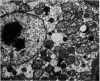
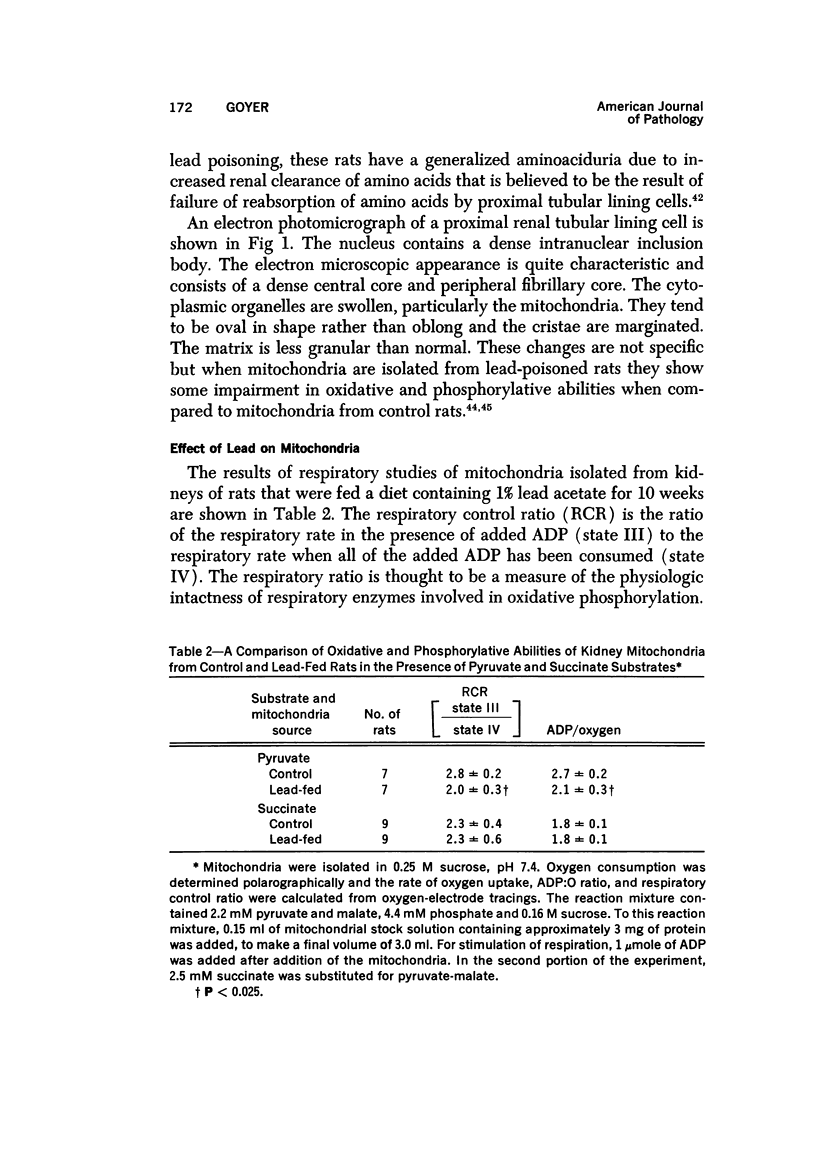
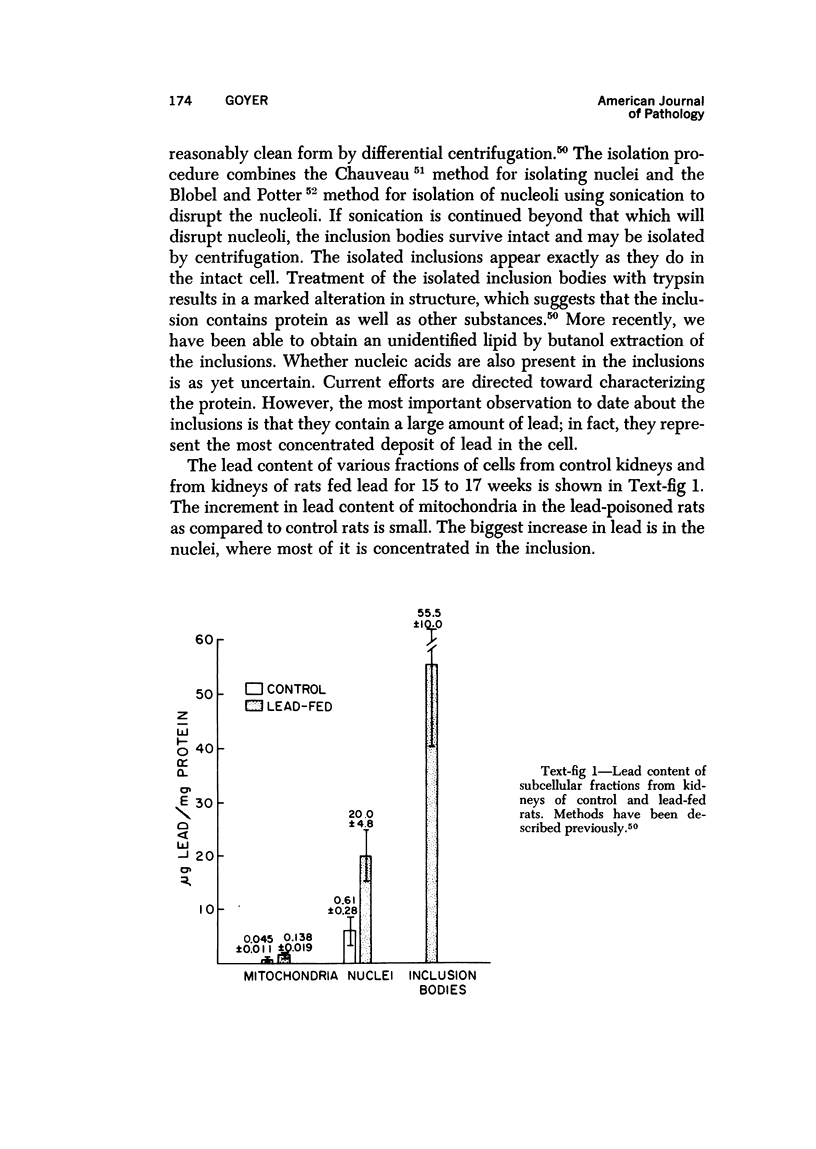
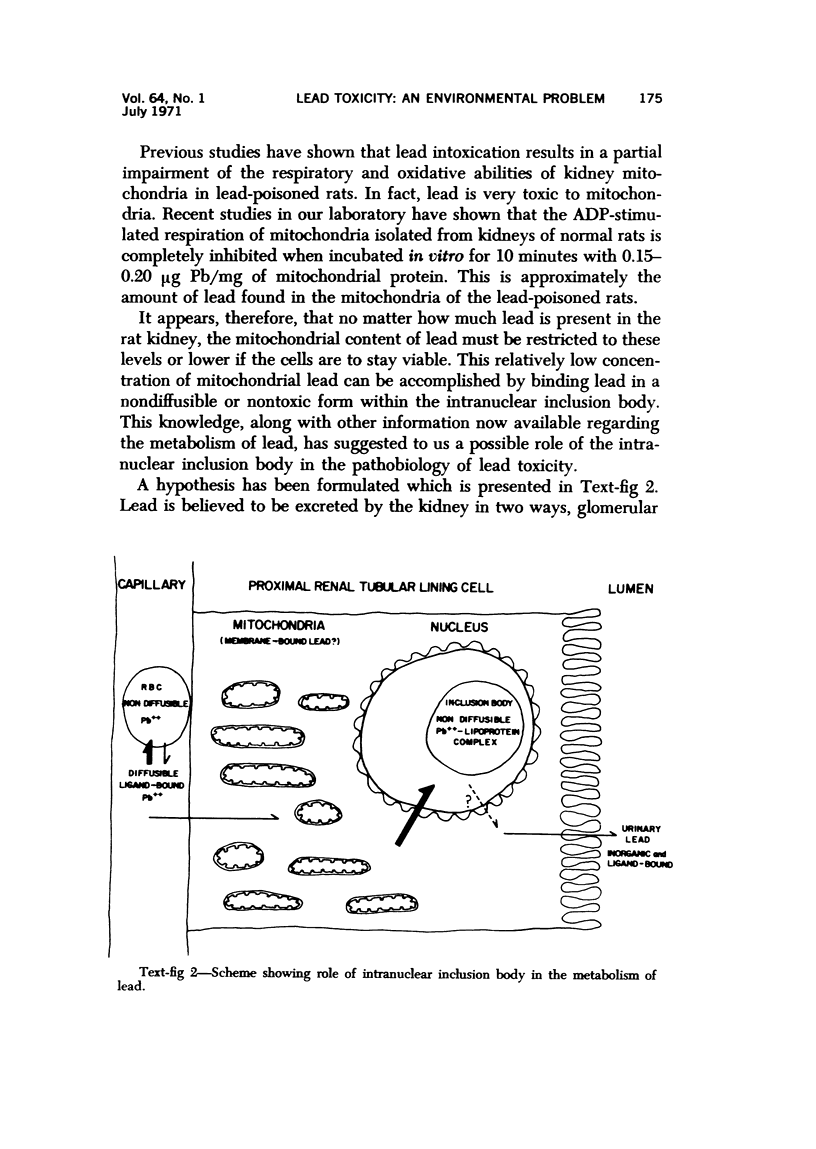
Full text
PDF










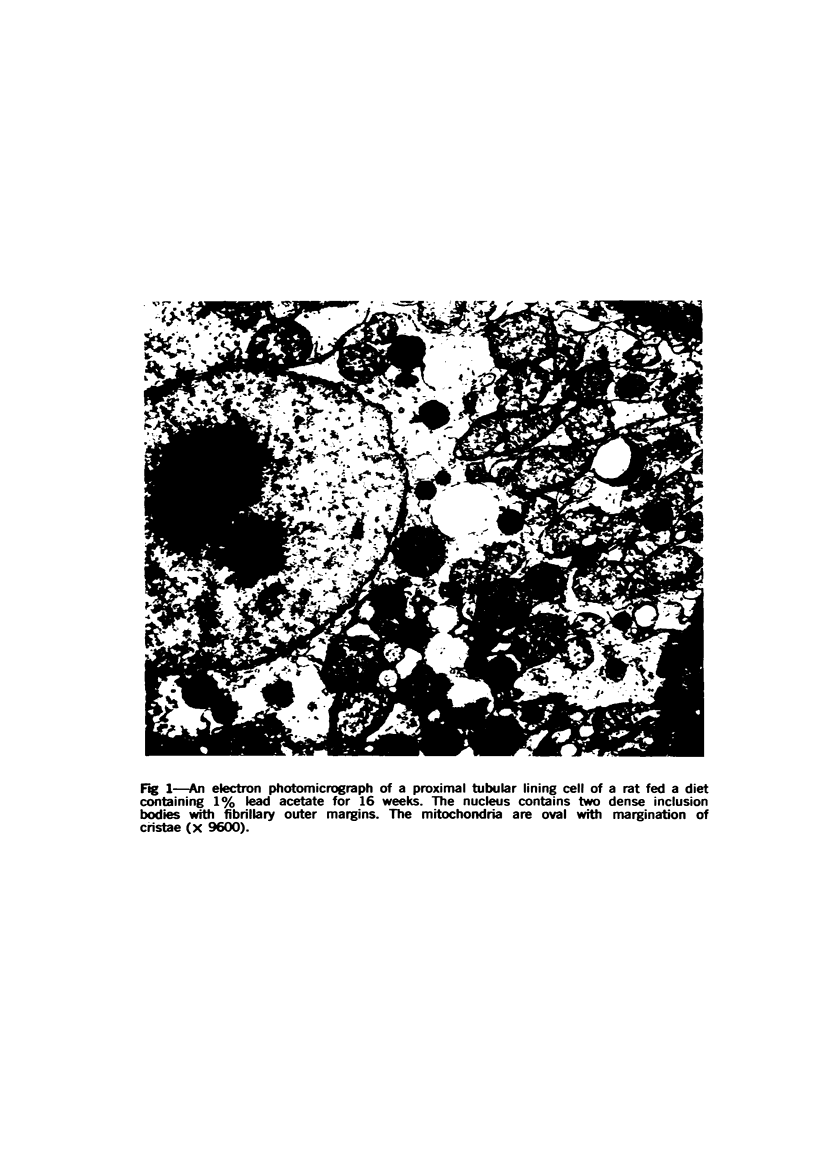

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BESSIS M. C., JENSEN W. N. SIDEROBLASTIC ANAEMIA, MITOCHONDRIA AND ERYTHROBLASTIC IRON. Br J Haematol. 1965 Jan;11:49–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb00083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball G. V., Sorensen L. B. Pathogenesis of hyperuricemia in saturinine gout. N Engl J Med. 1969 May 29;280(22):1199–1202. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196905292802203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barltrop D. Environmental lead and its paediatric significance. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Feb;45(520):129–134. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.45.520.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barltrop D., Killala N. J. Factors influencing exposure of children to lead. Arch Dis Child. 1969 Aug;44(236):476–479. doi: 10.1136/adc.44.236.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson P. Lead poisoning in children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1965 Oct;7(5):569–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1965.tb10970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk P. D., Tschudy D. P., Shepley L. A., Waggoner J. G., Berlin N. I. Hematologic and biochemical studies in a case of lead poisoning. Am J Med. 1970 Jan;48(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(70)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAUVEAU J., MOULE Y., ROUILLER C. Isolation of pure and unaltered liver nuclei morphology and biochemical composition. Exp Cell Res. 1956 Aug;11(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(56)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHISOLM J. J., Jr Aminoaciduria as a manifestation of renal tubular injury in lead intoxication and a comparison with patterns of aminoaciduria seen in other diseases. J Pediatr. 