Abstract
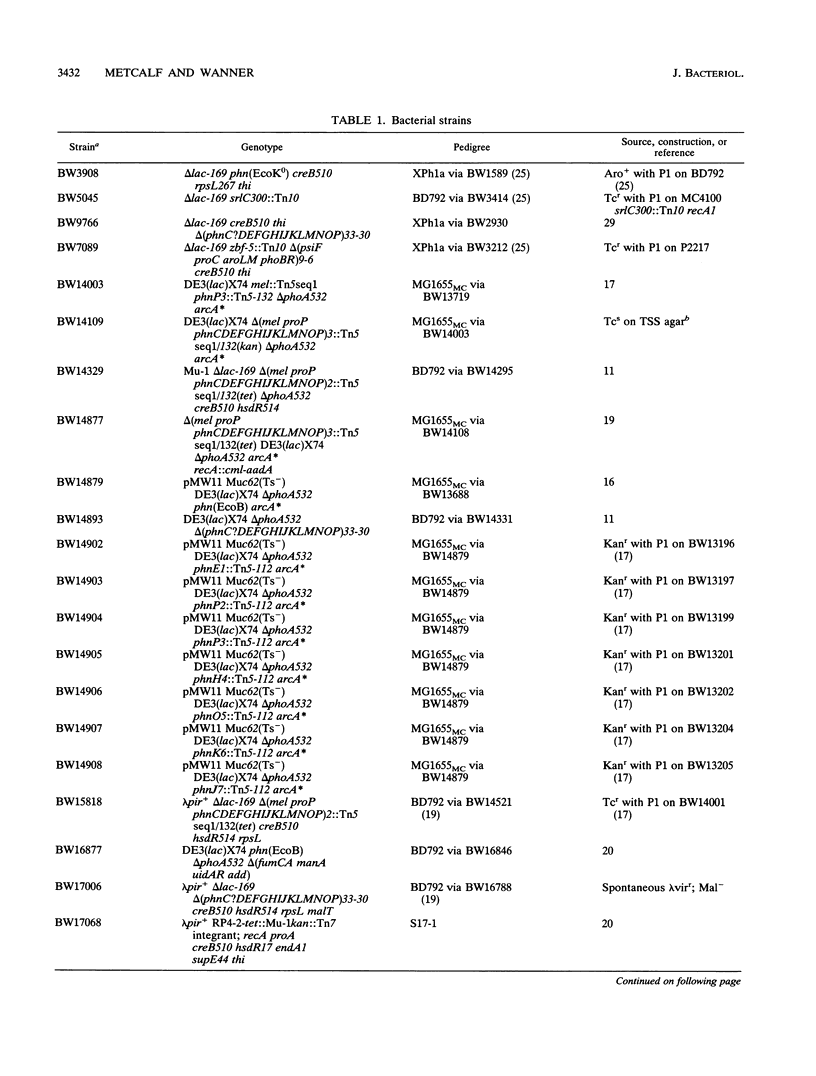
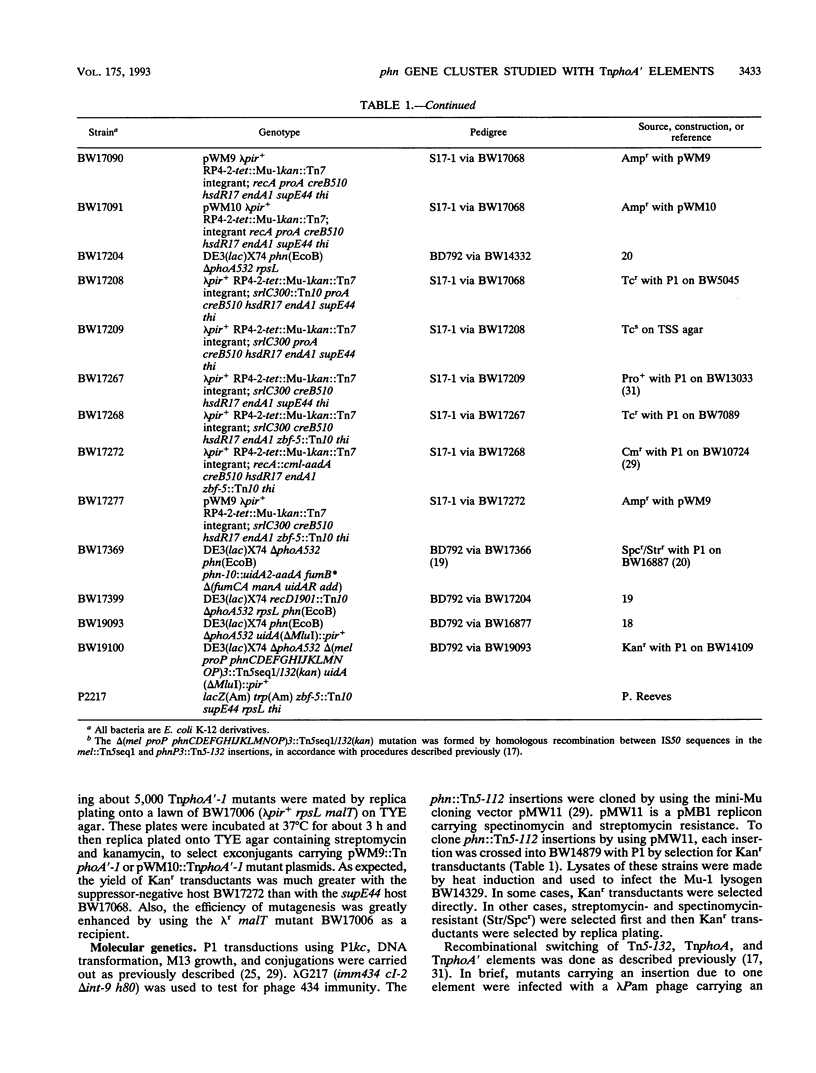
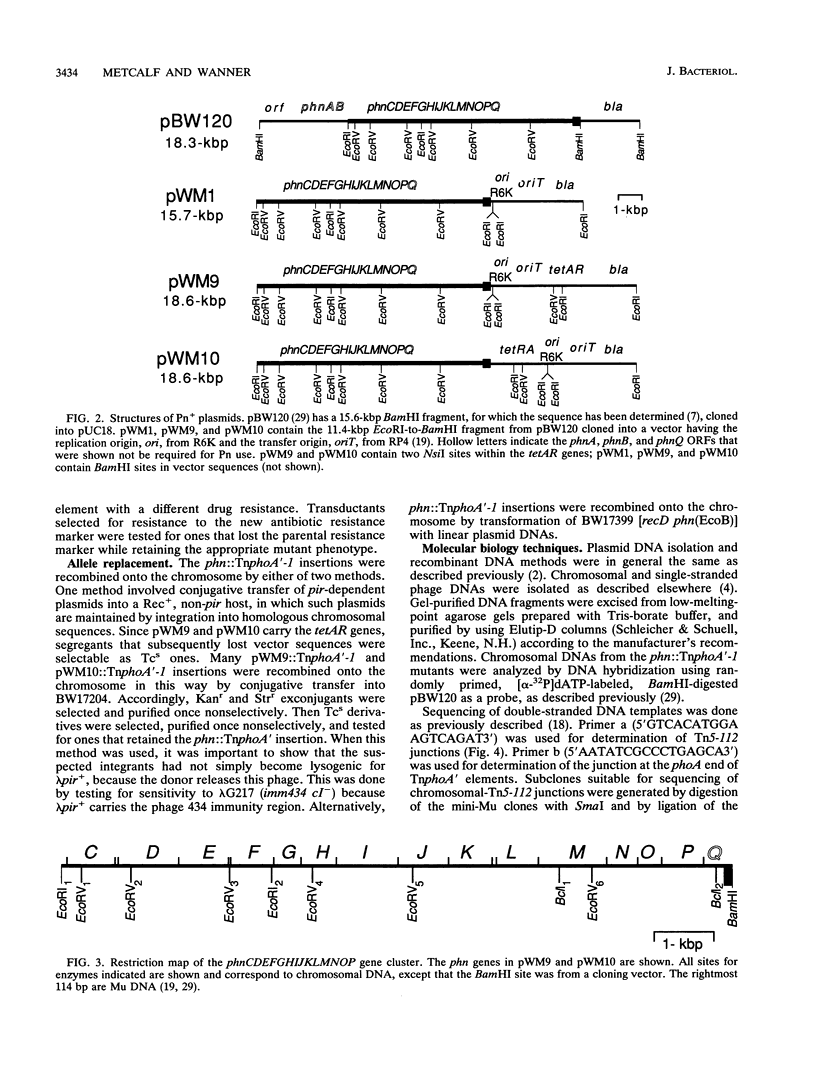
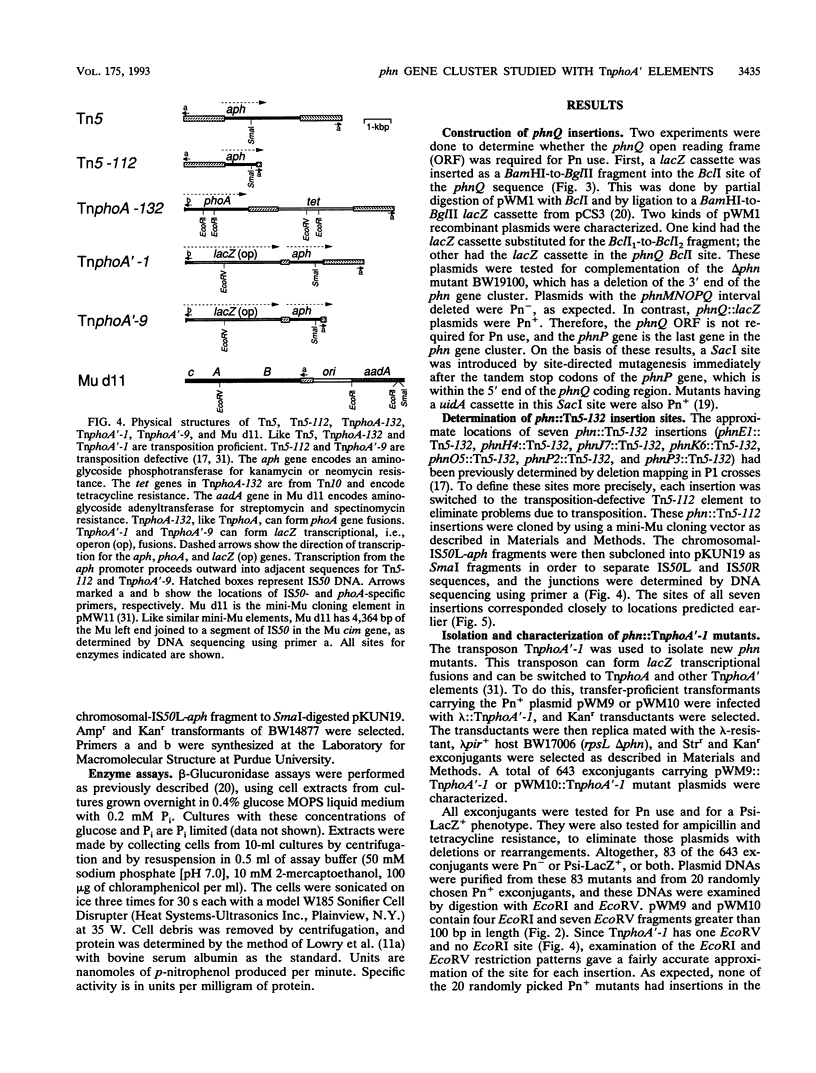
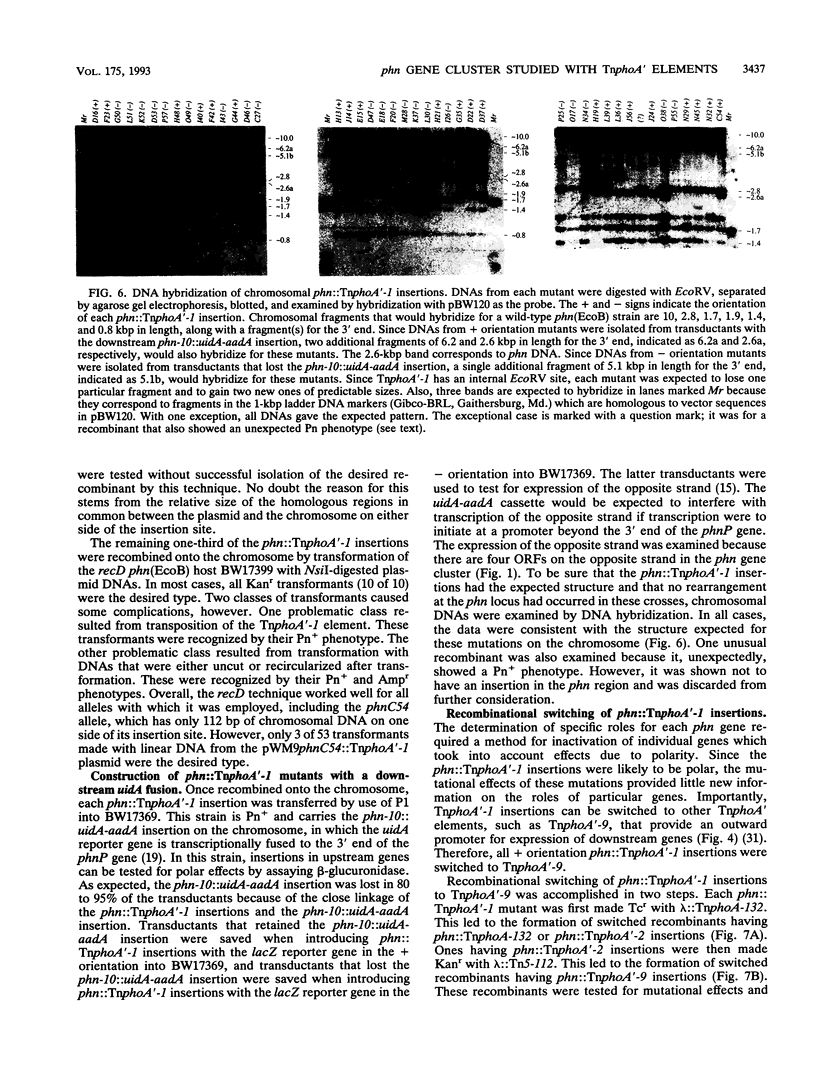
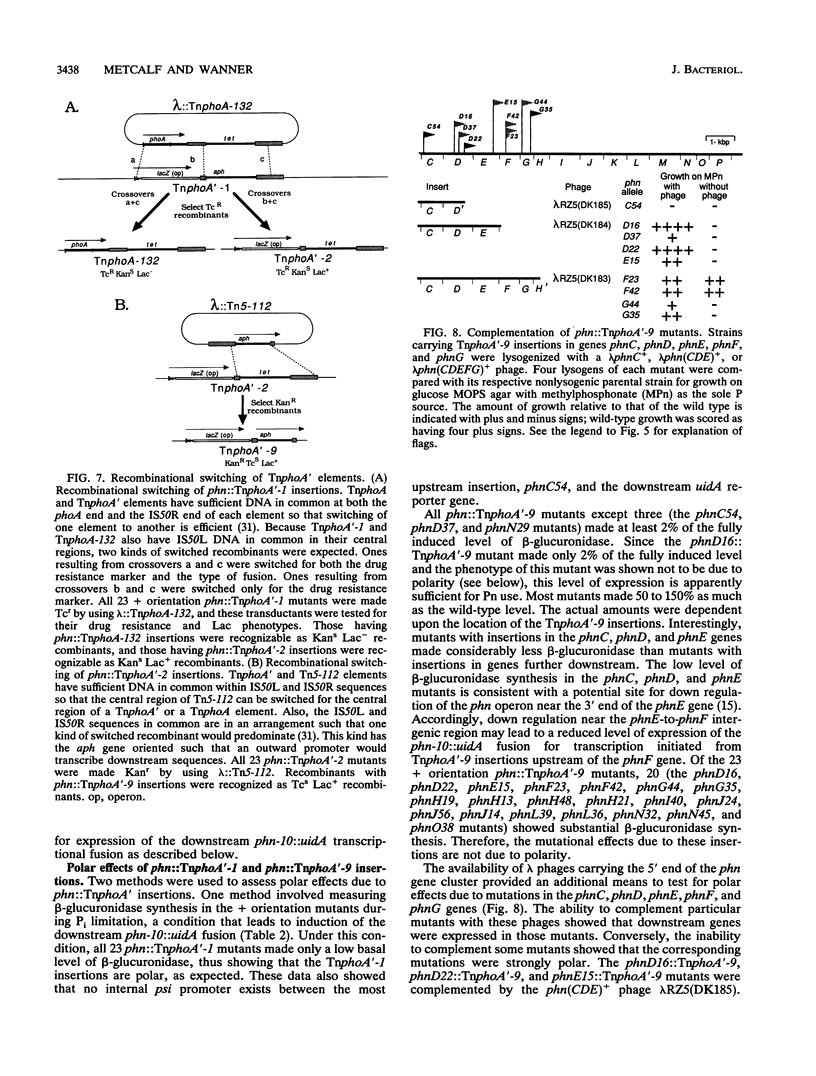
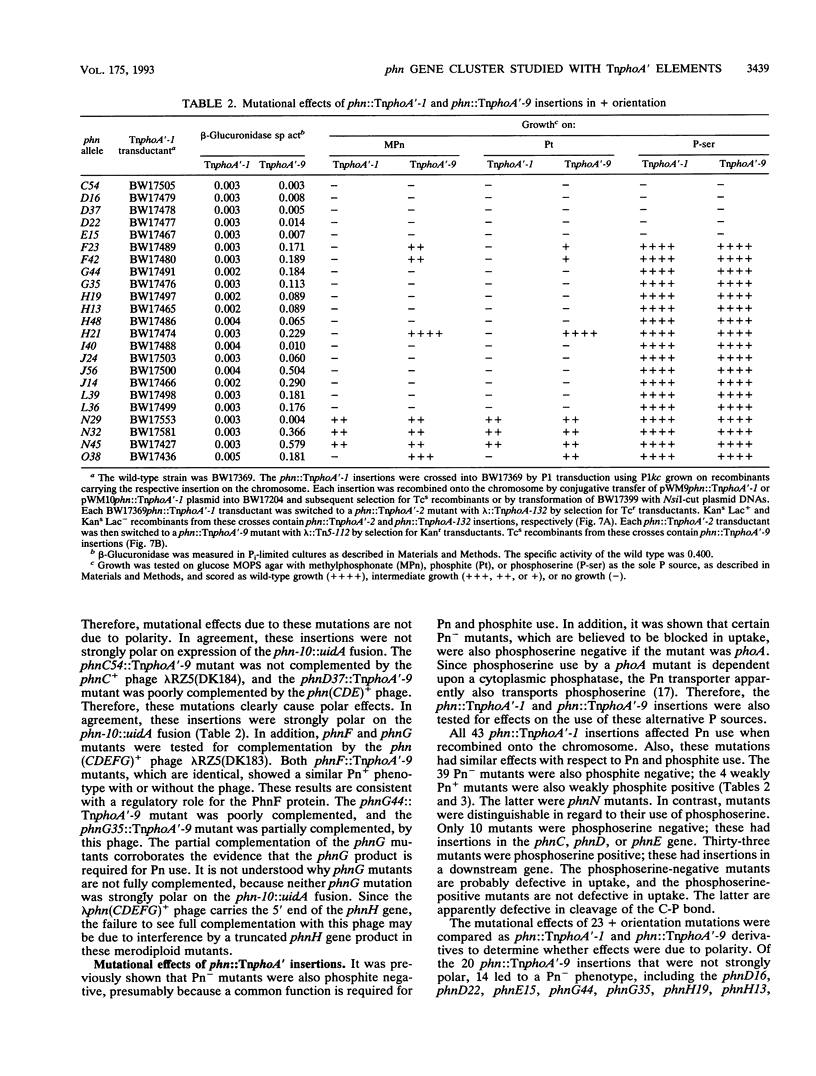
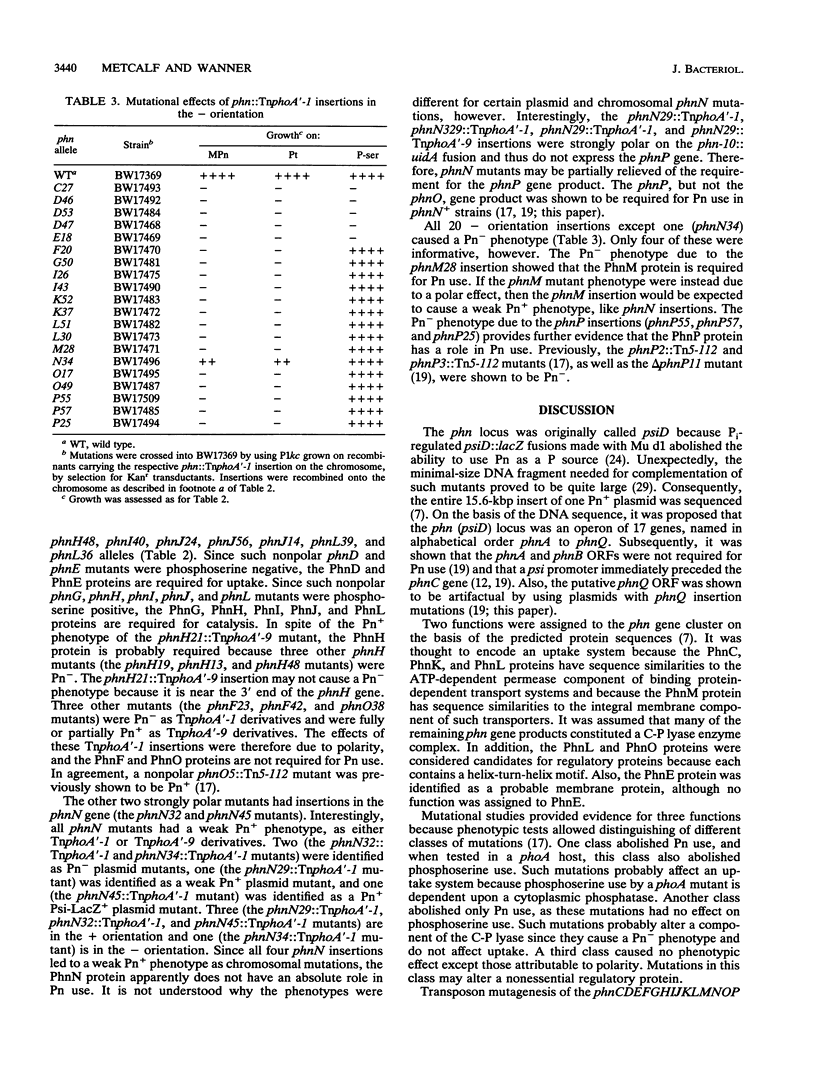
All genes for phosphonate (Pn) utilization in Escherichia coli are in a large cluster of 14 genes named, in alphabetical order, phnC to phnP. Plasmids carrying these genes were mutagenized by using TnphoA'-1, and 43 mutants containing simple insertions were studied in detail. Their insertion sites were defined by restriction mapping and by DNA sequencing. One or more mutations in each phn gene was identified. In 23 mutants, expression of the TnphoA'-1 lacZ gene was phosphate starvation inducible. These mutants had TnphoA'-1 oriented in line behind the phnC promoter, i.e., in the + orientation. In 20 mutants, the TnphoA'-1 lacZ gene was expressed at a low basal level. These mutants had insertions in the opposite