Abstract
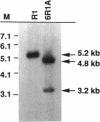
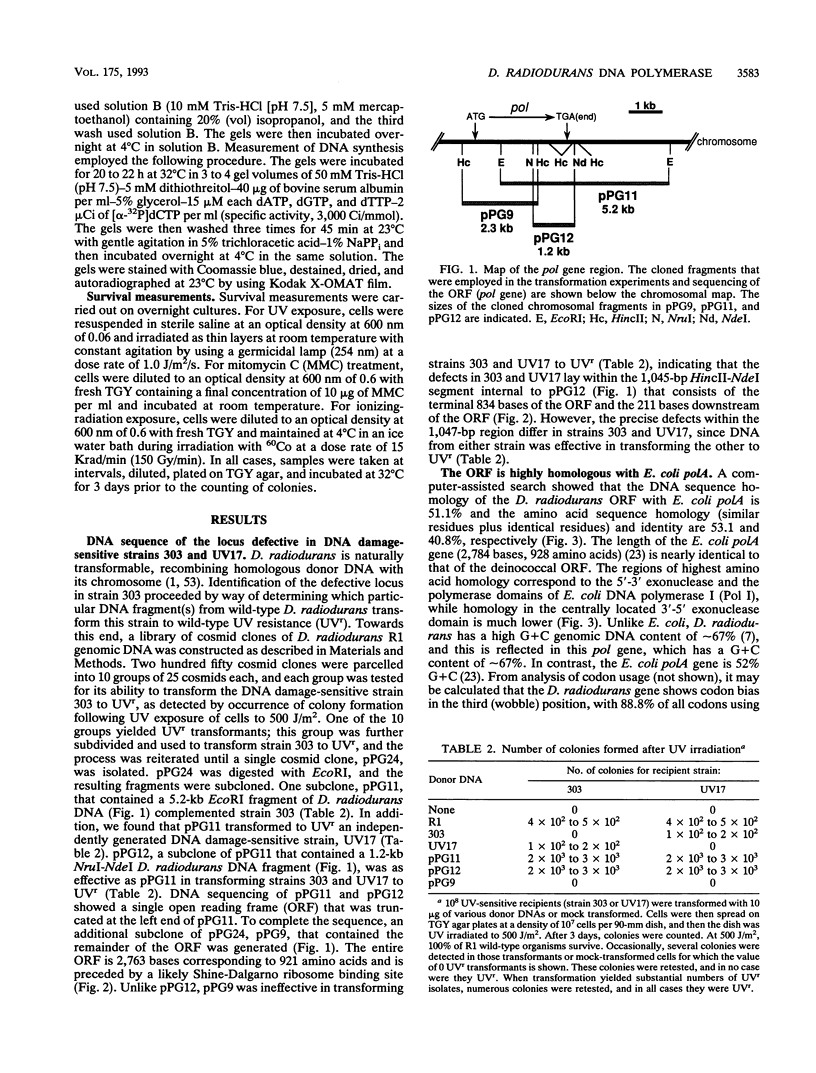
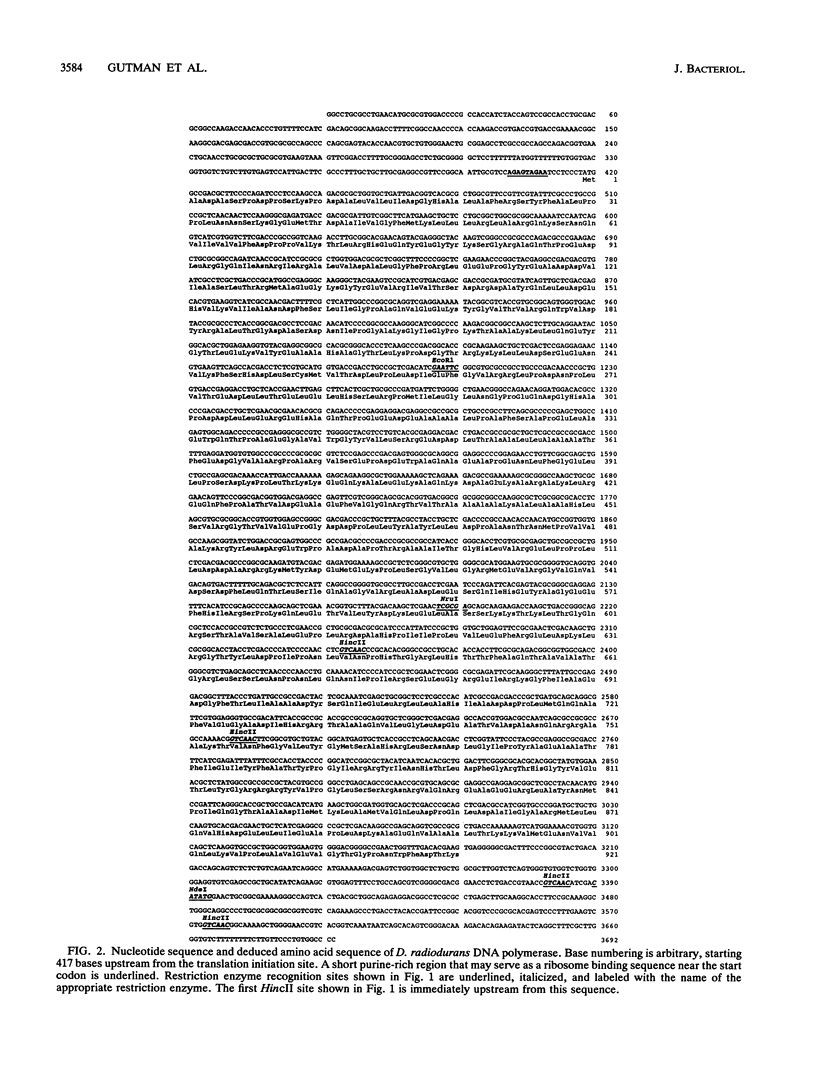
Deinococcus radiodurans and other species of the same genus share extreme resistance to ionizing radiation and many other agents that damage DNA. Two different DNA damage-sensitive strains generated by chemical mutagenesis were found to be defective in a gene that has extended DNA and protein sequence homology with polA of Escherichia coli. Both mutant strains lacked DNA polymerase, as measured in activity gels. Transformation of this gene from wild-type D. radiodurans restored to the mutants both polymerase activity and DNA damage resistance. A technique for targeted insertional mutagenesis in D. radiodurans is presented. This technique was employed to construct a pol mutant isogenic with the wild type (the first example of targeted mutagenesis in this eubacterial family). This insertional mutant lacked DNA polymerase activity and was even more sensitive to DNA damage than the mutants derived by chemical mutagenesis. In the case of ionizing radiation, the survival of the wild type after receiving 1 Mrad was 100% while survival of the insertional mutant extrapolated to 10(-24). These results demonstrate that the gene described here encodes a DNA polymerase and that defects in this pol gene cause a dramatic loss of resistance of D. radiodurans to DNA damage.
