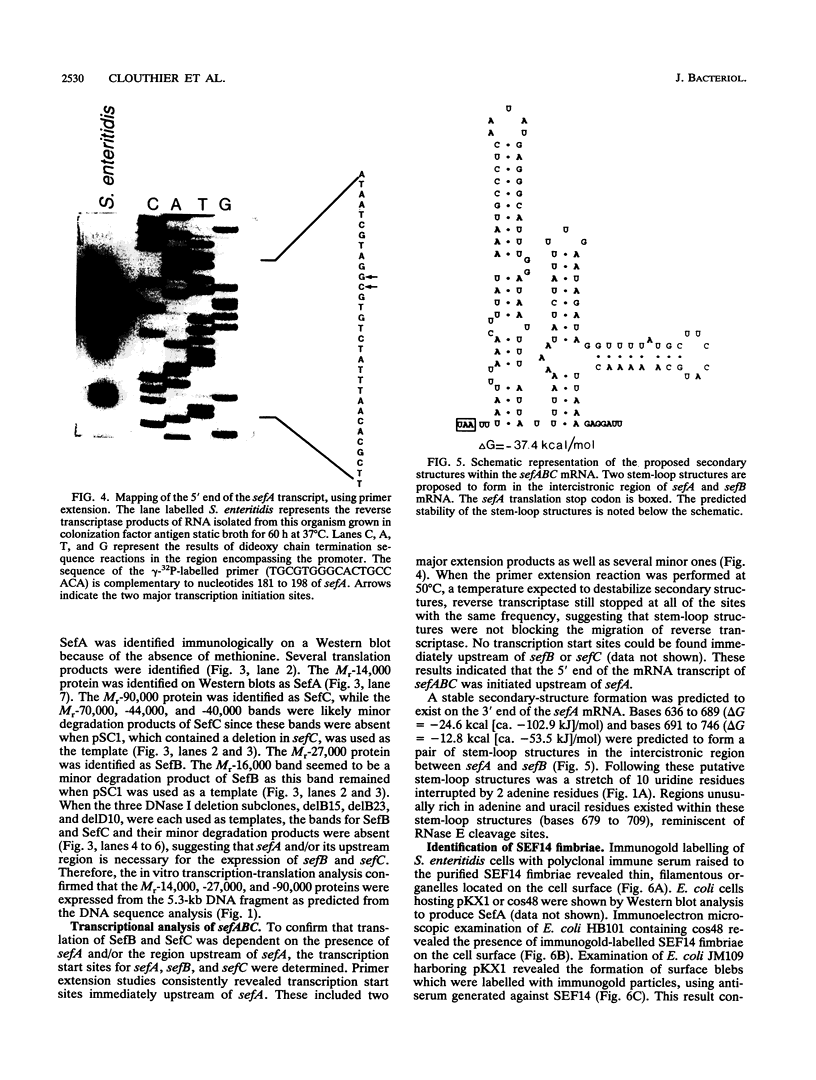
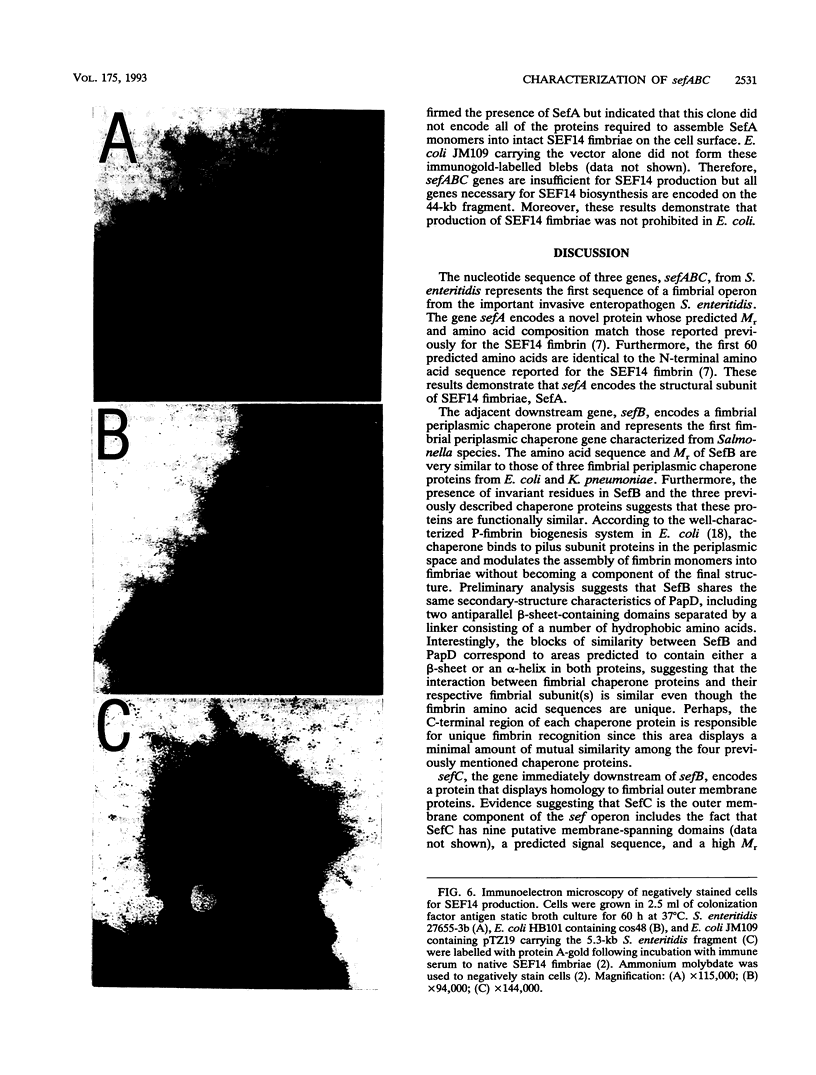
Salmonella enteritidis produces thin, filamentous fimbriae designated SEF14. A 3.9-kb region of a 5.3-kb fragment encoding genes responsible for SEF14 biosynthesis was sequenced and found to contain three genes, sefABC. sefA encoded a novel fimbrin, the structural subunit of SEF14 fimbriae. sefB and sefC encoded proteins homologous to Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae fimbrial periplasmic chaperone proteins and fimbrial outer membrane proteins, respectively, and are the first such genes to be characterized from Salmonella spp. in vitro expression directed by the 5.3-kb DNA fragment identified SefA, SefB, and SefC as approximately 14,000-, 28,000-, and 90,000-M(r) proteins, respectively, which correlated with their predicted amino acid sequences. sefB and sefC were not expressed in the absence of sefA. Primer extension analysis of sefABC revealed two major transcription start sites located upstream of sefA. Transcription of sefBC also initiated from the sefA promoter region. Secondary-structure analysis of the mRNA transcript for sefABC predicted the formation of two stable stem-loop structures in the intercistronic region between sefA and sefB indicative of differential regulation of SefA, SefB, and SefC translation. E. coli cells carrying the 5.3-kb DNA fragment of S. enteritidis DNA were unable to assemble distinguishable SEF14 fimbriae; however, immunogold-labelled SEF14 fimbriae were displayed on E. coli clones containing a 44-kb DNA fragment which encompassed the 5.3-kb region. Therefore, sefABC genes make up part of a complex sef operon responsible for the expression and assembly of SEF14 fimbriae.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen B. L., Gerlach G. F., Clegg S. Nucleotide sequence and functions of mrk determinants necessary for expression of type 3 fimbriae in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):916–920. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.916-920.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinson S. K., Emödy L., Müller K. H., Trust T. J., Kay W. W. Purification and characterization of thin, aggregative fimbriae from Salmonella enteritidis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4773–4781. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4773-4781.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinson S. K., Emödy L., Trust T. J., Kay W. W. Thin aggregative fimbriae from diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4490–4495. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4490-4495.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke E. M. Epidemiology of foodborne illness: UK. Lancet. 1990 Sep 29;336(8718):790–793. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93251-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Graaf F. K. Fimbrial structures of enterotoxigenic E. coli. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1988;54(5):395–404. doi: 10.1007/BF00461857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. Hemagglutination of human group A erythrocytes by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea: correlation with colonization factor. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):330–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.330-337.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feutrier J., Kay W. W., Trust T. J. Cloning and expression of a Salmonella enteritidis fimbrin gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4216–4222. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4216-4222.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feutrier J., Kay W. W., Trust T. J. Purification and characterization of fimbriae from Salmonella enteritidis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):221–227. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.221-227.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierasch L. M. Signal sequences. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):923–930. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnough M. C., Johnson E. A. Control of Salmonella enteritidis infections in poultry by polymyxin B and trimethoprim. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):785–788. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.785-788.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Ames G. F., Barnes W. M., Clement J. M., Hofnung M. A novel intercistronic regulatory element of prokaryotic operons. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):760–762. doi: 10.1038/298760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A., Bränden C. I. Crystal structure of chaperone protein PapD reveals an immunoglobulin fold. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):248–251. doi: 10.1038/342248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultgren S. J., Normark S., Abraham S. N. Chaperone-assisted assembly and molecular architecture of adhesive pili. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:383–415. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.002123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Discrimination between intracellular uptake and surface adhesion of bacterial pathogens. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):934–938. doi: 10.1126/science.1674624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalajakumari M. B., Thomas C. J., Halter R., Manning P. A. Genes for biosynthesis and assembly of CS3 pili of CFA/II enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: novel regulation of pilus production by bypassing an amber codon. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1685–1695. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Virkola R., Westurlund B., Holthöfer H., Parkkinen J. Tissue tropism of Escherichia coli adhesins in human extraintestinal infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;151:115–127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74703-8_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M. J., Heuser J., Normark S., Hultgren S. J. P pili in uropathogenic E. coli are composite fibres with distinct fibrillar adhesive tips. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):252–255. doi: 10.1038/356252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M. J., Normark S., Hultgren S. J. Immunoglobulin-like PapD chaperone caps and uncaps interactive surfaces of nascently translocated pilus subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10586–10590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Tennent J. M., Hultgren S. J., Lund B., Normark S. PapD, a periplasmic transport protein in P-pilus biogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6052–6058. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6052-6058.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. R., Zengel J. M., Lindahl L. Intermediates in the degradation of mRNA from the lactose operon of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2767–2776. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooi F. R., Claassen I., Bakker D., Kuipers H., de Graaf F. K. Regulation and structure of an Escherichia coli gene coding for an outer membrane protein involved in export of K88ab fimbrial subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2443–2457. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller K. H., Collinson S. K., Trust T. J., Kay W. W. Type 1 fimbriae of Salmonella enteritidis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4765–4772. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4765-4772.