Abstract
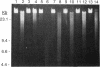
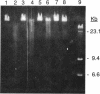
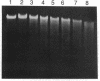
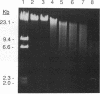
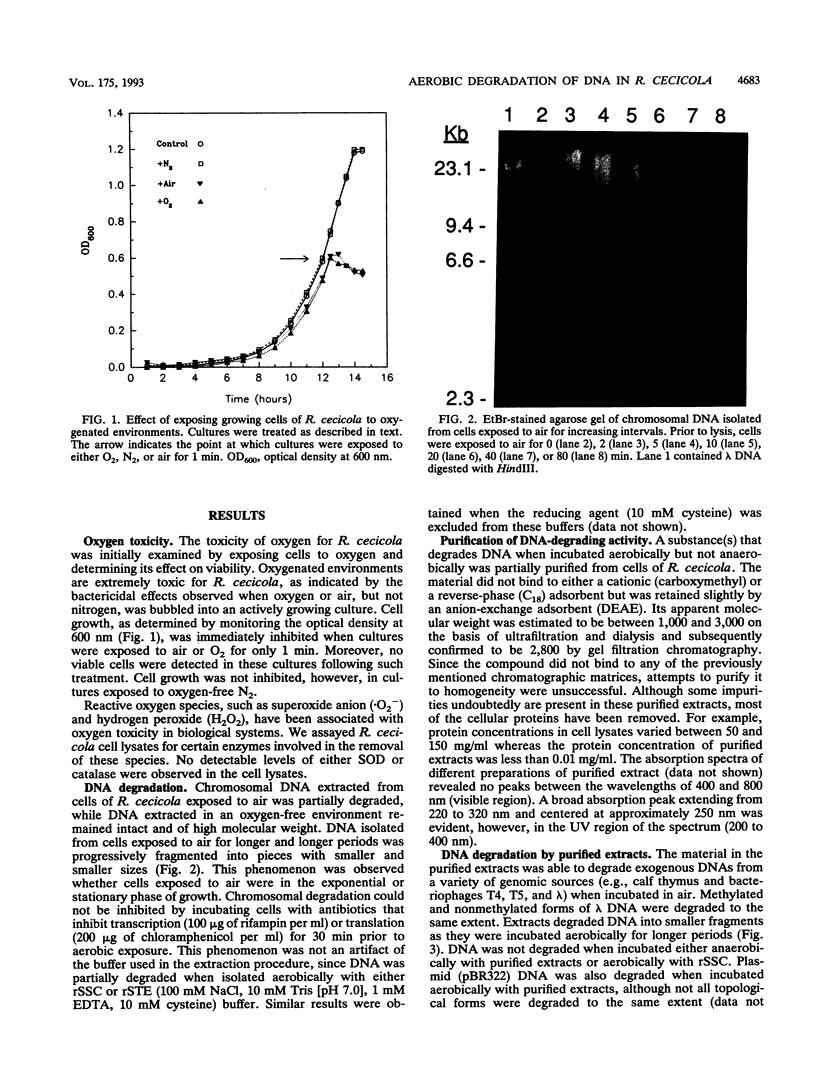
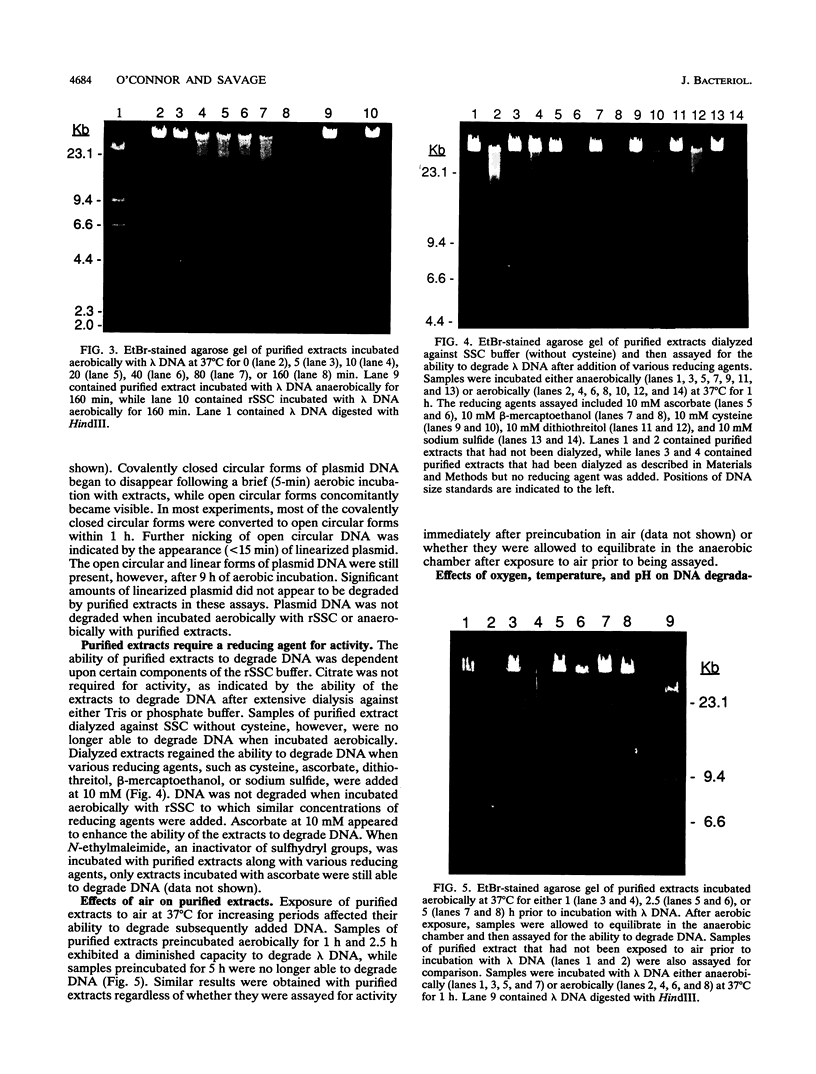
Roseburia cecicola is an obligately anaerobic bacterium that is extremely sensitive to oxygen. Genomic DNA isolated from cells exposed to air for even a brief period (< 5 min) is partially degraded, while DNA extracted from cells maintained in an anaerobic environment remains intact. Cells exposed to air for longer and longer periods yield DNA which is progressively degraded into fragments with decreasing sizes. Oxygen toxicity for this anaerobe appears to result, at least in part, from degradation of its genomic DNA. Cell lysates of the organism exhibited a similar ability to degrade exogenous sources of DNA when assayed in vitro under aerobic conditions. A substance that degrades both DNA and RNA when incubated aerobically was partially purified from such lysates. It has an approximate molecular weight of 2,800 and is unlikely to be a protein. It requires a reducing agent for activity and can be inhibited by catalase and peroxidase but not superoxide dismutase. The rate at which it degrades DNA in vitro can be enhanced by temperatures above 37 degrees C or by oxygen at partial pressures above atmospheric pressure. These results suggest that this substance degrades nucleic acids by a mechanism involving oxygen radicals.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aust S. D., Morehouse L. A., Thomas C. E. Role of metals in oxygen radical reactions. J Free Radic Biol Med. 1985;1(1):3–25. doi: 10.1016/0748-5514(85)90025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEERS R. F., Jr, SIZER I. W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawn K., Fridovich I. DNA strand scission by enzymically generated oxygen radicals. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Feb;206(2):414–419. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadenas E. Biochemistry of oxygen toxicity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:79–110. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. L., Riley B., Chang P., Sayahtaheri S., Tassell S., Hevelone J. Effects of molecular oxygen, oxidation-reduction potential, and antioxidants upon in vitro replication of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Oct;56(10):3063–3072. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.10.3063-3072.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing D. Synergistic damage from H2O2 and OH radicals in irradiated cells. Radiat Res. 1983 Apr;94(1):171–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:147–159. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb S. F. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:111–152. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.000551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. Oxygen free radicals and iron in relation to biology and medicine: some problems and concepts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 May 1;246(2):501–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90305-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassett D. J., Bean K., Biswas G., Cohen M. S. The role of hydroxyl radical in chromosomal and plasmid damage in Neisseria gonorrhoeae in vivo. Free Radic Res Commun. 1989;7(2):83–87. doi: 10.3109/10715768909087927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A., Linn S. DNA damage and oxygen radical toxicity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1302–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.3287616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham J. A., Cech T. R. Defining the inside and outside of a catalytic RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):276–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2501870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lickl E., Chao S. C., Chang W. C. Intracellular oxidative cleavage of DNA in Escherichia coli by the copper-1,10-phenanthroline complex. Free Radic Res Commun. 