Abstract
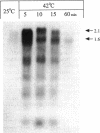
The groESL operon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens was cloned and sequenced and found to be highly homologous to previously analyzed groE operons in nucleotides of the coding region and in amino acid sequence. Transcription of this operon in A. tumefaciens was considerably stimulated by heat shock. Primer extension analysis revealed that the groE transcripts from cells under heat shock were initiated from the same promoter (a sigma-70-like promoter) as transcripts from untreated cells, and no sequence homology with the Escherichia coli heat shock promoters was observed. The DNA sequence downstream of the transcription start site contains an inverted repeat that has a strong similarity to other groESL operons of both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria (such as cyanobacteria and chlamydiae). This conserved region is thought to form a hairpin-loop structure and may play a role in gene regulation during heat shock.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom M., Skelly S., VanBogelen R., Neidhardt F., Brot N., Weissbach H. In vitro effect of the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory protein on expression of heat shock genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):380–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.380-384.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowing D. W., Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A., Woolford C., Hendrix R. W., Gross C. A. Consensus sequence for Escherichia coli heat shock gene promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch M., Moreno E., Stackebrandt E. Nucleotide sequence of the 16S rRNA from Brucella abortus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1765–1765. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvin L. D., Hardies S. C. Nucleotide sequence for the htpR gene from Citrobacter freundii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4889–4889. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. The htpR gene product of E. coli is a sigma factor for heat-shock promoters. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., Wong S. L. Cloning and characterization of the groESL operon from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):3981–3992. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.3981-3992.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J., Adams L. G., Ficht T. A. Characterization of the heat shock response in Brucella abortus and isolation of the genes encoding the GroE heat shock proteins. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2425–2431. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2425-2431.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantis N. J., Winans S. C. Characterization of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens heat shock response: evidence for a sigma 32-like sigma factor. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):991–997. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.991-997.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Belland R. J., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. The 57-kD chlamydial hypersensitivity antigen is a stress response protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1271–1283. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narberhaus F., Bahl H. Cloning, sequencing, and molecular analysis of the groESL operon of Clostridium acetobutylicum. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3282–3289. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3282-3289.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narberhaus F., Giebeler K., Bahl H. Molecular characterization of the dnaK gene region of Clostridium acetobutylicum, including grpE, dnaJ, and a new heat shock gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3290–3299. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3290-3299.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Schiesswohl M., Völker U., Hecker M., Schumann W. Cloning, sequencing, mapping, and transcriptional analysis of the groESL operon from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):3993–3999. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.3993-3999.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal G., Ron E. Z. Cloning, sequencing, and transcriptional analysis of the gene coding for the vegetative sigma factor of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(10):3026–3030. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.3026-3030.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb R., Reddy K. J., Sherman L. A. Regulation and sequence of the Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 groESL operon, encoding a cyanobacterial chaperonin. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5079–5088. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5079-5088.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzstein M., Völker U., Dedio J., Löbau S., Zuber U., Schiesswohl M., Herget C., Hecker M., Schumann W. Cloning, sequencing, and molecular analysis of the dnaK locus from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3300–3310. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3300-3310.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeilstra-Ryalls J., Fayet O., Georgopoulos C. The universally conserved GroE (Hsp60) chaperonins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:301–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]