Abstract
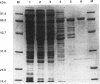
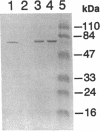
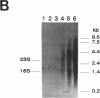
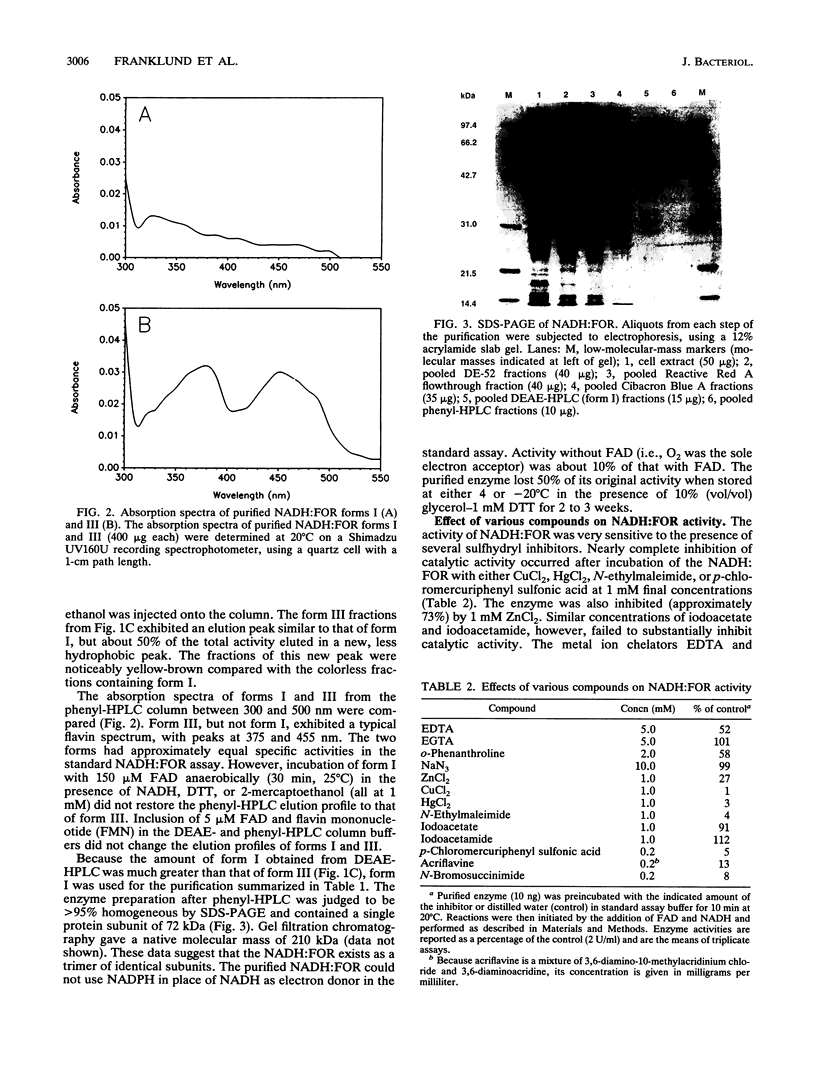
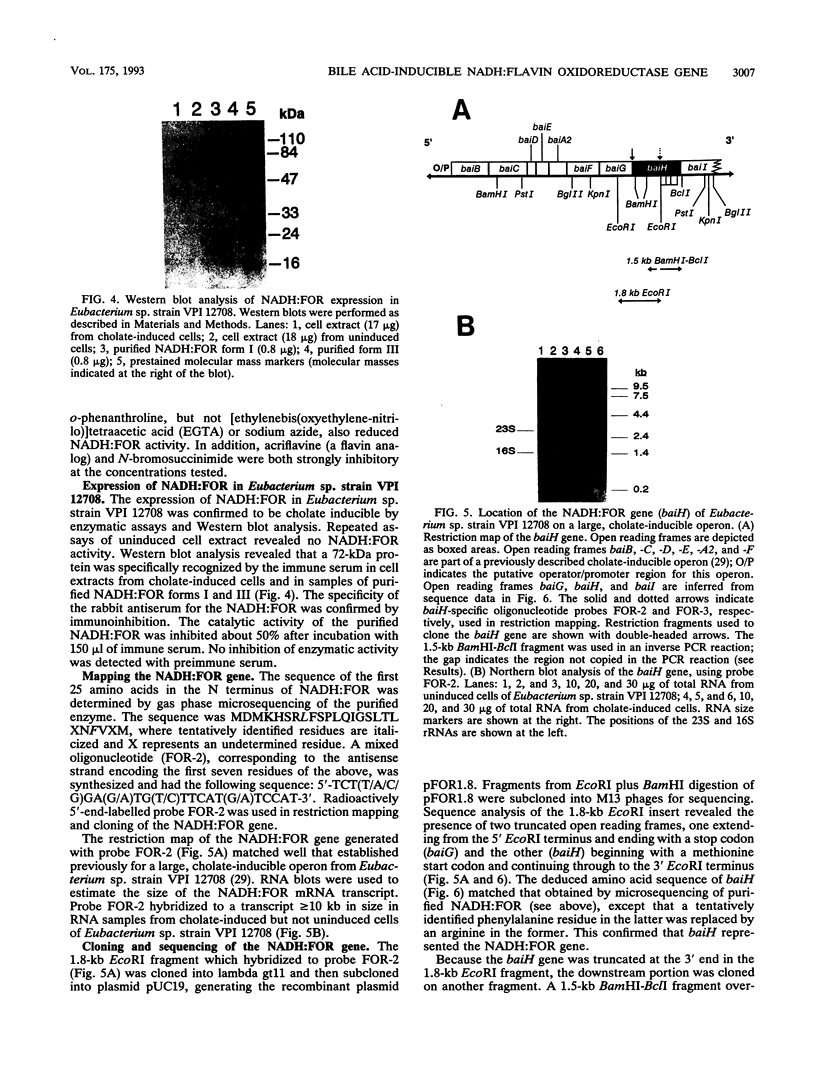
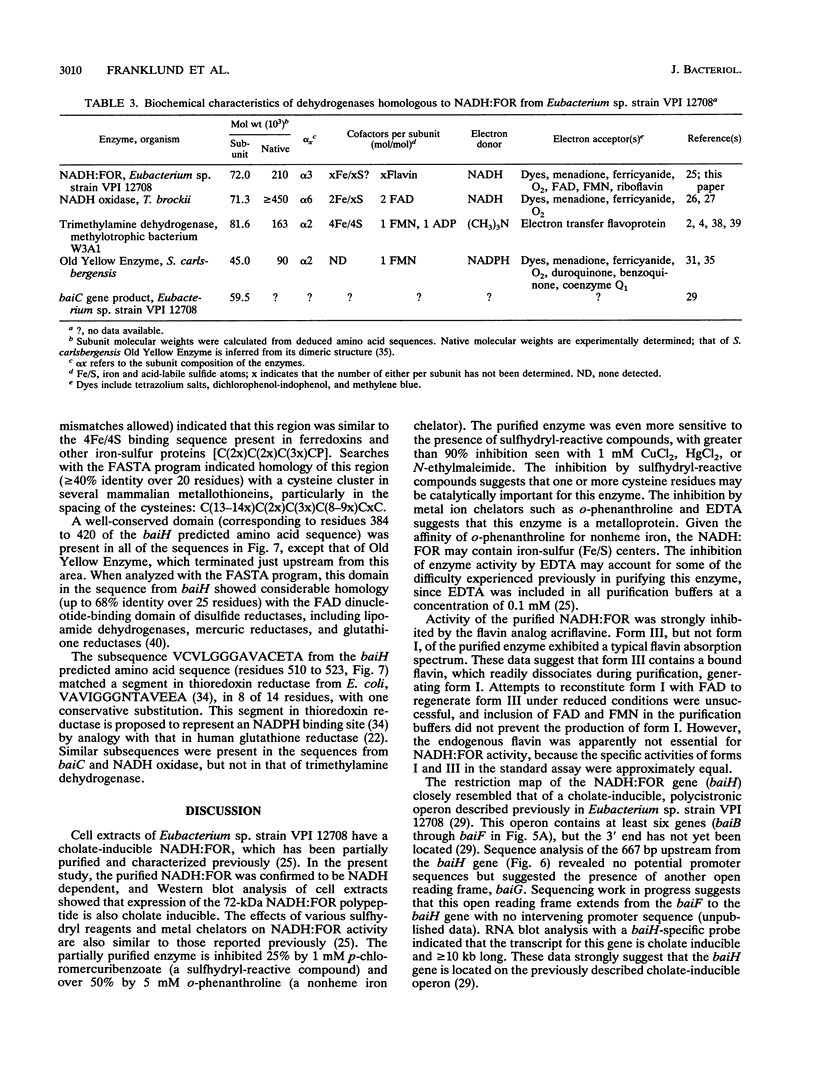
A cholate-inducible, NADH-dependent flavin oxidoreductase from the intestinal bacterium Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708 was purified 372-fold to apparent electrophoretic homogeneity. The subunit and native molecular weights were estimated to be 72,000 and 210,000, respectively, suggesting a homotrimeric organization. Three peaks of NADH:flavin oxidoreductase activity (forms I, II, and III) eluted from a DEAE-high-performance liquid chromatography column. Absorption spectra revealed that purified form III, but not form I, contained bound flavin, which dissociated during purification to generate form I. Enzyme activity was inhibited by sulfhydryl-reactive compounds, acriflavine, o-phenanthroline, and EDTA. Activity assays and Western blot (immunoblot) analysis confirmed that expression of the enzyme was cholate inducible. The first 25 N-terminal amino acid residues of purified NADH:flavin oxidoreductase were determined, and a corresponding oligonucleotide probe was synthesized for use in cloning of the associated gene, baiH. Restriction mapping, sequence data, and RNA blot analysis suggested that the baiH gene was located on a previously described, cholate-inducible operon > or = 10 kb long. The baiH gene encoded a 72,006-Da polypeptide containing 661 amino acids. The deduced amino acid sequence of the baiH gene was homologous to that of NADH oxidase from Thermoanaerobium brockii, trimethylamine dehydrogenase from methylotrophic bacterium W3A1, Old Yellow Enzyme from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis, and the product of the baiC gene of Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708, located upstream from the baiH gene in the cholate-inducible operon. Alignment of these five sequences revealed potential ligands for an iron-sulfur cluster, a putative flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding domain, and two other well-conserved domains of unknown function.
Full text
PDF


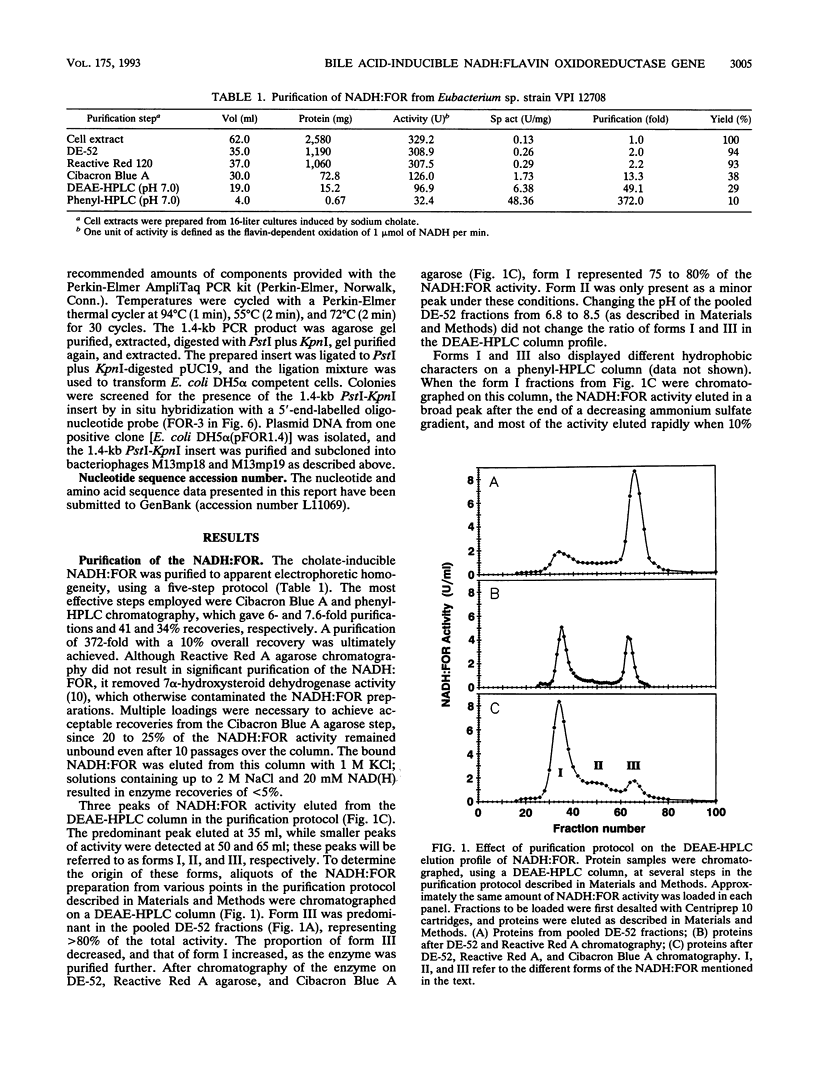




