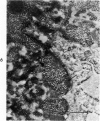
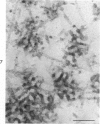
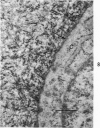
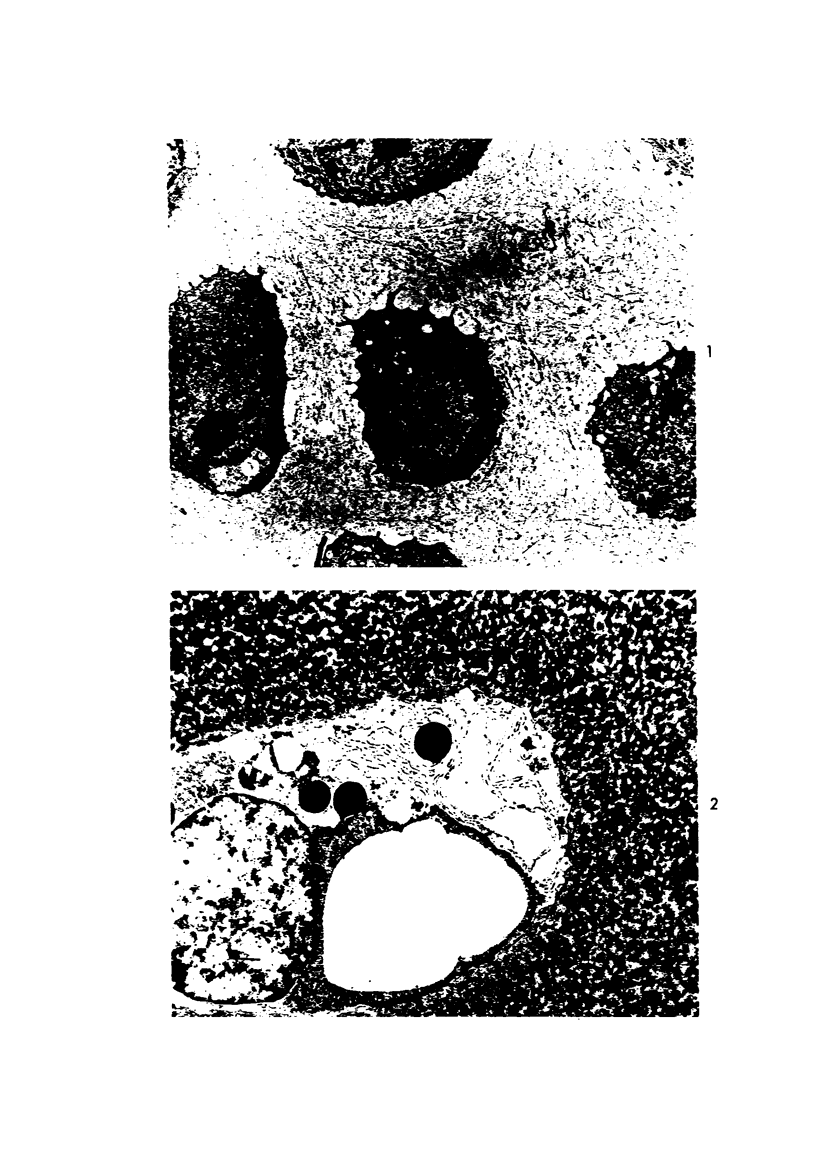
Abstract
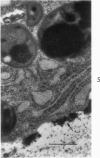
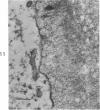
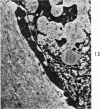
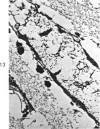
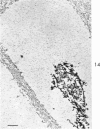
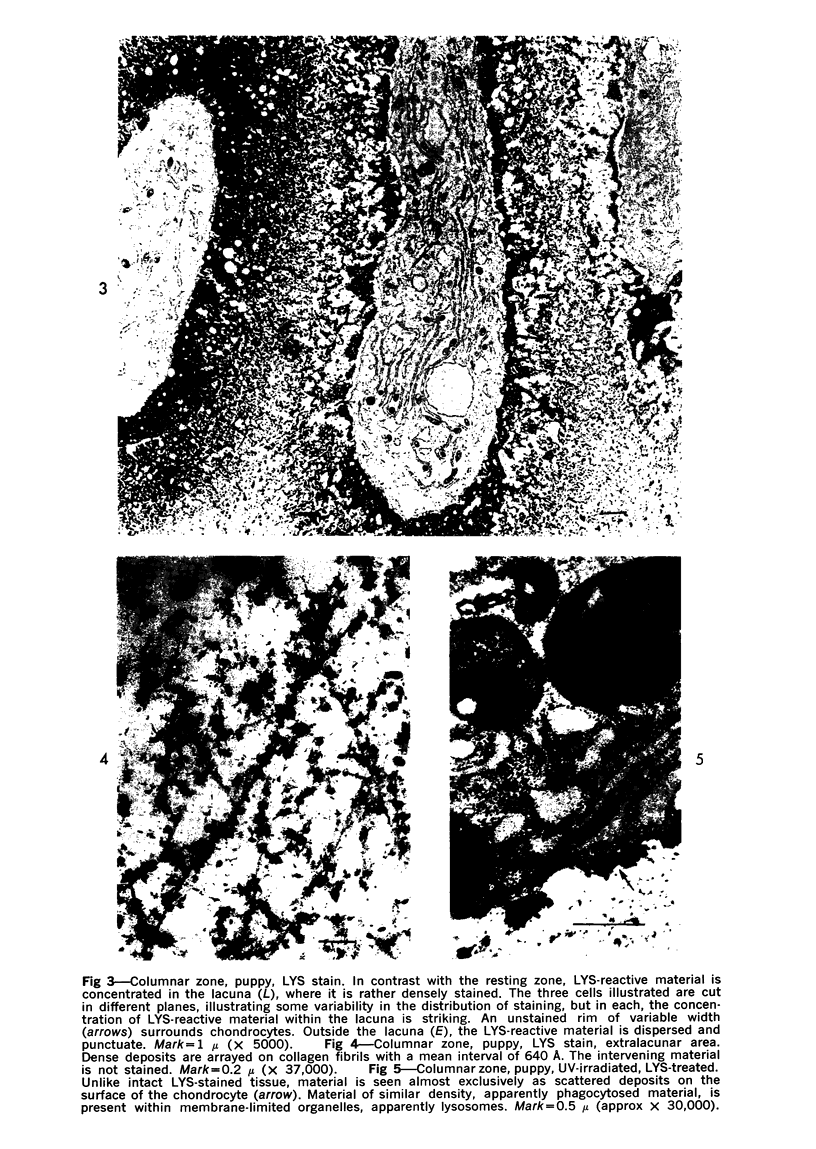
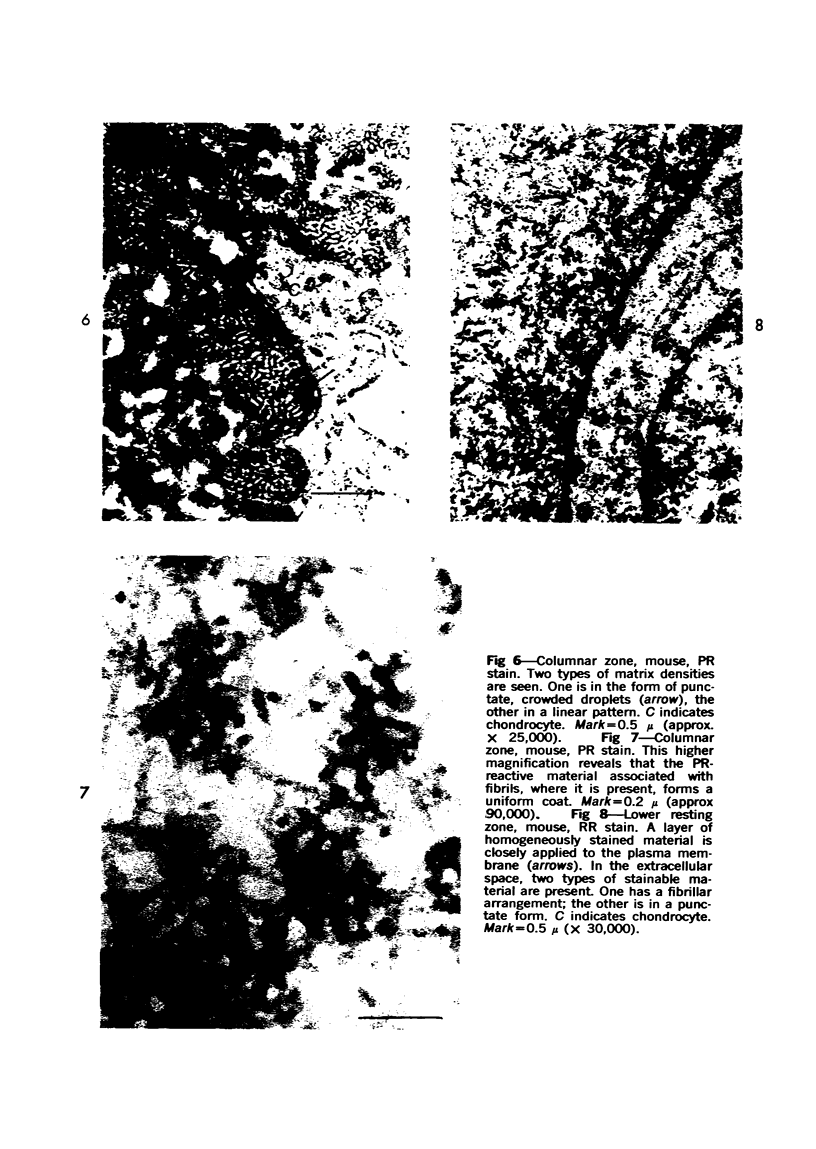
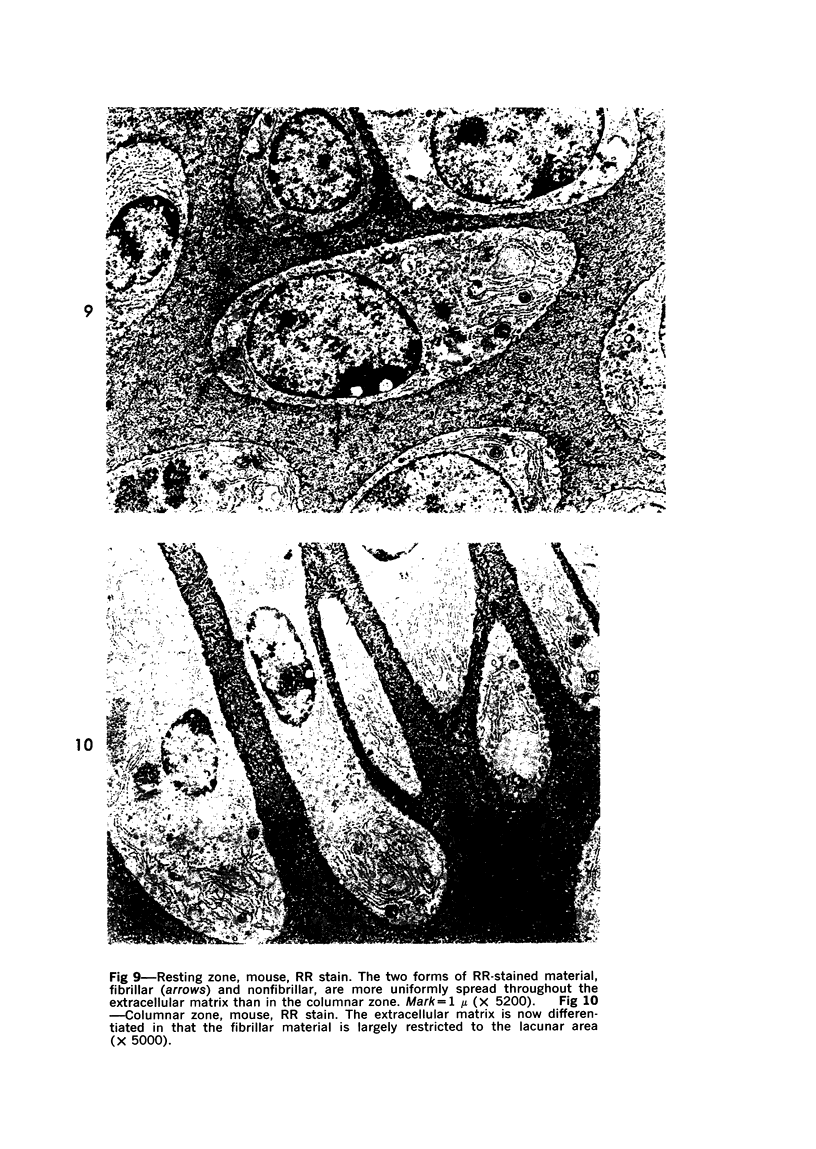
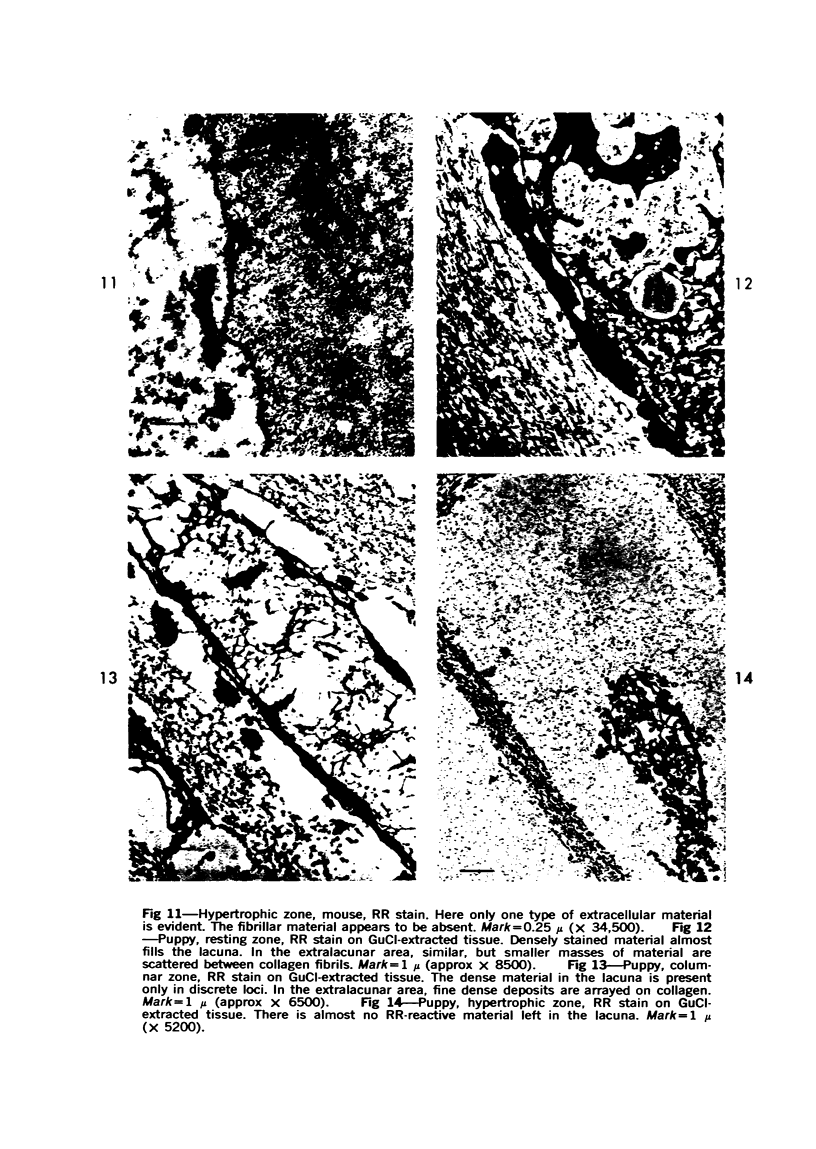
Three cations of varying size and charge density, egg-white lysozyme, protamine and ruthenium red, were used to stain the extracellular matrix of epiphyseal cartilage growth plate. With these stains, it was possible to distinguish three types of proteoglycans or materials associated with them, which may well have as their major differences the type of cross linking to the tissue. One type was stained by ruthenium red and protamine but not by lysozyme, was extractable with 3 M guanidinium chloride and was relatively uniformly dispersed throughout the matrix of the growth plate. The other two types were stained by all three cations, were not extractable with 3 M guanidinium chloride and were intimately associated with fibrils. One of these was found on the collagen fibrils, was relatively scanty in the resting zone near the articular surface, relatively restricted to the extralacunar area in the columnar zones and appeared to diminish in amount in the hypertrophic zone. This material often had a 640-Å periodic array on the surface of collagen fibrils. The third type also was stained by all three cations and was not extractable with 3 M guanidinium chloride. It was distinguished from the other class of lysozyme-reactive matrix components by the larger volume of distribution occupied by the stained material. It also had a different distribution in that it was widely dispersed in the resting zone, was restricted to the lacuna in the columnar zone and was absent in the hypertrophic zone. Thus, cartilage matrix as well as the chondrocytes undergo differentiation in the epiphyseal growth plate.