Abstract
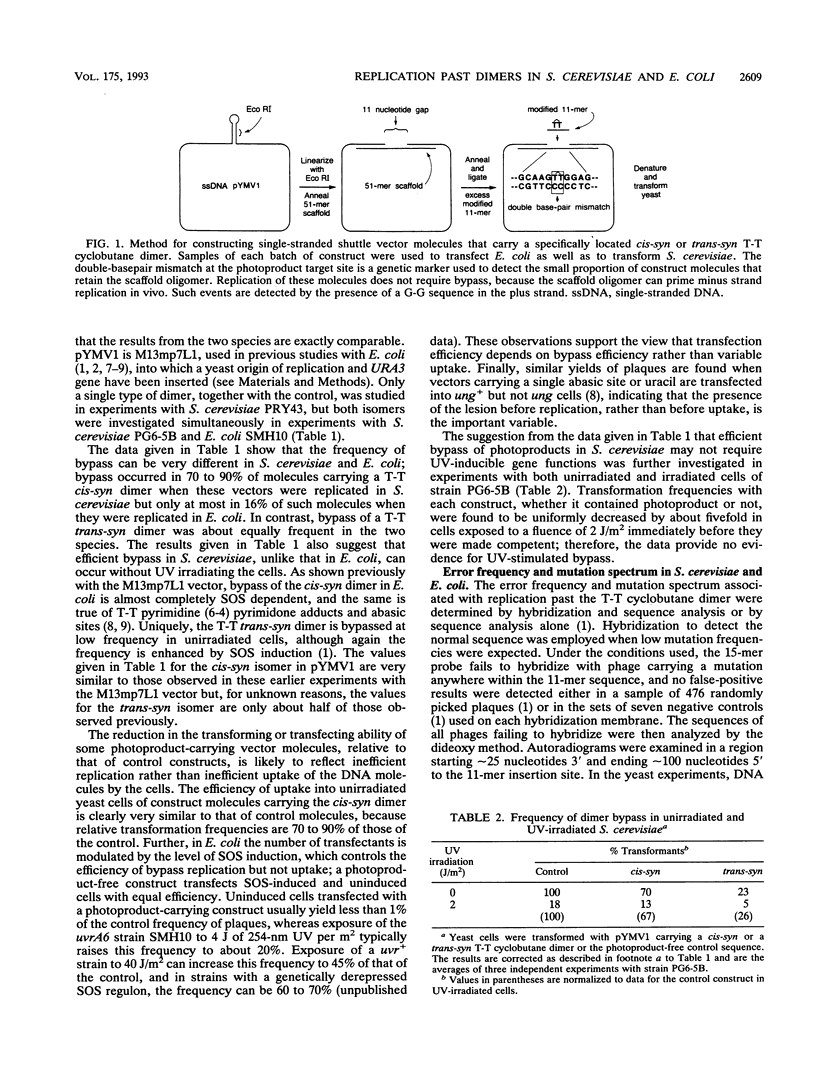
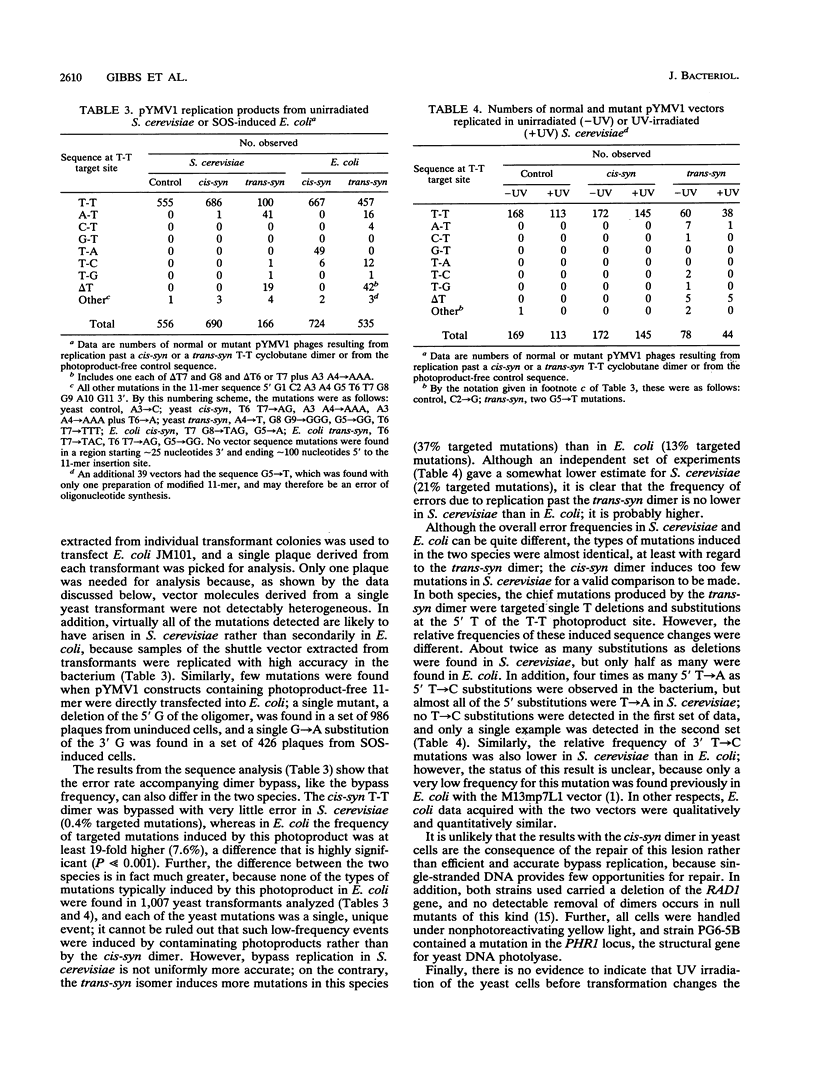
We have compared the mutagenic properties of a T-T cyclobutane dimer in baker's yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, with those in Escherichia coli by transforming each of these species with the same single-stranded shuttle vector carrying either the cis-syn or the trans-syn isomer of this UV photoproduct at a unique site. The mutagenic properties investigated were the frequency of replicational bypass of the photoproduct, the error rate of bypass, and the mutation spectrum. In SOS-induced E. coli, the cis-syn dimer was bypassed in approximately 16% of the vector molecules, and 7.6% of the bypass products had targeted mutations. In S. cerevisiae, however, bypass occurred in about 80% of these molecules, and the bypass was at least 19-fold more accurate (approximately 0.4% targeted mutations). Each of these yeast mutations was a single unique event, and none were like those in E. coli, suggesting that in fact the difference in error rate is much greater. Bypass of the trans-syn dimer occurred in about 17% of the vector molecules in both species, but with this isomer the error rate was higher in S. cerevisiae (21 to 36% targeted mutations) than in E. coli (13%). However, the spectra of mutations induced by the latter photoproduct were virtually identical in the two organisms. We conclude that bypass and error frequencies are determined both by the structure of the photoproduct-containing template and by the particular replication proteins concerned but that the types of mutations induced depend predominantly on the structure of the template. Unlike E. coli, bypass in S. cerevisiae did not require UV-induced functions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee S. K., Borden A., Christensen R. B., LeClerc J. E., Lawrence C. W. SOS-dependent replication past a single trans-syn T-T cyclobutane dimer gives a different mutation spectrum and increased error rate compared with replication past this lesion in uninduced cells. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2105–2112. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2105-2112.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee S. K., Christensen R. B., Lawrence C. W., LeClerc J. E. Frequency and spectrum of mutations produced by a single cis-syn thymine-thymine cyclobutane dimer in a single-stranded vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8141–8145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemmink J., Boelens R., Koning T., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Kaptein R. 1H NMR study of the exchangeable protons of the duplex d(GCGTTGCG).d(CGCAACGC) containing a thymine photodimer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4645–4653. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larimer F. W., Perry J. R., Hardigree A. A. The REV1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation, sequence, and functional analysis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):230–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.230-237.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C. W., Banerjee S. K., Borden A., LeClerc J. E. T-T cyclobutane dimers are misinstructive, rather than non-instructive, mutagenic lesions. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jun;222(1):166–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00283040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C. W., Borden A., Banerjee S. K., LeClerc J. E. Mutation frequency and spectrum resulting from a single abasic site in a single-stranded vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2153–2157. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClerc J. E., Borden A., Lawrence C. W. The thymine-thymine pyrimidine-pyrimidone(6-4) ultraviolet light photoproduct is highly mutagenic and specifically induces 3' thymine-to-cytosine transitions in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9685–9689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClerc J. E., Istock N. L., Saran B. R., Allen R., Jr Sequence analysis of ultraviolet-induced mutations in M13lacZ hybrid phage DNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):217–237. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagher D., Strauss B. Insertion of nucleotides opposite apurinic/apyrimidinic sites in deoxyribonucleic acid during in vitro synthesis: uniqueness of adenine nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4518–4526. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B., Essigmann J. M. Site-specific mutagenesis: retrospective and prospective. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Jun;12(6):949–955. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.6.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhal R. K., Hinkle D. C., Lawrence C. W. The REV3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is transcriptionally regulated more like a repair gene than one encoding a DNA polymerase. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Dec;236(1):17–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00279638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. S., Garrett D. S., Brockie I. R., Svoboda D. L., Telser J. 1H NMR assignment and melting temperature study of cis-syn and trans-syn thymine dimer containing duplexes of d(CGTATTATGC).d(GCATAATACG). Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8858–8866. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox D. R., Prakash L. Incision and postincision steps of pyrimidine dimer removal in excision-defective mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):618–623. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.618-623.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