1989;8(1):37–45. doi: 10.3109/10715768909087970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu M., Guo Q., Wink D. J., Kallenbach N. R. Charge dependence of Fe(II)-catalyzed DNA cleavage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3333–3337. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. H., Savage D. C. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and taxonomic implications of the flagellin gene of Roseburia cecicola. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2612–2617. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2612-2617.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. H., Savage D. C. Degradation of DNA in cells and extracts of the obligately anaerobic bacterium Roseburia cecicola upon exposure to air. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1619–1621. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1619-1621.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Keele B. B., Jr, Fridovich I. An enzyme-based theory of obligate anaerobiosis: the physiological function of superoxide dismutase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1024–1027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. A., Halliwell B. Superoxide-dependent formation of hydroxyl radicals in the presence of thiol compounds. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 8;138(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80388-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. E., Browning M. M., Floyd R. A. Ascorbate/iron mediation of hydroxyl free radical damage to PBR322 plasmid DNA. Free Radic Biol Med. 1988;5(5-6):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(88)90099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. E., Browning M. M., Zhu X., Eneff K. L., Floyd R. A. Characterization of hydroxyl free radical mediated damage to plasmid pBR322 DNA. Mutat Res. 1989 Sep;214(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(89)90194-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer G. E., Price M. A., Tullius T. D. Use of the hydroxyl radical and gel electrophoresis to study DNA structure. Electrophoresis. 1989 May-Jun;10(5-6):397–404. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simic M. G., Bergtold D. S., Karam L. R. Generation of oxy radicals in biosystems. Mutat Res. 1989 Sep;214(1):3–12. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(89)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner B. M., Wong G. H., Sutrave P., Graves S. Oxygen toxicity in Treponema pallidum: deoxyribonucleic acid single-stranded breakage induced by low doses of hydrogen peroxide. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Dec;30(12):1467–1476. doi: 10.1139/m84-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Christman M. F., Sies H., Ames B. N. Spontaneous mutagenesis and oxidative damage to DNA in Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8917–8921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachon P. Ferric and cupric ions requirement for DNA single-strand breakage by H2O2. Free Radic Res Commun. 1989;7(1):1–10. doi: 10.3109/10715768909088155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourn C. C. Comparison of superoxide with other reducing agents in the biological production of hydroxyl radicals. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):625–628. doi: 10.1042/bj1820625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]