Abstract
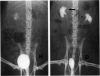
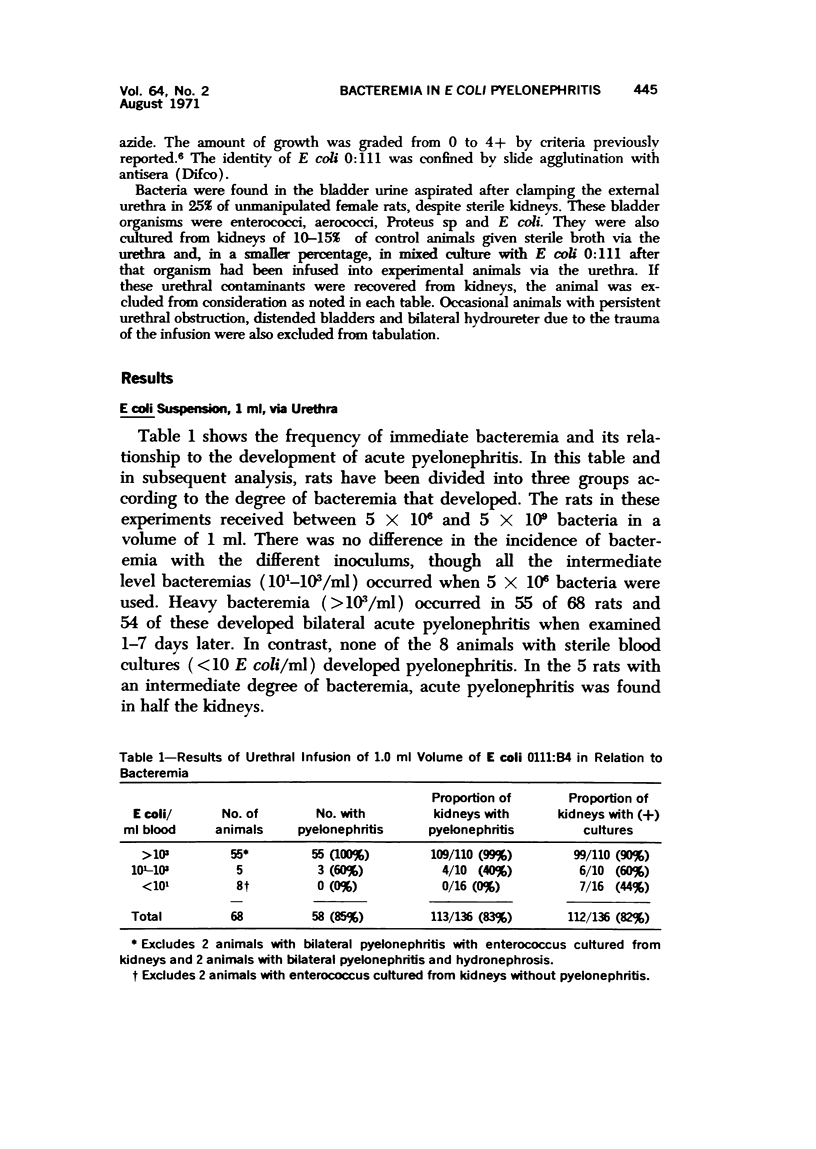
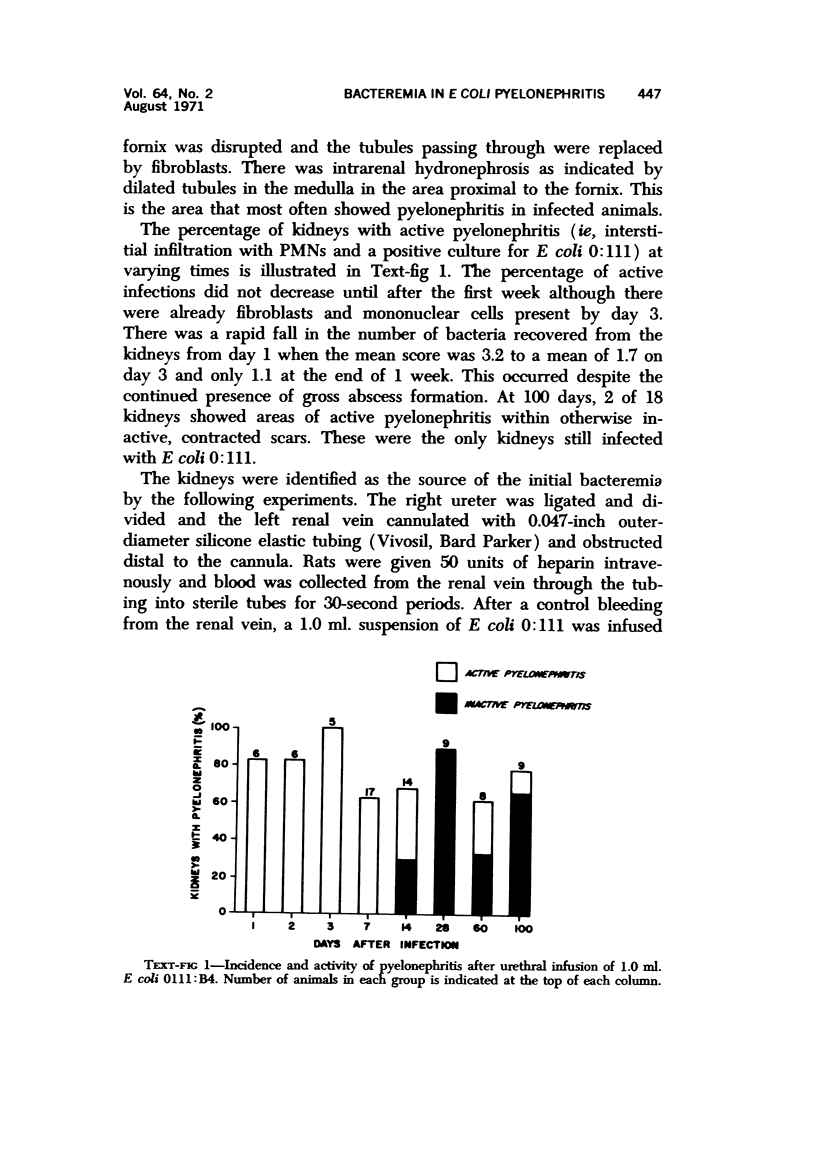
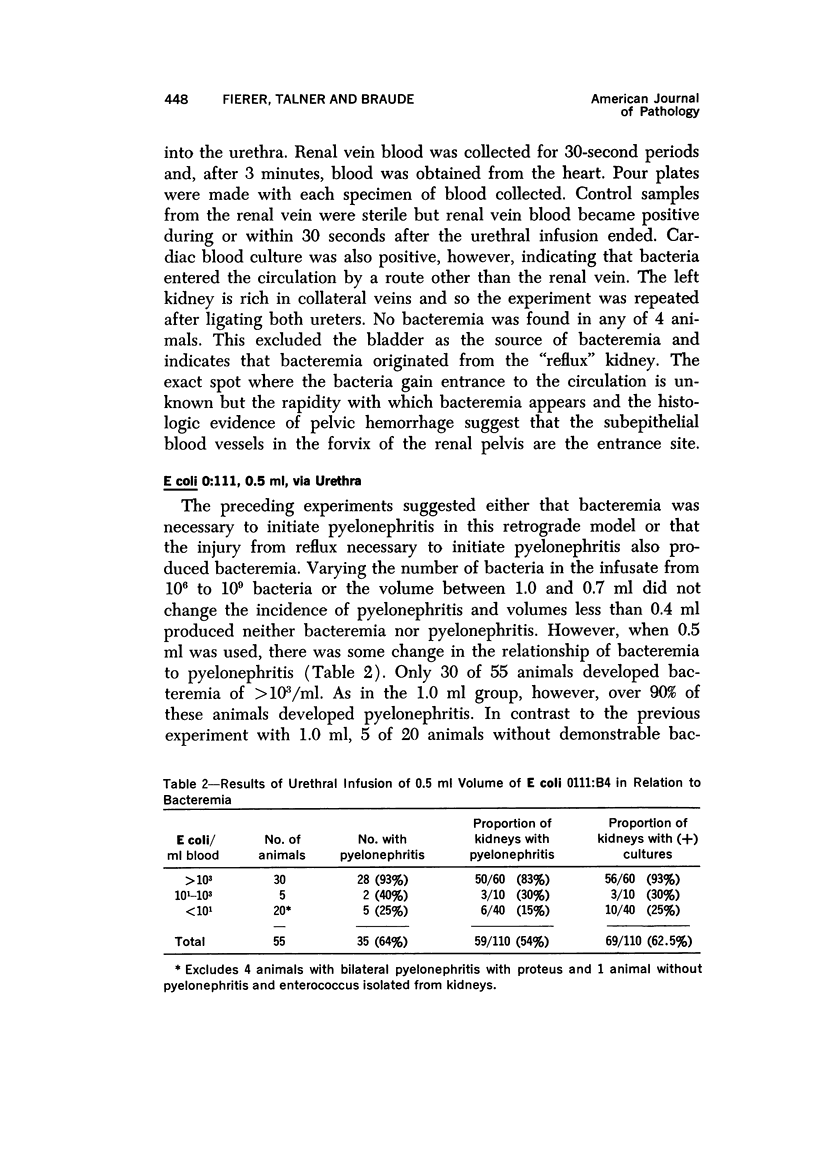
Female rats deprived of water overnight, and then given 1.0 ml of E coli 0111:B4 via the urethra, developed pyelonephritis. A nearly absolute association was found between the occurrence of bacteremia after the transurethral infusion and the development of pyelonephritis. An identical lesion was produced by a combination of forniceal damage and intravenous injection of E coli. The kidney damaged by reflux was shown to be more susceptible to hematogenous pyelonephritis than the obstructed kidney and the distribution of the infection was due to localization of bacteria in the damaged fornix but not to the route of infection. The induction of retrograde E coli pyelonephritis in the rat required a tear in the pelvic epithelium creating pyelovenous communications, and the resultant bacteremia produced pyelonephritis. The incidence of ureteral reflux and the volume of inoculum that refluxed to the renal pelvis was shown radiologically to be a function of bladder distensibility, which is reduced by withholding water for a few hours. In this system, retrograde E coli pyelonephritis developed from a combination of two factors: (1) reflux-induced damage to the renal pelvis so that E coli are introduced into the kidney and (2) hematogenous infection of the damaged kidney.
