Abstract
The obligate intracellular parasite, Rickettsia prowazekii, is a slowly growing bacterium with a doubling time of 8 to 12 h. The copy number of the 16S rRNA gene in the rickettsial chromosome was determined to be one. Genomic DNA from R. prowazekii was digested either by a variety of restriction enzymes known not to cut at any site in the rickettsial 16S rRNA gene or by a combination of these noncutting enzymes and SmaI, which cuts the gene only once. Only one DNA fragment in these digests hybridized to a biotinylated probe containing a portion of the rickettsial 16S rRNA gene. Moreover, the density of the rickettsial 16S rRNA gene fragment after hybridization was equal to the density of each of the seven 16S rRNA gene fragments in Escherichia coli.
Full text
PDF
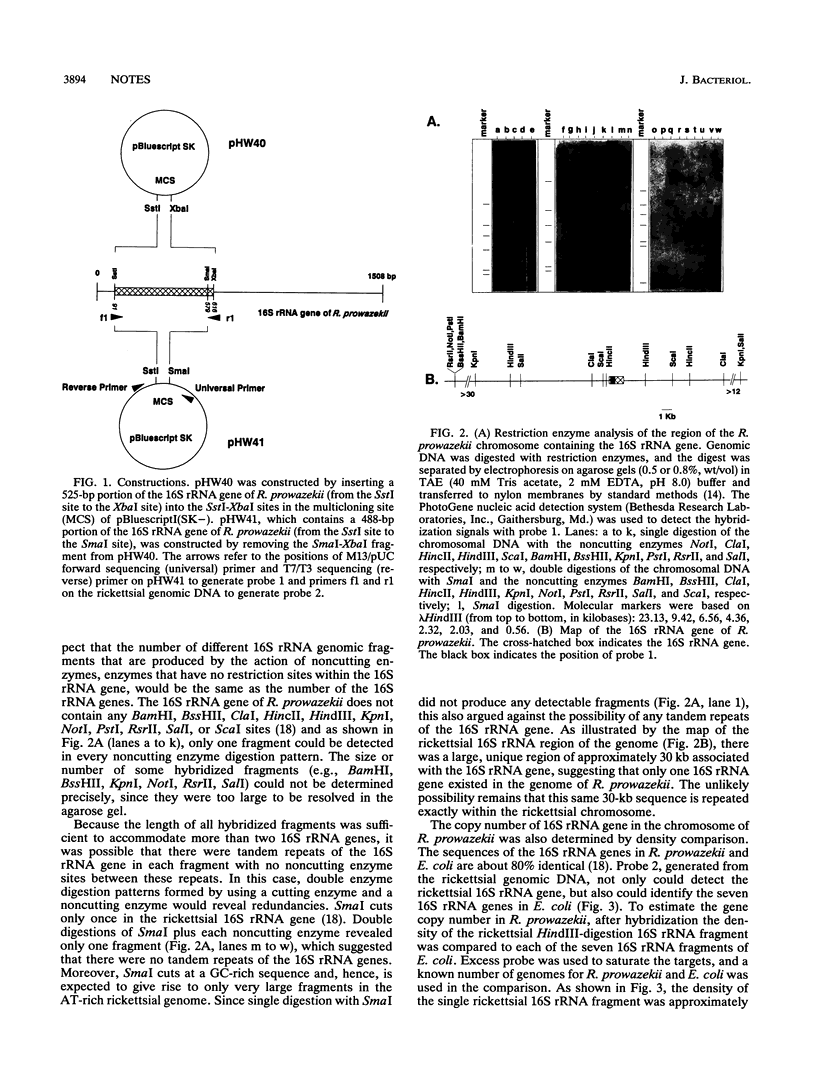

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amikam D., Glaser G., Razin S. Mycoplasmas (Mollicutes) have a low number of rRNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):376–378. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.376-378.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bercovier H., Kafri O., Sela S. Mycobacteria possess a surprisingly small number of ribosomal RNA genes in relation to the size of their genome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 14;136(3):1136–1141. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90452-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch G. A., Weiss E. Characterization of the Madrid E strain of Rickettsia prowazekii purified by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):280–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.280-286.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. DNA determinants of rRNA synthesis in E. coli: growth rate dependent regulation, feedback inhibition, upstream activation, antitermination. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. A., Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A., Silverman D. J. Some characteristics of heavy and light bands of Rickettsia prowazekii on Renografin gradients. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):596–604. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.596-604.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman J. D., Lau R. H., Doolittle W. F. The number, physical organization and transcription of ribosomal RNA cistrons in an archaebacterium: Halobacterium halobium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1321–1333. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura A., Morita M., Nishimura Y., Sugino Y. A rapid and highly efficient method for preparation of competent Escherichia coli cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6169–6169. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Morgan E. A. Genetics of bacterial ribosomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:297–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace N. R. Structure and synthesis of the ribosomal ribonucleic acid of prokaryotes. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Dec;37(4):562–603. doi: 10.1128/br.37.4.562-603.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela S., Clark-Curtiss J. E., Bercovier H. Characterization and taxonomic implications of the rRNA genes of Mycobacterium leprae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):70–73. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.70-73.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava A. K., Schlessinger D. Structure and organization of ribosomal DNA. Biochimie. 1991 Jun;73(6):631–638. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90042-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Isolation of Rickettsia prowazekii with reduced sensitivity to gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1765–1772. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1765-1772.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Dobson M. E., Samuel J. E., Dasch G. A., Mallavia L. P., Baca O., Mandelco L., Sechrest J. E., Weiss E., Woese C. R. Phylogenetic diversity of the Rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4202–4206. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4202-4206.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. Growth and physiology of rickettsiae. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):259–283. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.259-283.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Rickettsia species (as organisms). Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:131–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Rickettsial permeability. An ADP-ATP transport system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Edlinger E. A., Waddell A. D., Jones M. R. Infection cycle of Rickettsia rickettsii in chicken embryo and L-929 cells in culture. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1052–1064. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1052-1064.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D. In vitro studies on rickettsia-host cell interactions: intracellular growth cycle of virulent and attenuated Rickettsia prowazeki in chicken embryo cells in slide chamber cultures. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1391–1404. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1391-1401.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Steitz J. A. Tandem promoters direct E. coli ribosomal RNA synthesis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. A., Gilbert S. F., Nomura M. DNA sequences of promoter regions for rRNA operons rrnE and rrnA in E. coli. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]