Abstract
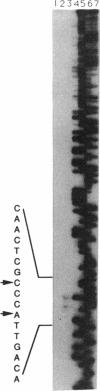
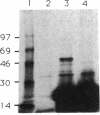
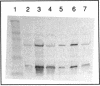
Two promoters required for expression of the ask-asd genes, encoding aspartokinase (AK) and aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (ASD), in Corynebacterium flavum N13, askP1 and askP2, have been identified by deletion analysis and S1 nuclease mapping. Transcription from askP1 initiates 35 and 38 bp upstream of the ask structural gene. A second promoter, askP2, lies within the ask coding region, upstream of the translation start site of the AK beta subunit and can direct the expression of AK beta and ASD. Western immunoblot analysis and heterologous expression in Escherichia coli demonstrate that two separate polypeptides, a 44.8-kDa alpha subunit and an 18.5-kDa beta subunit, are expressed from the C. flavum N13 ask gene from distinct, in-frame translation initiation sites. A second AK mutation, G345D, which reduces the sensitivity of AK to concerted feedback inhibition by threonine plus lysine, was identified.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bondaryk R. P., Paulus H. Cloning and structure of the gene for the subunits of aspartokinase II from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):585–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondaryk R. P., Paulus H. Expression of the gene for Bacillus subtilis aspartokinase II in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):592–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen N. Y., Hu F. M., Paulus H. Nucleotide sequence of the overlapping genes for the subunits of Bacillus subtilis aspartokinase II and their control regions. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8787–8798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen N. Y., Paulus H. Mechanism of expression of the overlapping genes of Bacillus subtilis aspartokinase II. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9526–9532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follettie M. T., Shin H. K., Sinskey A. J. Organization and regulation of the Corynebacterium glutamicum hom-thrB and thrC loci. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):53–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalinowski J., Bachmann B., Thierbach G., Pühler A. Aspartokinase genes lysC alpha and lysC beta overlap and are adjacent to the aspartate beta-semialdehyde dehydrogenase gene asd in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Dec;224(3):317–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00262424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalinowski J., Cremer J., Bachmann B., Eggeling L., Sahm H., Pühler A. Genetic and biochemical analysis of the aspartokinase from Corynebacterium glutamicum. Mol Microbiol. 1991 May;5(5):1197–1204. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y., Chen N. Y., Paulus H. Identification of aecA mutations in Bacillus subtilis as nucleotide substitutions in the untranslated leader region of the aspartokinase II operon. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 May;137(5):1135–1143. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-5-1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima R., Otsuka S., Shiio I. Regulation of aspartate family amino acid biosynthesis in Brevibacterium flavum. I. Inhibition by amino acids of the enzymes in threonine biosynthesis. J Biochem. 1968 Feb;63(2):139–148. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir D., Paulus H. Immunological and chemical comparison of the nonidentical subunits of aspartokinase II from Bacillus subtilis VB217. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4655–4661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir D., Paulus H. Properties and subunit structure of aspartokinase II from Bacillus subtilis VB217. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4648–4651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omori K., Imai Y., Suzuki S., Komatsubara S. Nucleotide sequence of the Serratia marcescens threonine operon and analysis of the threonine operon mutations which alter feedback inhibition of both aspartokinase I and homoserine dehydrogenase I. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):785–794. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.785-794.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peoples O. P., Liebl W., Bodis M., Maeng P. J., Follettie M. T., Archer J. A., Sinskey A. J. Nucleotide sequence and fine structural analysis of the Corynebacterium glutamicum hom-thrB operon. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):63–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiio I., Miyajima R. Concerted inhibition and its reversal by end products of aspartate kinase in Brevibacterium flavum. J Biochem. 1969 Jun;65(6):849–859. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihama M., Higashiro K., Rao E. A., Akedo M., Shanabruch W. G., Follettie M. T., Walker G. C., Sinskey A. J. Cloning vector system for Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):591–597. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.591-597.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]