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTONOPOULOS C. A., GARDELL S., SZIRMAI J. A., DETYSSONSK E. R. DETERMINATION OF GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS (MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES) FROM TISSUE ON THE MICROGRAM SCALE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 2;83:1–19. doi: 10.1016/0926-6526(64)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. Y., Sajdera S. W., Anderson H. C. Isolation and characterization of calcifying matrix vesicles from epiphyseal cartilage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1513–1520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar R. S., Prockop D. J. Dissociation of the synthesis of sulphated mucopolysaccharides and the synthesis of collagen in embryonic cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 28;130(2):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOGANGES P. T., SCHUBERT M. THE USE OF LANTHANUM TO STUDY THE DEGRADATION OF A PROTEINPOLYSACCHARIDE FROM CARTILAGE. J Biol Chem. 1964 May;239:1498–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein R., Arsenis C., Kuettner K. E. Electron microscopic studies of cartilage matrix using lysozyme as a vital stain. J Cell Biol. 1970 Sep;46(3):626–631. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.3.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein R., Soble L. W., Kuettner K. E. Lysozyme in epiphyseal cartilage. 3. Effects of protamine, toluidine blue and histamine on mouse embryonic cartilage in organ culture. Am J Pathol. 1970 Jul;60(1):43–56. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engfeldt B. Studies on the epiphysial growth zone. 3. Electronmicroscopic studies on the normal epiphysial growth zone. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;75(2):201–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GODMAN G. C., PORTER K. R. Chondrogenesis, studied with the electron microscope. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Dec;8:719–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. The function of glycoprotein in the formation of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2384–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman A., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Protein-polysaccharide loss during endochondral ossification: immunochemical evidence. Science. 1966 Oct 21;154(3747):393–395. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3747.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell D. S., Pita J. C., Marquez J. F., Gatter R. A. Demonstration of macromolecular inhibitors of calcification and nucleational factors in fluid from calcifying sites in cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1969 Apr;48(4):630–641. doi: 10.1172/JCI106021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuettner K. E., Soble L. W., Eisenstein R., Yaeger J. A. The influence of lysozyme on the appearance of epiphyseal cartilage in organ culture. Calcif Tissue Res. 1968 Jul 15;2(1):93–105. doi: 10.1007/BF02279198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuettner K. E., Soble L. W., Guenther H. L., Croxen R. L., Eisenstein R. Lysozyme in epiphyseal cartilage. I. The nature of the morphologic response of cartilage in culture to exogenous lysozym. Calcif Tissue Res. 1970;5(1):56–63. doi: 10.1007/BF02017534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenbaum A., Kuettner K. E. Mucopolysaccharides and mucoproteins of calf scapula. Calcif Tissue Res. 1967;1(2):153–165. doi: 10.1007/BF02008085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewi G. Localization of chondromucoprotein in cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1965 Nov;24(6):528–535. doi: 10.1136/ard.24.6.