Abstract
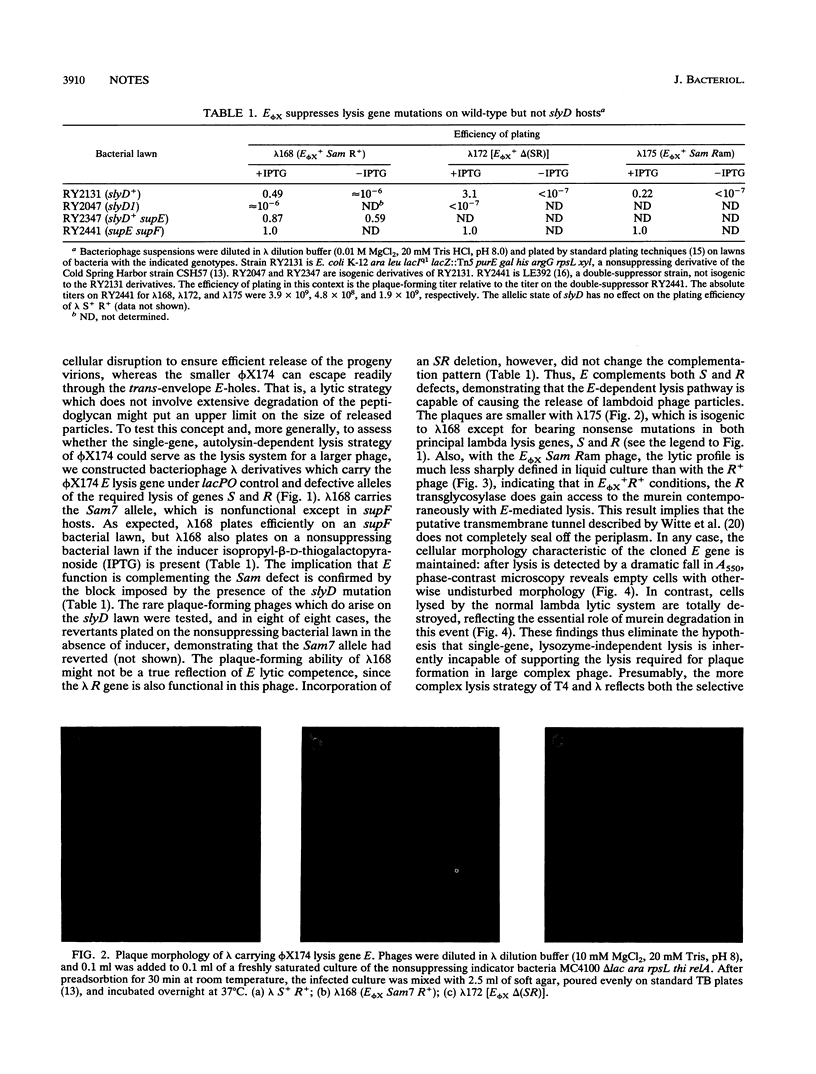
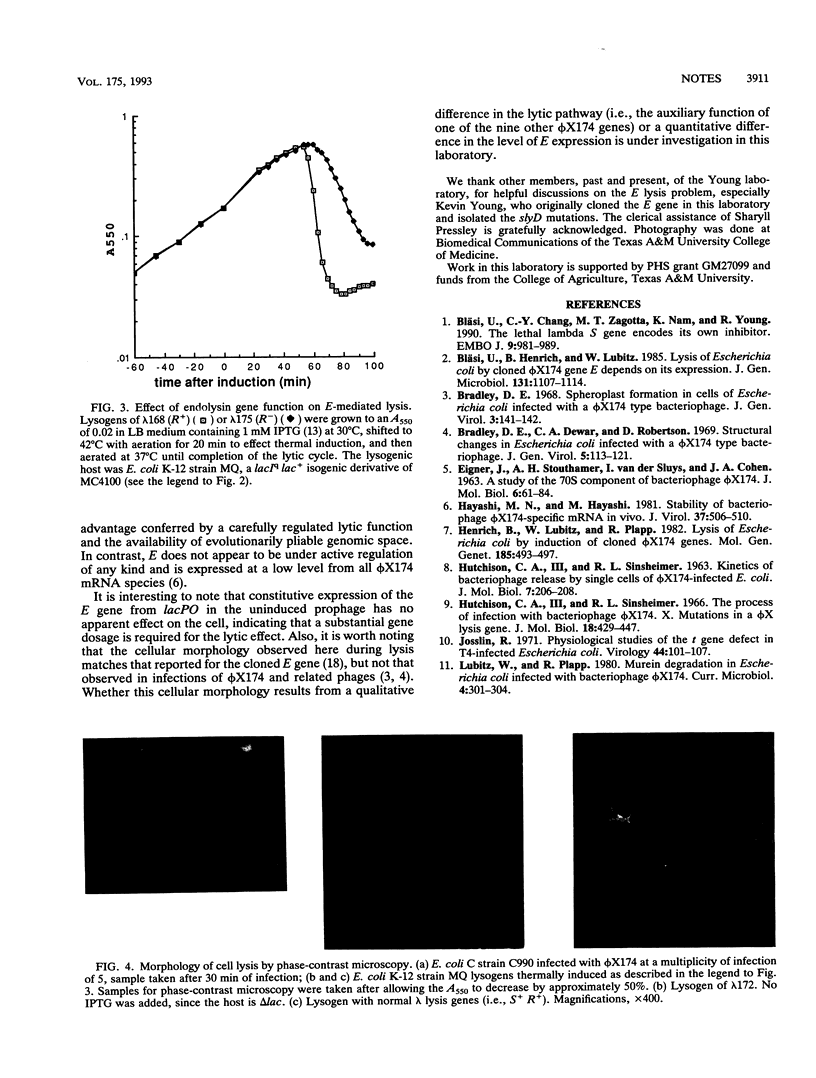
Hybrid lambda phages which have the E lysis gene of the bacteriophage phi X174 in cis to defective nonsense and deletion alleles of the normal lambda lysis genes S and R have been constructed and shown to be fully competent for plaque-forming ability, which demonstrates that the single-gene, lysozyme-independent lysis system of phi X174 and related phages can serve the lytic function for large complex phages. These hybrid phages are unable to form plaques on a slyD host. Moreover, plaque morphology indicates that in E-mediated lysis the soluble lambda R endolysin can participate in lysis, indicating that the protein E-mediated lesions are not completely sealed off from the periplasm.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bläsi U., Chang C. Y., Zagotta M. T., Nam K. B., Young R. The lethal lambda S gene encodes its own inhibitor. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):981–989. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Henrich B., Lubitz W. Lysis of Escherichia coli by cloned phi X174 gene E depends on its expression. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 May;131(5):1107–1114. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-5-1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E., Dewar C. A., Robertson D. Structural changes in Escherichia coli infected with a phi X174 type bacteriophage. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jul;5(1):113–121. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-5-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Spheroplast formation in cells of Escherichia coli infected with a phi-X 174 type bacteriophage. J Gen Virol. 1968 Jul;3(1):141–142. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-1-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTCHISON C. A., SINSHEIMER R. L. KINETICS OF BACTERIOPHAGE RELEASE BY SINGLE CELLS OF PHI X174-INFECTED E. COLI. J Mol Biol. 1963 Aug;7:206–208. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M. N., Hayashi M. Stability of bacteriophage phi X174-specific mRNA in vivo. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):506–510. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.506-510.