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber M. J., Neame P. J., Lim L. W., White S., Matthews F. S. Correlation of x-ray deduced and experimental amino acid sequences of trimethylamine dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6611–6619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Einarsson K., Melone P., Hylemon P. Mechanism of intestinal formation of deoxycholic acid from cholic acid in humans: evidence for a 3-oxo-delta 4-steroid intermediate. J Lipid Res. 1989 Jul;30(7):1033–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd G., Mathews F. S., Packman L. C., Scrutton N. S. Trimethylamine dehydrogenase of bacterium W3A1. Molecular cloning, sequence determination and over-expression of the gene. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 24;308(3):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81291-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. I., Raicht R. F., Deschner E. E., Takahashi M., Sarwal A. N., Fazzini E. Effect of cholic acid feeding on N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced colon tumors and cell kinetics in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Mar;64(3):573–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. P., White W. B., Egestad B., Sjövall J., Hylemon P. B. Biosynthesis of a novel bile acid nucleotide and mechanism of 7 alpha-dehydroxylation by an intestinal Eubacterium species. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4701–4707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. P., White W. B., Hylemon P. B. Molecular cloning of bile acid 7-dehydroxylase from Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1516–1521. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1516-1521.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. P., White W. B., Lijewski M., Hylemon P. B. Nucleotide sequence and regulation of a gene involved in bile acid 7-dehydroxylation by Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2070–2077. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2070-2077.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson V. L., Kumar M. A. Inhibition by trimethylamine of methylamine oxidation by Paracoccus denitrificans and bacterium W3A1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 26;1016(3):339–343. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90166-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklund C. V., de Prada P., Hylemon P. B. Purification and characterization of a microbial, NADP-dependent bile acid 7 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9842–9849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopal-Srivastava R., Mallonee D. H., White W. B., Hylemon P. B. Multiple copies of a bile acid-inducible gene in Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4420–4426. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4420-4426.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuman D. M., Vlahcevic Z. R., Bailey M. L., Hylemon P. B. Regulation of bile acid synthesis. II. Effect of bile acid feeding on enzymes regulating hepatic cholesterol and bile acid synthesis in the rat. Hepatology. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):892–897. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Roda A. Physicochemical properties of bile acids and their relationship to biological properties: an overview of the problem. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 15;25(13):1477–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Melone P. D., Franklund C. V., Lund E., Björkhem I. Mechanism of intestinal 7 alpha-dehydroxylation of cholic acid: evidence that allo-deoxycholic acid is an inducible side-product. J Lipid Res. 1991 Jan;32(1):89–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauth-Siegel R. L., Blatterspiel R., Saleh M., Schiltz E., Schirmer R. H., Untucht-Grau R. Glutathione reductase from human erythrocytes. The sequences of the NADPH domain and of the interface domain. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jan;121(2):259–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L. W., Mathews F. S., Steenkamp D. J. Identification of ADP in the iron-sulfur flavoprotein trimethylamine dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3075–3078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky R. H., Hylemon P. B. Characterization of a NADH:flavin oxidoreductase induced by cholic acid in a 7 alpha-dehydroxylating intestinal Eubacterium species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 11;612(2):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda K., Truscott K., Liu X. L., Scopes R. K. A thermostable NADH oxidase from anaerobic extreme thermophiles. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):551–555. doi: 10.1042/bj2840551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallonee D. H., Adams J. L., Hylemon P. B. The bile acid-inducible baiB gene from Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708 encodes a bile acid-coenzyme A ligase. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2065–2071. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2065-2071.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallonee D. H., White W. B., Hylemon P. B. Cloning and sequencing of a bile acid-inducible operon from Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7011–7019. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7011-7019.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Schopfer L. M. Reactivity of old yellow enzyme with alpha-NADPH and other pyridine nucleotide derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1215–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mower H. F., Ray R. M., Shoff R., Stemmermann G. N., Nomura A., Glober G. A., Kamiyama S., Shimada A., Yamakawa H. Fecal bile acids in two Japanese populations with different colon cancer risks. Cancer Res. 1979 Feb;39(2 Pt 1):328–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Model P. Sequence of thioredoxin reductase from Escherichia coli. Relationship to other flavoprotein disulfide oxidoreductases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):9015–9019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Thiele D. J., Davio M., Lockridge O., Massey V. The cloning and expression of a gene encoding Old Yellow Enzyme from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20720–20724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenkamp D. J., Gallup M. The natural flavorprotein electron acceptor of trimethylamine dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4086–4089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenkamp D. J., Mallinson J. Trimethylamine dehydrogenase from a methylotrophic bacterium. I. Isolation and steady-state kinetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 13;429(3):705–719. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Untucht-Grau R., Schirmer R. H., Schirmer I., Krauth-Siegel R. L. Glutathione reductase from human erythrocytes: amino-acid sequence of the structurally known FAD-binding domain. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):407–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Cacciapuoti A. F., Fricke R. J., Whitehead T. R., Mosbach E. H., Hylemon P. B. Cofactor requiremets for 7 alpha-dehydroxylation of cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid in cell extracts of the intestinal anaerobic bacterium, Eubacterium species V.P.I. 13708. J Lipid Res. 1981 Aug;22(6):891–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Fricke R. J., Hylemon P. B. 7 beta-Dehydroxylation of ursodeoxycholic acid by whole cells and cell extracts of the intestinal anaerobic bacterium, Eubacterium species V.P.I. 12708. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jan;23(1):145–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Lipsky R. L., Fricke R. J., Hylemon P. B. Bile acid induction specificity of 7 alpha-dehydroxylase activity in an intestinal Eubacterium species. Steroids. 1980 Jan;35(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(80)90115-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Paone D. A., Cacciapuoti A. F., Fricke R. J., Mosbach E. H., Hylemon P. B. Regulation of bile acid 7-dehydroxylase activity by NAD+ and NADH in cell extracts of Eubacterium species V.P.I. 12708. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jan;24(1):20–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White W. B., Coleman J. P., Hylemon P. B. Molecular cloning of a gene encoding a 45,000-dalton polypeptide associated with bile acid 7-dehydroxylation in Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):611–616. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.611-616.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White W. B., Franklund C. V., Coleman J. P., Hylemon P. B. Evidence for a multigene family involved in bile acid 7-dehydroxylation in Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4555–4561. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4555-4561.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]