1962 Jan;60:1–17. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(62)80002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. R., CELEWYCZ B. S., ANDELMAN S. L. A THREE-YEAR STUDY OF LEAD POISONING IN CHICAGO. II. CASE FINDING IN ASYMPTOMATIC CHILDREN USING URINARY COPROPORPHYRIN AS A SCREENING TEST. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1964 Aug;54:1245–1251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKSON T. W., KENCH J. E. Urinary excretion of amino acids by men absorbing heavy metals. Biochem J. 1956 Mar;62(3):361–372. doi: 10.1042/bj0620361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. M., Williams E. R. Chronic lead intoxication mimicking motor neurone disease. Br Med J. 1968 Nov 30;4(5630):582–582. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5630.582-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramér K., Selander S. Studies in lead poisoning. Comparison between different laboratory tests. Br J Ind Med. 1965 Oct;22(4):311–314. doi: 10.1136/oem.22.4.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGG J. H., GOLDBERG A., LOCHHEAD A., SMITH J. A. THE RELATIONSHIP OF LEAD POISONING TO ACUTE INTERMITTENT PORPHYRIA. Q J Med. 1965 Apr;34:163–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINISCHIOTU G. T., NESTORESCU B., RADULESCU I. C., IONESCU C., PREDA N., ILUTZA G. Studies on the chemical forms of urinary lead. Br J Ind Med. 1960 Apr;17:141–145. doi: 10.1136/oem.17.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMMERSON B. T. CHRONIC LEAD NEPHROPATHY: THE DIAGNOSTIC USE OF CALCIUM EDTA AND THE ASSOCIATION WITH GOUT. Australas Ann Med. 1963 Nov;12:310–324. doi: 10.1111/imj.1963.12.4.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerson B. T. The clinical differentiation of lead gout from primary gout. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Oct;11(5):623–634. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIGGS R. C. LEAD POISONING: HEMATOLOGIC ASPECTS. Prog Hematol. 