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Fine structures of capillary and endocapillary layer as revealed by ruthenium red. Fed Proc. 1966 Nov-Dec;25(6):1773–1783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matukas V. J., Panner B. J., Orbison J. L. Studies on ultrastructural identification and distribution of protein-polysaccharide in cartilage matrix. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):365–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohos S. C., Wagner B. M. Damage to collagen in corneal immune injury. Observation of connective tissue structure. Arch Pathol. 1969 Jul;88(1):3–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers D. B., Highton T. C., Rayns D. G. Acid mucopolysaccharides closely associated with collagen fibrils in normal human synovium. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Aug;28(3):203–213. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal S., Doganges P. T., Schubert M. The separation of new forms of the proteinpolysaccharides of bovine nasal cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 25;241(18):4261–4266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Hellmann W., Kleinschmidt A. K. Macromolecular models of proteinpolysaccharides from bovine nasal cartilage based on electron microscopic studies. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 25;245(16):4123–4130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Johnson B., Schubert M. The proteinpolysaccharides of human costal cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1969 Mar;48(3):543–552. doi: 10.1172/JCI106012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Pal S., Beale R., Schubert M. A comparison of proteinpolysaccharides of bovine nasal cartilage isolated and fractionated by different methods. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 25;245(16):4112–4122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Schubert M. The proteinpolysaccharides of bovine nucleus pulposus. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 25;242(20):4691–4701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajdera S. W., Hascall V. C. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. A comparison of low and high shear extraction procedures. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):77–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk R. K., Spiro D., Wiener J. Cartilage resorption in the tibial epiphyseal plate of growing rats. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):275–291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Fracassini A., Smith J. W. Observations on the morphology of the proteinpolysaccharide complex of bovine nasal cartilage and its relationship to collagen. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Oct 11;165(1001):440–449. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Peters T. J., Serafini-Fracassini A. Observations on the distribution of the proteinpolysaccharide complex and collagen in bovine articular cartilage. J Cell Sci. 1967 Mar;2(1):129–136. doi: 10.1242/jcs.2.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani E., Ametani T. Substructure of microtubules in brain nerve cells as revealed by ruthenium red. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jul;46(1):159–165. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel M. G., Wetzel B. K., Spicer S. S. Ultrastructural localization of acid mucosubstances in the mouse colon with iron-containing stains. J Cell Biol. 1966 Aug;30(2):299–315. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]