Abstract
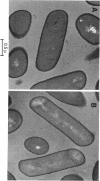
The spoIIM locus of Bacillus subtilis is the most recently discovered of six genetic loci in which mutations can prevent the synthesis of a normal asymmetric septum or prevent migration of the septal structure to engulf the forespore compartment of the sporangium. Ultrastructure studies of a spoIIM mutant confirmed a block prior to the completion of engulfment. Introduction of a spoIIM mutation into a panel of strains containing lacZ fusions belonging to different regulatory classes allowed us to determine that the spoIIM gene product is required for the efficient expression of genes transcribed by sigma G-associated RNA polymerase but is not required for the expression of sigma F-controlled genes, including spoIIIG, which encodes sigma G. The results of complementation studies, gene disruption analysis, and DNA sequencing revealed that the spoIIM locus contains a single sporulation-essential gene encoding a polypeptide with a predicted molecular mass of 24,850 Da. The predicted spoIIM gene product is highly hydrophobic and very basic, and it does not exhibit significant homology to sequence files in several major data bases.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backman K., Ptashne M., Gilbert W. Construction of plasmids carrying the cI gene of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4174–4178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall B., Lutkenhaus J. Nucleotide sequence and insertional inactivation of a Bacillus subtilis gene that affects cell division, sporulation, and temperature sensitivity. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6821–6834. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6821-6834.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppolecchia R., DeGrazia H., Moran C. P., Jr Deletion of spoIIAB blocks endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis at an early stage. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):6678–6685. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6678-6685.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting S., Driks A., Schmidt R., Kunkel B., Losick R. Forespore-specific transcription of a gene in the signal transduction pathway that governs Pro-sigma K processing in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):456–466. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting S., Oke V., Driks A., Losick R., Lu S., Kroos L. A forespore checkpoint for mother cell gene expression during development in B. subtilis. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90362-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting S., Roels S., Losick R. Sporulation operon spoIVF and the characterization of mutations that uncouple mother-cell from forespore gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1237–1256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90931-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Piggot P. J. Nucleotide sequence of sporulation locus spoIIA in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2147–2153. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulger D., Errington J. Sequential activation of dual promoters by different sigma factors maintains spoVJ expression during successive developmental stages of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1363–1373. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán P., Westpheling J., Youngman P. Characterization of the promoter region of the Bacillus subtilis spoIIE operon. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1598–1609. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1598-1609.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland S. K., Cutting S., Mandelstam J. The possible DNA-binding nature of the regulatory proteins, encoded by spoIID and gerE, involved in the sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Sep;133(9):2381–2391. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-9-2381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illing N., Errington J. Genetic regulation of morphogenesis in Bacillus subtilis: roles of sigma E and sigma F in prespore engulfment. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(10):3159–3169. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.10.3159-3169.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illing N., Errington J. The spoIIIA operon of Bacillus subtilis defines a new temporal class of mother-cell-specific sporulation genes under the control of the sigma E form of RNA polymerase. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1927–1940. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireton K., Grossman A. D. Interactions among mutations that cause altered timing of gene expression during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3185–3195. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3185-3195.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas R. M., Weaver E. A., Kenney T. J., Moran C. P., Jr, Haldenwang W. G. The Bacillus subtilis spoIIG operon encodes both sigma E and a gene necessary for sigma E activation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):507–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.507-511.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmazyn-Campelli C., Bonamy C., Savelli B., Stragier P. Tandem genes encoding sigma-factors for consecutive steps of development in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):150–157. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney T. J., Moran C. P., Jr Genetic evidence for interaction of sigma A with two promoters in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3282–3290. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3282-3290.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel B., Kroos L., Poth H., Youngman P., Losick R. Temporal and spatial control of the mother-cell regulatory gene spoIIID of Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1735–1744. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg E. M., Cohen S. N. Transformation of Salmonella typhimurium by plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):1072–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.1072-1074.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. D., Parkinson J. S. Genetics and sequence analysis of the pcnB locus, an Escherichia coli gene involved in plasmid copy number control. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1254–1261. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1254-1261.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Diaz I., Clarke S., Mandelstam J. spoIID operon of Bacillus subtilis: cloning and sequence. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):341–354. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopilato J., Bortner S., Beckwith J. Mutations in a new chromosomal gene of Escherichia coli K-12, pcnB, reduce plasmid copy number of pBR322 and its derivatives. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Nov;205(2):285–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00430440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Stragier P. Crisscross regulation of cell-type-specific gene expression during development in B. subtilis. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):601–604. doi: 10.1038/355601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Youngman P., Piggot P. J. Genetics of endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:625–669. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu S., Halberg R., Kroos L. Processing of the mother-cell sigma factor, sigma K, may depend on events occurring in the forespore during Bacillus subtilis development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9722–9726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis P., Driks A., Losick R. Differentiation and the establishment of cell type during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Oct;1(3):330–335. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80296-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis P., Driks A., Losick R. Establishment of cell type by compartmentalized activation of a transcription factor. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):562–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1948031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. M., Hackett R. H., Setlow P. Regulation of expression of genes coding for small, acid-soluble proteins of Bacillus subtilis spores: studies using lacZ gene fusions. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):239–244. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.239-244.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani Y., Nicholson W. L., Neitzke K. D., Setlow P., Freese E. Sigma-G RNA polymerase controls forespore-specific expression of the glucose dehydrogenase operon in Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):999–1017. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson W. L., Sun D. X., Setlow B., Setlow P. Promoter specificity of sigma G-containing RNA polymerase from sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis: identification of a group of forespore-specific promoters. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2708–2718. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2708-2718.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge S. R., Foulger D., Errington J. The role of sigma F in prespore-specific transcription in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):757–767. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Coote J. G. Genetic aspects of bacterial endospore formation. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):908–962. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.908-962.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rather P. N., Moran C. P., Jr Compartment-specific transcription in Bacillus subtilis: identification of the promoter for gdh. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5086–5092. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5086-5092.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricca E., Cutting S., Losick R. Characterization of bofA, a gene involved in intercompartmental regulation of pro-sigma K processing during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3177–3184. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3177-3184.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rong S., Rosenkrantz M. S., Sonenshein A. L. Transcriptional control of the Bacillus subtilis spoIID gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):771–779. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.771-779.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rong S., Sonenshein A. L. Mutations in the precursor region of a Bacillus subtilis sporulation sigma factor. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3812–3817. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3812-3817.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R., Toye P. A., Korman R. Z., Zahler S. A. The prophage of SP beta c2dcitK1, A defective specialized transducing phage of Bacillus subtilis. Genetics. 1979 Jul;92(3):721–739. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandman K., Losick R., Youngman P. Genetic analysis of Bacillus subtilis spo mutations generated by Tn917-mediated insertional mutagenesis. Genetics. 1987 Dec;117(4):603–617. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.4.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R., Margolis P., Duncan L., Coppolecchia R., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Control of developmental transcription factor sigma F by sporulation regulatory proteins SpoIIAA and SpoIIAB in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9221–9225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K., Youngman P. Evidence that the spoIIM gene of Bacillus subtilis is transcribed by RNA polymerase associated with sigma E. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3618–3627. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3618-3627.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K., Youngman P. Use of a new integrational vector to investigate compartment-specific expression of the Bacillus subtilis spoIIM gene. Biochimie. 1992 Jul-Aug;74(7-8):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(92)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Bonamy C., Karmazyn-Campelli C. Processing of a sporulation sigma factor in Bacillus subtilis: how morphological structure could control gene expression. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90407-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Bouvier J., Bonamy C., Szulmajster J. A developmental gene product of Bacillus subtilis homologous to the sigma factor of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):376–378. doi: 10.1038/312376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. X., Cabrera-Martinez R. M., Setlow P. Control of transcription of the Bacillus subtilis spoIIIG gene, which codes for the forespore-specific transcription factor sigma G. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2977–2984. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2977-2984.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. X., Stragier P., Setlow P. Identification of a new sigma-factor involved in compartmentalized gene expression during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):141–149. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M. D., Setlow P. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and regulation of the Bacillus subtilis gpr gene, which codes for the protease that initiates degradation of small, acid-soluble proteins during spore germination. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):291–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.291-300.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatti K. M., Jones C. H., Moran C. P., Jr Genetic evidence for interaction of sigma E with the spoIIID promoter in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7828–7833. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7828-7833.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vellanoweth R. L., Rabinowitz J. C. The influence of ribosome-binding-site elements on translational efficiency in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli in vivo. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(9):1105–1114. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman P., Perkins J. B., Losick R. A novel method for the rapid cloning in Escherichia coli of Bacillus subtilis chromosomal DNA adjacent to Tn917 insertions. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(3):424–433. doi: 10.1007/BF00341443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman P., Perkins J. B., Losick R. Construction of a cloning site near one end of Tn917 into which foreign DNA may be inserted without affecting transposition in Bacillus subtilis or expression of the transposon-borne erm gene. Plasmid. 1984 Jul;12(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudkin M. D. Structure and function in a Bacillus subtilis sporulation-specific sigma factor: molecular nature of mutations in spoIIAC. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):475–481. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Losick R. Role of AbrB in Spo0A- and Spo0B-dependent utilization of a sporulation promoter in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2223–2230. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2223-2230.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]