Full text
PDF


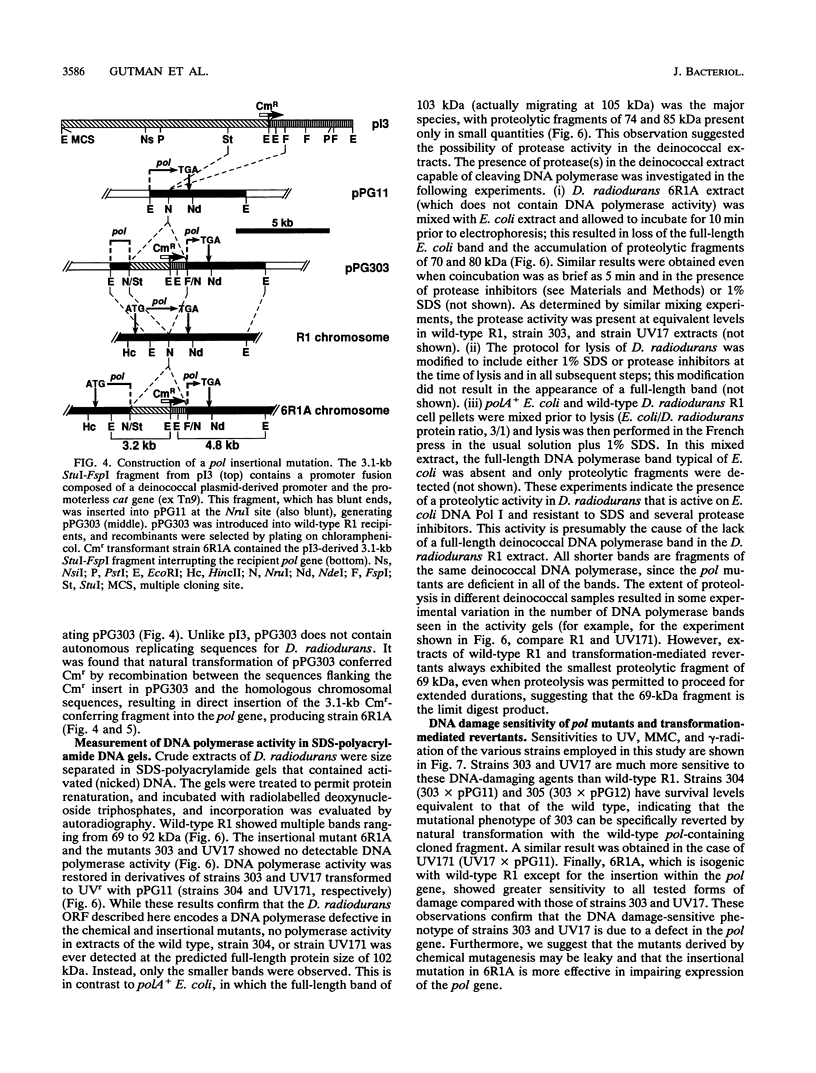

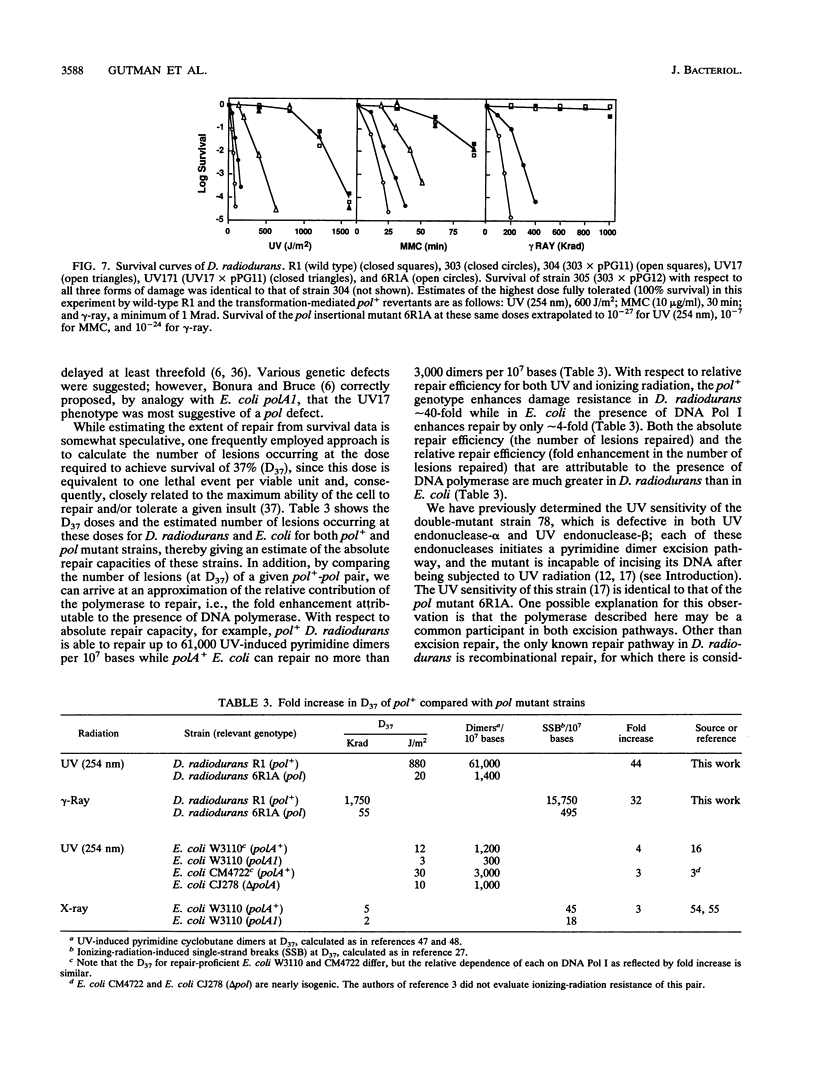


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Bakri G. H., Mackay M. W., Whittaker P. A., Moseley B. E. Cloning of the DNA repair genes mtcA, mtcB, uvsC, uvsD, uvsE and the leuB gene from Deinococcus radiodurans. Gene. 1985;33(3):305–311. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates H., Randall S. K., Rayssiguier C., Bridges B. A., Goodman M. F., Radman M. Spontaneous and UV-induced mutations in Escherichia coli K-12 strains with altered or absent DNA polymerase I. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2480–2484. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2480-2484.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beese L. S., Steitz T. A. Structural basis for the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I: a two metal ion mechanism. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):25–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank A., Silber J. R., Thelen M. P., Dekker C. A. Detection of enzymatic activities in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels: DNA polymerases as model enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1983 Dec;135(2):423–430. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90705-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonura T., Bruce A. K. The repair of single-strand breaks in a radiosensitive mutant of Micrococcus radiodurans. Radiat Res. 1974 Feb;57(2):260–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N., Clark A. J. Deletions generated by the transposon Tn10 in the srl recA region of the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. Genetics. 1979 Oct;93(2):321–343. doi: 10.1093/genetics/93.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delarue M., Poch O., Tordo N., Moras D., Argos P. An attempt to unify the structure of polymerases. Protein Eng. 1990 May;3(6):461–467. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.6.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire V., Freemont P. S., Sanderson M. R., Beese L., Friedman J. M., Joyce C. M., Steitz T. A. Genetic and crystallographic studies of the 3',5'-exonucleolytic site of DNA polymerase I. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):199–201. doi: 10.1126/science.2832946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire V., Grindley N. D., Joyce C. M. The 3'-5' exonuclease of DNA polymerase I of Escherichia coli: contribution of each amino acid at the active site to the reaction. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):17–24. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07916.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Moseley B. E. Deinococcus radiodurans UV endonuclease beta DNA incisions do not generate photoreversible thymine residues. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar-Apr;207(3-4):117–119. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(88)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Moseley B. E. Identification and initial characterisation of a pyrimidine dimer UV endonuclease (UV endonuclease beta) from Deinococcus radiodurans; a DNA-repair enzyme that requires manganese ions. Mutat Res. 1985 May;145(3):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(85)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Moseley B. E. Roles of the uvsC, uvsD, uvsE, and mtcA genes in the two pyrimidine dimer excision repair pathways of Deinococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):576–583. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.576-583.