Abstract
The IncN plasmid pKM101 (a derivative of R46) encodes the antirestriction protein ArdB (alleviation of restriction of DNA) in addition to another antirestriction protein, ArdA, described previously. The relevant gene, ardB, was located in the leading region of pKM101, about 7 kb from oriT. The nucleotide sequence of ardB was determined, and an appropriate polypeptide was identified in maxicells of Escherichia coli. Like ArdA, ArdB efficiently inhibits restriction by members of the three known families of type I systems of E. coli and only slightly affects the type II enzyme, EcoRI. However, in contrast to ArdA, ArdB is ineffective against the modification activity of the type I (EcoK) system. Comparison of deduced amino acid sequences of ArdA and ArdB revealed only one small region of similarity (nine residues), suggesting that this region may be somehow involved in the interaction with the type I restriction systems. We also found that the expression of both ardA and ardB genes is controlled jointly by two pKM101-encoded proteins, ArdK and ArdR, with molecular weights of about 15,000 and 20,000, respectively. The finding that the sequences immediately upstream of ardA and ardB share about 94% identity over 218 bp suggests that their expression may be controlled by ArdK and ArdR at the transcriptional level. Deletion studies and promoter probe analysis of these sequences revealed the regions responsible for the action of ArdK and ArdR as regulatory proteins. We propose that both types of antirestriction proteins may play a pivotal role in overcoming the host restriction barrier by self-transmissible broad-host-range plasmids. It seems likely that the ardKR-dependent regulatory system serves in this case as a genetic switch that controls the expression of plasmid-encoded antirestriction functions during mating.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
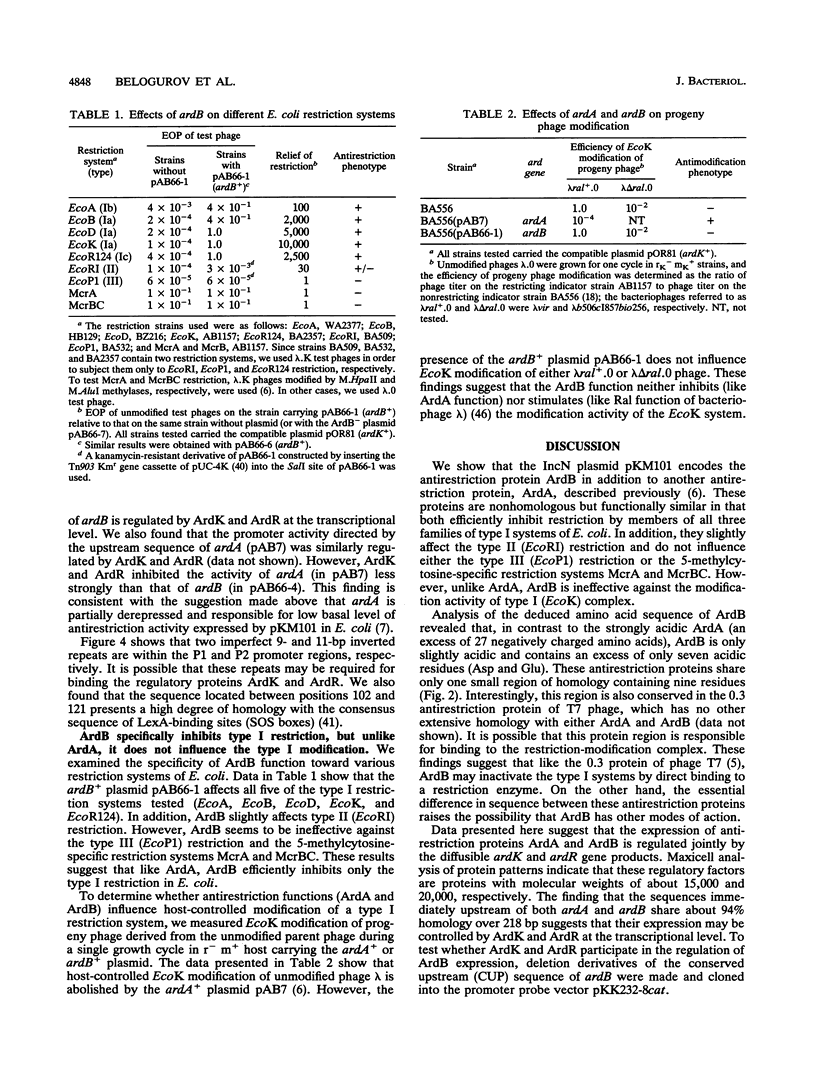
- Arber W., Wauters-Willems D. Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli. XII. The two restriction and modification systems of strain 15T-. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(3):203–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00283350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerswald E. A., Ludwig G., Schaller H. Structural analysis of Tn5. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):107–113. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTANI G., WEIGLE J. J. Host controlled variation in bacterial viruses. J Bacteriol. 1953 Feb;65(2):113–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.2.113-121.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay P. K., Studier F. W., Hamilton D. L., Yuan R. Inhibition of the type I restriction-modification enzymes EcoB and EcoK by the gene 0.3 protein of bacteriophage T7. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belogurov A. A., Delver E. P., Rodzevich O. V. IncN plasmid pKM101 and IncI1 plasmid ColIb-P9 encode homologous antirestriction proteins in their leading regions. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5079–5085. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5079-5085.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belogurov A. A., Yussifov T. N., Kotova V. U., Zavilgelsky G. B. The novel gene(s) ARD of plasmid pKM101: alleviation of EcoK restriction. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(3):509–513. doi: 10.1007/BF00332948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J. Plasmid vectors for the selection of promoters. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J. Toxicity of an overproduced foreign gene product in Escherichia coli and its use in plasmid vectors for the selection of transcription terminators. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Willetts N. S. A physical and genetic map of the IncN plasmid R46. Plasmid. 1981 Mar;5(2):188–201. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland G. M., Brown A. M., Willetts N. S. The origin of transfer (oriT) of the conjugative plasmid R46: characterization by deletion analysis and DNA sequencing. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):219–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00330445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N. Plasmids as organisms. Basic Life Sci. 1985;30:3–16. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2447-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delver E. P., Kotova V. U., Zavilgelsky G. B., Belogurov A. A. Nucleotide sequence of the gene (ard) encoding the antirestriction protein of plasmid colIb-P9. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5887–5892. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5887-5892.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmalingam K., Revel H. R., Goldberg E. B. Physical mapping and cloning of bacteriophage T4 anti-restriction endonuclease gene. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):694–699. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.694-699.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Elzinga M., Mark K. K., Studier F. W. Amino acid sequence of the gene 0.3 protein of bacteriophage T7 and nucleotide sequence of its mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2579–2585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Datta N. R124, an fi R factor of a new compatibility class. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jul;71(2):403–405. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-2-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Barth P. T., Wilkins B. M. Zygotic induction of plasmid ssb and psiB genes following conjugative transfer of Incl1 plasmid Collb-P9. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(5):605–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger D. H., Bickle T. A. Bacteriophage survival: multiple mechanisms for avoiding the deoxyribonucleic acid restriction systems of their hosts. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):345–360. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.345-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Reznikoff W. S. Use of transcriptional repressors to stabilize plasmid copy number of transcriptional fusion vectors. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):441–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.441-444.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. J., Walker G. C. Restriction endonuclease cleavage map of pKM101: relationship to parental plasmid R46. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):268–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00269669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark K. K., Studier F. W. Purification of the gene 0.3 protein of bacteriophage T7, an inhibitor of the DNA restriction system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2573–2578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazodier P., Davies J. Gene transfer between distantly related bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:147–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffatt B. A., Studier F. W. Entry of bacteriophage T7 DNA into the cell and escape from host restriction. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2095–2105. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2095-2105.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry K. L., Elledge S. J., Mitchell B. B., Marsh L., Walker G. C. umuDC and mucAB operons whose products are required for UV light- and chemical-induced mutagenesis: UmuD, MucA, and LexA proteins share homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4331–4335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read T. D., Thomas A. T., Wilkins B. M. Evasion of type I and type II DNA restriction systems by IncI1 plasmid CoIIb-P9 during transfer by bacterial conjugation. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jul;6(14):1933–1941. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roulland-Dussoix D., Boyer H. W. The Escherichia coli B restriction endonuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 19;195(1):219–229. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90618-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spoerel N., Herrlich P., Bickle T. A. A novel bacteriophage defence mechanism: the anti-restriction protein. Nature. 1979 Mar 1;278(5699):30–34. doi: 10.1038/278030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Gene 0.3 of bacteriophage T7 acts to overcome the DNA restriction system of the host. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 15;94(2):283–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stueber D., Bujard H. Transcription from efficient promoters can interfere with plasmid replication and diminish expression of plasmid specified genes. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1399–1404. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N., Wilkins B. Processing of plasmid DNA during bacterial conjugation. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):24–41. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.24-41.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. G., Murray N. E. Restriction and modification systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:585–627. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.003101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C., Walker G. C. Conjugal transfer system of the IncN plasmid pKM101. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):402–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.402-410.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabeau M., Friedman S., Van Montagu M., Schell J. The ral gene of phage lambda. I. Identification of a non-essential gene that modulates restriction and modification in E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(1):63–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00268447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]