Abstract
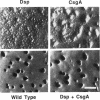
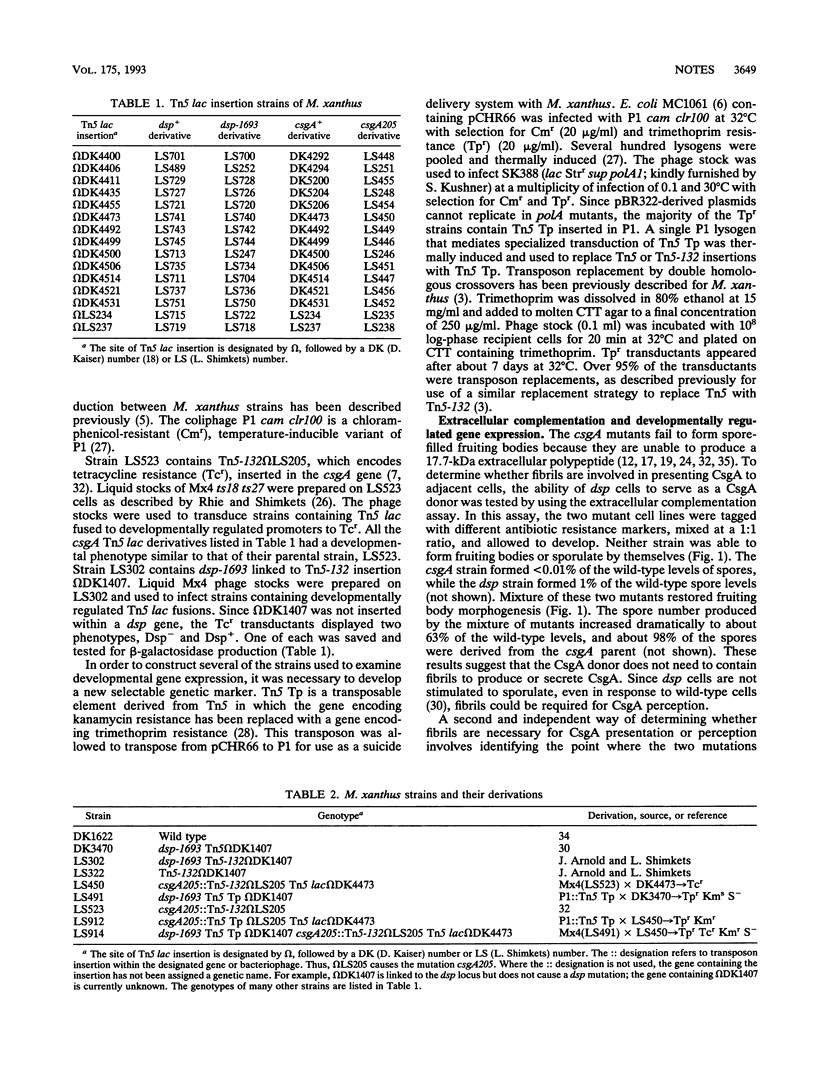
The dsp locus contains genes involved in the subunit synthesis and/or assembly of fibrils that radiate outward from the Myxococcus xanthus cell surface and attach to other cells. The csgA gene encodes an extracellular protein morphogen which is essential for fruiting body development. The question of whether fibrils are involved in the transmission of CsgA to adjacent cells was investigated in three ways. First, the dsp and csgA mutants were mixed in a ratio of 1:1 and allowed to develop; fruiting bodies containing spores derived from the csgA mutant were formed, suggesting efficient CsgA transfer. Second, the csgA mutation affected expression of many developmentally regulated genes differently from the way dsp affected their expression. Third, the expression of one developmentally regulated gene, which was partially expressed in csgA and dsp backgrounds, was almost completely inhibited in the presence of both mutations, suggesting that its promoter is regulated independently by two distinct stimuli, one that is csgA dependent and one that is dsp dependent. Together these results argue that fibrils are not necessary for cell-to-cell transmission or perception of CsgA, and their precise function remains unknown.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold J. W., Shimkets L. J. Cell surface properties correlated with cohesion in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5771–5777. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5771-5777.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold J. W., Shimkets L. J. Inhibition of cell-cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus by congo red. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5765–5770. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5765-5770.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avery L., Kaiser D. In situ transposon replacement and isolation of a spontaneous tandem genetic duplication. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):99–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00330896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behmlander R. M., Dworkin M. Extracellular fibrils and contact-mediated cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7810–7820. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7810-7820.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J. M., Geisselsoder J., Zusman D. R. Isolation of bacteriophage MX4, a generalized transducing phage for Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. W., Kuspa A., Keseler I. M., Shimkets L. J. Physical map of the Myxococcus xanthus chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):2109–2115. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.2109-2115.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemans D. L., Chance C. M., Dworkin M. A development-specific protein in Myxococcus xanthus is associated with the extracellular fibrils. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):6749–6759. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6749-6759.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dana J. R., Shimkets L. J. Regulation of cohesion-dependent cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3636–3647. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3636-3647.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M., Kaiser D. Cell interactions in myxobacterial growth and development. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):18–24. doi: 10.1126/science.3929384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen T. J., Shimkets L. J. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional products of the csg locus of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):15–23. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.15-23.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J., Kaiser D. Cell-to-cell stimulation of movement in nonmotile mutants of Myxococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2938–2942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Kaiser D. C-factor has distinct aggregation and sporulation thresholds during Myxococcus development. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1722–1728. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1722-1728.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Kaiser D. C-factor: a cell-cell signaling protein required for fruiting body morphogenesis of M. xanthus. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90211-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Kaiser D. Cell motility is required for the transmission of C-factor, an intercellular signal that coordinates fruiting body morphogenesis of Myxococcus xanthus. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):896–904. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Hartzell P., Stephens K., Kaiser D. A link between cell movement and gene expression argues that motility is required for cell-cell signaling during fruiting body development. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1677–1685. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Expression of many developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus depends on a sequence of cell interactions. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):840–854. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuner J. M., Kaiser D. Fruiting body morphogenesis in submerged cultures of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):458–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.458-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Lee B. U., Shimkets L. J. csgA expression entrains Myxococcus xanthus development. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):401–410. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCVITTIE A., MESSIK F., ZAHLER S. A. Developmental biology of Myxococcus. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84:546–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.546-551.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhie H. G., Shimkets L. J. Developmental bypass suppression of Myxococcus xanthus csgA mutations. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3268–3276. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3268-3276.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner J. L. Formation, induction, and curing of bacteriophage P1 lysogens. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):679–689. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Asher S. J. Use of recombination techniques to examine the structure of the csg locus of Myxococcus xanthus. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jan;211(1):63–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00338394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Correlation of energy-dependent cell cohesion with social motility in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):837–841. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.837-841.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Gill R. E., Kaiser D. Developmental cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus and the spoC locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1406–1410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Kaiser D. Induction of coordinated movement of Myxococcus xanthus cells. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):451–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.451-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Rafiee H. CsgA, an extracellular protein essential for Myxococcus xanthus development. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5299–5306. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5299-5306.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Role of cell cohesion in Myxococcus xanthus fruiting body formation. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):842–848. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.842-848.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Social and developmental biology of the myxobacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):473–501. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.473-501.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]