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimsley J. K., Masters C. I., Clark E. P., Minton K. W. Analysis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of DNA double-strand breakage and repair in Deinococcus radiodurans and a radiosensitive mutant. Int J Radiat Biol. 1991 Oct;60(4):613–626. doi: 10.1080/09553009114552441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J., Gross M. Genetic analysis of an E. coli strain with a mutation affecting DNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1166–1168. doi: 10.1038/2241166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman P. D., Yao H. L., Minton K. W. Partial complementation of the UV sensitivity of Deinococcus radiodurans excision repair mutants by the cloned denV gene of bacteriophage T4. Mutat Res. 1991 May;254(3):207–215. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(91)90058-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. T. Multiplicity of genome equivalents in the radiation-resistant bacterium Micrococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):71–75. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.71-75.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce C. M., Fujii D. M., Laks H. S., Hughes C. M., Grindley N. D. Genetic mapping and DNA sequence analysis of mutations in the polA gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):283–293. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce C. M., Kelley W. S., Grindley N. D. Nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli polA gene and primary structure of DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1958–1964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitayama S., Ishizaka Y., Miyai S., Matsuyama A. An exonuclease activity associated with DNA polymerase I of Micrococcus radiodurans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 23;520(1):122–130. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitayama S., Matsuyama A. Separation of DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activities in Micrococcus radiodurans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 2;475(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasin F., Hutchinson F. Repair of DNA double-strand breaks in Escherichia coli, which requires recA function and the presence of a duplicate genome. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 15;116(1):81–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawyer F. C., Stoffel S., Saiki R. K., Myambo K., Drummond R., Gelfand D. H. Isolation, characterization, and expression in Escherichia coli of the DNA polymerase gene from Thermus aquaticus. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6427–6437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon E., Minton K. W. Gene fusions with lacZ by duplication insertion in the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2955–2961. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2955-2961.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay M. W., al-Bakri G. H., Moseley B. E. The plasmids of Deinococcus spp. and the cloning and restriction mapping of the D. radiophilus plasmid pUE1. Arch Microbiol. 1985 Feb;141(1):91–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00446746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. I., Minton K. W. Promoter probe and shuttle plasmids for Deinococcus radiodurans. Plasmid. 1992 Nov;28(3):258–261. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(92)90057-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. I., Smith M. D., Gutman P. D., Minton K. W. Heterozygosity and instability of amplified chromosomal insertions in the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6110–6117. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6110-6117.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley B. E., Copland H. F. Four mutants of Micrococcus radiodurans defective in the ability to repair DNA damaged by mitomycin-C, two of which have wild-type resistance to ultraviolet radiation. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Apr 17;160(3):331–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00332977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley B. E., Copland H. J. Isolation and properties of a recombination-deficient mutant of Micrococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):422–428. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.422-428.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley B. E., Evans D. M. Isolation and properties of strains of Micrococcus (Deinococcus) radiodurans unable to excise ultraviolet light-induced pyrimidine dimers from DNA: evidence for two excision pathways. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Aug;129(8):2437–2445. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-8-2437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley B. E., Mattingly A. Repair of irradiation transforming deoxyribonucleic acid in wild type and a radiation-sensitive mutant of Micrococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):976–983. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.976-983.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley B. E. Repair of ultraviolet radiation damage in sensitive mutants of Micrococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):647–652. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.647-652.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley B. E. The isolation and some properties of radiation-sensitive mutants of Micrococcus radiodurans. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Nov;49(2):293–300. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Clowes R. C., Cohen S. N., Curtiss R., 3rd, Datta N., Falkow S. Uniform nomenclature for bacterial plasmids: a proposal. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):168–189. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.168-189.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SETLOW J. K., DUGGAN D. E. THE RESISTANCE OF MICROCOCCUS RADIODURANS TO ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION. I. ULTRAVIOLET-INDUCED LESIONS IN THE CELL'S DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 12;87:664–668. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90284-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers J. R., Eckstein F. A single-strand specific endonuclease activity copurifies with overexpressed T5 D15 exonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4127–4132. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B., Carrier W. L. Pyrimidine dimers in ultraviolet-irradiated DNA's. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):237–254. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., Abrahamson R., Minton K. W. Shuttle plasmids constructed by the transformation of an Escherichia coli cloning vector into two Deinococcus radiodurans plasmids. Plasmid. 1989 Sep;22(2):132–142. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., Masters C. I., Lennon E., McNeil L. B., Minton K. W. Gene expression in Deinococcus radiodurans. Gene. 1991 Feb 1;98(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90102-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest P. R., Moseley B. E. Defective excision repair in a mutant of Micrococcus radiodurans hypermutable by some monofunctional alkylating agents. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(1):191–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00268463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Town C. D., Smith K. C., Kaplan H. S. DNA polymerase required for rapid repair of x-ray--induced DNA strand breaks in vivo. Science. 1971 May 21;172(3985):851–854. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3985.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngs D. A., Smith K. C. X-ray sensitivity and repair capacity of a polA1 exrA strain of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):121–127. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.121-127.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]