Abstract
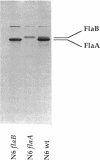
Helicobacter pylori is one of the most common human pathogens. It causes chronic gastritis and is involved in the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal ulcer disease and possibly gastric carcinoma. Helicobacter mustelae is a bacterium closely related to H. pylori that causes gastritis and ulcer disease in ferrets and is therefore considered an important animal model of gastric Helicobacter infections. Motility, even in a viscous environment, is conferred to the bacteria by several sheathed flagella and is regarded as one of their principal virulence factors. The flagellar filament of H. pylori consists of two different flagellin species expressed in different amounts. The gene (flaA) encoding the major flagellin has recently been cloned and sequenced. Here we report the cloning and sequencing of two highly homologous new flagellin genes from H. pylori 85P and H. mustelae NCTC 12032. The nucleotide sequence of the H. pylori gene proved that it encoded the second flagellin molecule found in H. pylori flagellar filaments. The genes were named flaB. The H. mustelae and H. pylori flaB genes both coded for proteins with 514 amino acids and molecular masses of 54.0 and 53.9 kDa, respectively. The proteins shared 81.7% identical amino acids. The degree of conservation between H. pylori FlaB and the H. pylori FlaA major flagellin was much lower (58%). Both flaB genes were preceded by sigma 54-like promoter sequences. Mapping of the transcription start site for the H. pylori flaB gene by a primer extension experiment confirmed the functional activity of the sigma 54 promoter. To evaluate the importance of both genes for motility, flaA- and flaB-disrupted mutants of H. pylori N6 were constructed by electroporation-mediated allelic exchange and characterized by Western blot (immunoblot) analysis and motility testing. Both mutations selectively abolished the expression of the targeted gene without affecting the synthesis of the other flagellin molecule. Whereas flaA mutants were completely nonmotile, flaB mutants retained motility.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J. Helicobacter pylori and the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal inflammation. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):626–633. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J. Hypotheses on the pathogenesis and natural history of Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation. Gastroenterology. 1992 Feb;102(2):720–727. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90126-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cussac V., Ferrero R. L., Labigne A. Expression of Helicobacter pylori urease genes in Escherichia coli grown under nitrogen-limiting conditions. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2466–2473. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2466-2473.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick J. D. Helicobacter (Campylobacter) pylori: a new twist to an old disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:249–269. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.001341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton K. A., Brooks C. L., Morgan D. R., Krakowka S. Essential role of urease in pathogenesis of gastritis induced by Helicobacter pylori in gnotobiotic piglets. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2470–2475. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2470-2475.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton K. A., Morgan D. R., Krakowka S. Campylobacter pylori virulence factors in gnotobiotic piglets. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1119–1125. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1119-1125.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton K. A., Morgan D. R., Krakowka S. Motility as a factor in the colonisation of gnotobiotic piglets by Helicobacter pylori. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Aug;37(2):123–127. doi: 10.1099/00222615-37-2-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero R. L., Cussac V., Courcoux P., Labigne A. Construction of isogenic urease-negative mutants of Helicobacter pylori by allelic exchange. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4212–4217. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4212-4217.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Correa P., Taylor N. S., Lee A., Otto G., Murphy J. C., Rose R. Helicobacter mustelae-associated gastritis in ferrets. An animal model of Helicobacter pylori gastritis in humans. Gastroenterology. 1990 Aug;99(2):352–361. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91016-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Otto G., Murphy J. C., Taylor N. S., Lee A. Gastric colonization of the ferret with Helicobacter species: natural and experimental infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jul-Aug;13 (Suppl 8):S671–S680. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.supplement_8.s671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Otto G., Taylor N. S., Rosenblad W., Murphy J. C. Helicobacter mustelae-induced gastritis and elevated gastric pH in the ferret (Mustela putorius furo). Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1875–1880. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1875-1880.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geis G., Leying H., Suerbaum S., Mai U., Opferkuch W. Ultrastructure and chemical analysis of Campylobacter pylori flagella. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):436–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.436-441.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., McCulloch R. K., Armstrong J. A., Wee S. H. Unusual cellular fatty acids and distinctive ultrastructure in a new spiral bacterium (Campylobacter pyloridis) from the human gastric mucosa. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Apr;19(2):257–267. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-2-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., Logan S. M., Thornton S., Trust T. J. Genomic organization and expression of Campylobacter flagellin genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1853–1860. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1853-1860.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazell S. L., Lee A., Brady L., Hennessy W. Campylobacter pyloridis and gastritis: association with intercellular spaces and adaptation to an environment of mucus as important factors in colonization of the gastric epithelium. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):658–663. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D. Alternative sigma factors and the regulation of flagellar gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Dec;5(12):2875–2882. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostrzynska M., Betts J. D., Austin J. W., Trust T. J. Identification, characterization, and spatial localization of two flagellin species in Helicobacter pylori flagella. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):937–946. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.937-946.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Santero E., Keener J., Popham D., Weiss D. Expression of sigma 54 (ntrA)-dependent genes is probably united by a common mechanism. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):367–376. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.367-376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne-Roussel A., Courcoux P., Tompkins L. Gene disruption and replacement as a feasible approach for mutagenesis of Campylobacter jejuni. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1704–1708. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1704-1708.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne A., Courcoux P., Tompkins L. Cloning of Campylobacter jejuni genes required for leucine biosynthesis, and construction of leu-negative mutant of C. jejuni by shuttle transposon mutagenesis. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jan;143(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90030-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne A., Cussac V., Courcoux P. Shuttle cloning and nucleotide sequences of Helicobacter pylori genes responsible for urease activity. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):1920–1931. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.1920-1931.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A., Fox J. G., Otto G., Murphy J. A small animal model of human Helicobacter pylori active chronic gastritis. Gastroenterology. 1990 Nov;99(5):1315–1323. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91156-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leying H., Suerbaum S., Geis G., Haas R. Cloning and genetic characterization of a Helicobacter pylori flagellin gene. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Oct;6(19):2863–2874. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J., Guerry P. Evidence for posttranslational modification and gene duplication of Campylobacter flagellin. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3031–3038. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3031-3038.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewski S. I., Goodwin C. S. Restriction endonuclease analysis of the genome of Campylobacter pylori with a rapid extraction method: evidence for considerable genomic variation. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):465–471. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura A., Stemmermann G. N., Chyou P. H., Kato I., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinoma among Japanese Americans in Hawaii. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 17;325(16):1132–1136. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110173251604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijten P. J., van Asten F. J., Gaastra W., van der Zeijst B. A. Structural and functional analysis of two Campylobacter jejuni flagellin genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17798–17804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke J., Lee A., Fox J. G. An ultrastructural study of Helicobacter mustelae and evidence of a specific association with gastric mucosa. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Jun;36(6):420–427. doi: 10.1099/00222615-36-6-420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Friedman G. D., Vandersteen D. P., Chang Y., Vogelman J. H., Orentreich N., Sibley R. K. Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 17;325(16):1127–1131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110173251603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson W. L. Helicobacter pylori and peptic ulcer disease. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 11;324(15):1043–1048. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104113241507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suerbaum S., Geis G., Josenhans C., Opferkuch W. Biochemical studies of Helicobacter mustelae fatty acid composition and flagella. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1695–1698. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1695-1698.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny B., Hennecke H. The -24/-12 promoter comes of age. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;5(4):341–357. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trieu-Cuot P., Gerbaud G., Lambert T., Courvalin P. In vivo transfer of genetic information between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3583–3587. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04120.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]