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller K. H., Trust T. J., Kay W. W. Fimbriation genes of Salmonella enteritidis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4648–4654. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4648-4654.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson P., Uhlin B. E. Differential decay of a polycistronic Escherichia coli transcript is initiated by RNaseE-dependent endonucleolytic processing. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1791–1799. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgren M., Båga M., Tennent J. M., Normark S. Nucleotide sequence, regulation and functional analysis of the papC gene required for cell surface localization of Pap pili of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Sep;1(2):169–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Falkow S. Organization and expression of genes responsible for type 1 piliation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):736–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.736-744.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., De Graaf F. K. Genetic organization and biogenesis of adhesive fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1988;54(4):285–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00393521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranchych W., Frost L. S. The physiology and biochemistry of pili. Adv Microb Physiol. 1988;29:53–114. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen C. Control of functional mRNA stability in bacteria: multiple mechanisms of nucleolytic and non-nucleolytic inactivation. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(3):277–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl P., Lintermans P., Marin M., Couturier M. Epidemiological study of Salmonella enteritidis strains of animal origin in Belgium. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Feb;106(1):11–16. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800056399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampling A., Anderson J. R., Upson R., Peters E., Ward L. R., Rowe B. Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 infection of broiler chickens: a hazard to public health. Lancet. 1989 Aug 19;2(8660):436–438. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera M. J., Rivera N., Castillo J., Rubio M. C., Gómez-Lus R. Molecular and epidemiological study of Salmonella clinical isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):927–932. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.927-932.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roosendaal B., de Graaf F. K. The nucleotide sequence of the fanD gene encoding the large outer membrane protein involved in the biosynthesis of K99 fimbriae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1263–1263. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner J. L. Formation, induction, and curing of bacteriophage P1 lysogens. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):679–689. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers G., Böck A. Novel transcriptional control of the pyruvate formate-lyase gene: upstream regulatory sequences and multiple promoters regulate anaerobic expression. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2485–2498. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2485-2498.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd E. Epidemiology of foodborne illness: North America. Lancet. 1990 Sep 29;336(8718):788–790. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93250-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. How signal sequences maintain cleavage specificity. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 25;173(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]