orientation. All 43 phn::TnphoA'-1 insertions were recombined onto the chromosome to test for mutational effects, and their structures on the chromosome were verified by DNA hybridization. Those in the + orientation were switched to TnphoA'-9, which has an outward promoter for expression of downstream genes. These insertions were tested for polar effects by measuring beta-glucuronidase synthesis from a uidA gene transcriptionally fused to the 3' end of the phnP gene. The results indicate the following: (i) the phnC-to-phnP gene cluster is an operon of 14 genes, and the phnC promoter is the sole psi promoter; (ii) three gene products (PhnC, PhnD, and PhnE) probably constitute a binding protein-dependent Pn transporter; (iii) seven gene products (PhnG, PhnH, PhnI, PhnJ, PhnK, PhnL, and PhnM) are required for catalysis and are likely to constitute a membrane-associated carbon-phosphorus (C-P) lyase; (iv) two gene products (PhnN and PhnP) are not absolutely required and may therefore be accessory proteins for the C-P lyase; and (v) two gene products (PhnF and PhnO) are not required for Pn use and may have a regulatory role because they have sequence similarities to regulatory proteins. The mechanism for breaking the C-P bond by a lyase is discussed in light of these results.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal D. K., Wanner B. L. A phoA structural gene mutation that conditionally affects formation of the enzyme bacterial alkaline phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3180–3190. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3180-3190.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Huang H. C., Schieven G. L., Ames B. N. Positive selection for loss of tetracycline resistance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):926–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.926-933.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. M., Ye Q. Z., Zhu Z. M., Wanner B. L., Walsh C. T. Molecular biology of carbon-phosphorus bond cleavage. Cloning and sequencing of the phn (psiD) genes involved in alkylphosphonate uptake and C-P lyase activity in Escherichia coli B. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4461–4471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. J., Guest J. R. A new family of bacterial regulatory proteins. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Apr 15;63(2-3):291–295. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90101-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Metcalf W. W., Wanner B. L. Evidence for two phosphonate degradative pathways in Enterobacter aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2501–2510. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2501-2510.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Kim S. K., Shinagawa H., Amemura M., Nakata A. Molecular analysis of the cryptic and functional phn operons for phosphonate use in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2665–2672. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2665-2672.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullan G., Watkins R., Harper D. B., Quinn J. P. Carbon-phosphorus bond cleavage activity in cell-free extracts of Enterobacter aerogenes ATCC 15038 and Pseudomonas sp. 4ASW. Biochem Int. 1991 Sep;25(2):271–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf W. W., Steed P. M., Wanner B. L. Identification of phosphate starvation-inducible genes in Escherichia coli K-12 by DNA sequence analysis of psi::lacZ(Mu d1) transcriptional fusions. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3191–3200. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3191-3200.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf W. W., Wanner B. L. Involvement of the Escherichia coli phn (psiD) gene cluster in assimilation of phosphorus in the form of phosphonates, phosphite, Pi esters, and Pi. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):587–600. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.587-600.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata K., Higaki N., Kimura A. A microbial carbon-phosphorus bond cleavage enzyme requires two protein components for activity. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4504–4506. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4504-4506.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Shames S. L., Venditti C. P., Walsh C. T. Bacterial carbon-phosphorus lyase: products, rates, and regulation of phosphonic and phosphinic acid metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):710–717. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.710-717.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Wanner B. L., Venditti C. P., Walsh C. T. Involvement of the phosphate regulon and the psiD locus in carbon-phosphorus lyase activity of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1753–1756. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1753-1756.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Boline J. A. Mapping and molecular cloning of the phn (psiD) locus for phosphonate utilization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1186–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1186-1196.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L. Gene regulation by phosphate in enteric bacteria. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Jan;51(1):47–54. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240510110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Metcalf W. W. Molecular genetic studies of a 10.9-kb operon in Escherichia coli for phosphonate uptake and biodegradation. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 15;100(1-3):133–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb14031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L. Novel regulatory mutants of the phosphate regulon in Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):39–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90421-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmes-Riesenberg M. R., Wanner B. L. TnphoA and TnphoA' elements for making and switching fusions for study of transcription, translation, and cell surface localization. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4558–4575. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4558-4575.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]