Full text
PDF








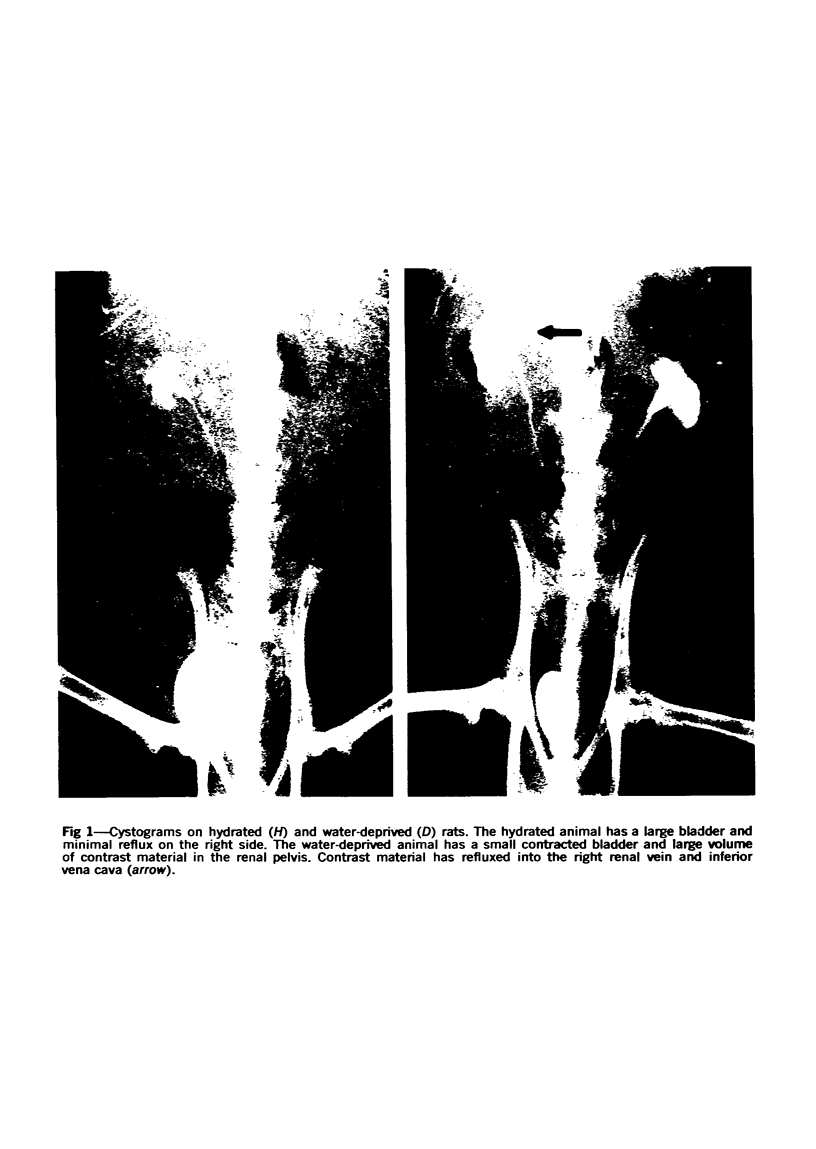
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN B. R., JACKSON G. G. Pyelitis, an important factor in the pathogenesis of retrograde pyelonephritis. J Exp Med. 1961 Sep 1;114:375–384. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.3.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARANA J. A., KOZIJ V. M., JACKSON G. G. RETROGRADE E COLI URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN RATS. PATHOLOGIC AND BACTERIOLOGIC CHARACTERISTICS OF ASCENDING PYELONEPHRITIS. Arch Pathol. 1964 Nov;78:558–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEESON P. B. Factors in the pathogenesis of pyelonephritis. Yale J Biol Med. 1955 Nov;28(2):81–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I., SHAPIRO A. P., SIEMIENSKI J. Hematogenous pyelonephritis in rats. I. Its pathogenesis when produced by a simple new method. J Clin Invest. 1955 Oct;34(10):1489–1497. doi: 10.1172/JCI103200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTRAN R. S. Retrograde Proteus pyelonephritis in rats. Localization of antigen and antibody in treated sterile pyelonephritic kidneys. J Exp Med. 1963 May 1;117:813–822. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.5.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTRAN R. S., THRUPP L. D., HAJJ S. N., ZANGWILL D. P., VIVALDI E., KASS E. H. Retrograde E. coli pyelonephritis in the rat: a bacteriologic, pathologic, and fluorescent antibody study. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Jun;61:987–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPTINSTALL R. H. EXPERIMENTAL PYELONEPHRITIS. BACTERIOLOGICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE ASCENDING ROUTE OF INFECTION IN THE RAT. Nephron. 1964;1:73–92. doi: 10.1159/000179321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAPIRO A. P., BRAUDE A. I., SIEMIENSKI J. Hematogenous pyelonephritis in rats. IV. Relationship of bacterial species to the pathogenesis and sequelae of chronic pyelonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jul;38(7):1228–1240. doi: 10.1172/JCI103898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]