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich B., Lubitz W., Plapp R. Lysis of Escherichia coli by induction of cloned phi X174 genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):493–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00334146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Sinsheimer R. L. The process of infection with bacteriophage phi-X174. X. Mutations in a phi-X Lysis gene. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(3):429–447. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josslin R. Physiological studies on the t gene defect in T4-infected Escherichia coli. Virology. 1971 Apr;44(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maratea D., Young K., Young R. Deletion and fusion analysis of the phage phi X174 lysis gene E. Gene. 1985;40(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab R., Neal G., Sohaskey C., Smith J., Young R. Dominance in lambda S mutations and evidence for translational control. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte A., Bläsi U., Halfmann G., Szostak M., Wanner G., Lubitz W. Phi X174 protein E-mediated lysis of Escherichia coli. Biochimie. 1990 Feb-Mar;72(2-3):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte A., Lubitz W., Bakker E. P. Proton-motive-force-dependent step in the pathway to lysis of Escherichia coli induced by bacteriophage phi X174 gene E product. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1750–1752. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1750-1752.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte A., Wanner G., Bläsi U., Halfmann G., Szostak M., Lubitz W. Endogenous transmembrane tunnel formation mediated by phi X174 lysis protein E. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4109–4114. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4109-4114.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. D., Young R. Lytic action of cloned phi X174 gene E. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):993–1002. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.993-1002.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. Bacteriophage lysis: mechanism and regulation. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Sep;56(3):430–481. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.3.430-481.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