1964;4:117–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIGGS R. C., SUNSHINE I., NEWILL V. A., NEWTON B. W., BUCHANAN S., RASCH C. A. ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS IN CHILDHOOD LEAD POISONING. JAMA. 1964 Mar 7;187:703–707. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03060230031008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyer R. A., Krall A., Kimball J. P. The renal tubule in lead poisoning. II. In vitro studies of mitochondrial structure and function. Lab Invest. 1968 Jul;19(1):78–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyer R. A., Krall R. Ultrastructural transformation in mitochondria isolated from kidneys of normal and lead-intoxicated rats. J Cell Biol. 1969 May;41(2):393–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyer R. A., May P., Cates M. M., Krigman M. R. Lead and protein content of isolated intranuclear inclusion bodies from kidneys of lead-poisoned rats. Lab Invest. 1970 Mar;22(3):245–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyer R. A. The renal tubule in lead poisoning. I. mMitochondrial swelling and aminoacidura. Lab Invest. 1968 Jul;19(1):71–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDERSON D. A. Chronic nephritis in Queensland. Australas Ann Med. 1955 Aug;4(3):163–177. doi: 10.1111/imj.1955.4.3.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. W., Elsea W. R. Ceramic glaze as a source of lead poisoning. JAMA. 1967 Nov 6;202(6):544–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEHOE R. A. The Harben Lectures, 1960: The metabolism of lead in man in health and disease. 3. Present hygienic problems relating to the absorption of lead. J R Inst Public Health. 1961 Aug;24:177–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinenberg J. R. Saturnine gout--a moonshine malady. N Engl J Med. 1969 May 29;280(22):1238–1239. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196905292802213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambie J. A. Lead poisoning in missile-silo workers. JAMA. 1967 May 29;200(9):797–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Schochet S. S., Jr Demyelination and remyelination in lead neuropathy. Electron microscopic studies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1968 Oct;27(4):527–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livesley B., Sissons C. E. Chronic lead intoxication mimicking motor neurone disease. Br Med J. 1968 Nov 9;4(5627):387–388. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5627.387-d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONCRIEFF A. A., KOUMIDES O. P., CLAYTON B. E., PATRICK A. D., RENWICK A. G., ROBERTS G. E. LEAD POISONING IN CHILDREN. Arch Dis Child. 1964 Feb;39:1–13. doi: 10.1136/adc.39.203.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRIS C. E., HEYMAN A., POZEFSKY T. LEAD ENCEPHALOPATHY CAUSED BY INGESTION OF ILLICITLY DISTILLED WHISKEY. Neurology. 1964 Jun;14:493–499. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.6.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. M., Hartley M. W., Miller R. E. Nephropathy in chronic lead poisoning. Arch Intern Med. 1966 Jul;118(1):17–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON C. C. CONTAMINATED AND NATURAL LEAD ENVIRONMENTS OF MAN. Arch Environ Health. 1965 Sep;11:344–360. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1965.10664229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHET G., MIGNON F., ARDAILLOU R. GOUTTE SECONDAIRE DES N'EPHROPATHIES CHRONIQUES. Presse Med. 1965 Mar 6;73:633–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennert O. M., Weiner P., Madden J. Asymptomatic lead poisoning in 85 chicago children. Some diagnostic, therapeutic, prognostic and sociologic considerations. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1970 Jan;9(1):9–13. doi: 10.1177/000992287000900104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter G. W., Kress Y., Cornwall C. C. Another look at lead inclusion bodies. Am J Pathol. 1968 Aug;53(2):189–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimington C. Porphyrin and haem biosynthesis and its control. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1966;445:11–24. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb02334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLANG H. A. Poisoning caused by tetraethyl lead. Aerosp Med. 1961 Apr;32:333–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandstead H. H., Michelakis A. M., Temple T. E. Lead intoxication: its effect on the renin-aldosterone response to sodium deprivation. Arch Environ Health. 1970 Mar;20(3):356–363. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1970.10665604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandstead H. H., Stant E. G., Brill A. B., Arias L. I., Terry R. T. Lead intoxication and the thyroid. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Jun;123(6):632–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. A., Tipton I. H. The human body burden of lead. Arch Environ Health. 1968 Dec;17(6):965–978. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1968.10665354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPER L. B. RENAL FUNCTION SUBSEQUENT TO CHILDHOOD PLUMBISM. Arch Environ Health. 1963 Jul;7:76–85. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1963.10663496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vostál J., Heller J. Renal excretory mechanisms of heavy metals. I. Transtubular transport of heavy metal ions in the avian kidney. Environ Res. 1968 Sep;2(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(68)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON V. K., THOMSON M. L., DENT C. E. Amino-aciduria in lead poisoning; a case in childhood. Lancet. 1953 Jul 11;265(6776):66–68. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)91087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron H. A. The anaemia of lead poisoning: a review. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Apr;23(2):83–100. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.2.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]