Abstract
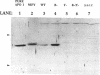
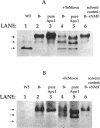
Apodinitrogenase, which lacks the iron-molybdenum cofactor at its active site, is an oligomer that contains an additional protein not found in the active dinitrogenase tetramer. This associated protein in Klebsiella pneumoniae is shown to be the product of the nifY gene. When apodinitrogenase is activated by the addition of the iron-molybdenum cofactor, NifY dissociates from the apodinitrogenase complex. The conditions for this dissociation are described. Finally, there are aspects of the dissociation and insertion process in K. pneumoniae that are different from that in Azotobacter vinelandii.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandner J. P., McEwan A. G., Kaplan S., Donohue T. J. Expression of the Rhodobacter sphaeroides cytochrome c2 structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):360–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.360-368.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govezensky D., Zamir A. Structure-function relationships in the alpha subunit of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase MoFe protein from analysis of nifD mutants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5729–5735. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5729-5735.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G. S., White T. C., Flory J. E., Orme-Johnson W. H. Genes required for formation of the apoMoFe protein of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15909–15919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes T. R., Smith B. E. Purification and characterization of the inactive MoFe protein (NifB-Kp1) of the nitrogenase from nifB mutants of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):43–50. doi: 10.1042/bj2090043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. R., Brigle K. E., Bennett L. T., Setterquist R. A., Wilson M. S., Cash V. L., Beynon J., Newton W. E., Dean D. R. Physical and genetic map of the major nif gene cluster from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1017–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1017-1027.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNeil T., MacNeil D., Roberts G. P., Supiano M. A., Brill W. J. Fine-structure mapping and complementation analysis of nif (nitrogen fixation) genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):253–266. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.253-266.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paustian T. D., Shah V. K., Roberts G. P. Apodinitrogenase: purification, association with a 20-kilodalton protein, and activation by the iron-molybdenum cofactor in the absence of dinitrogenase reductase. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 10;29(14):3515–3522. doi: 10.1021/bi00466a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., Brill W. J. Gene-product relationships of the nif regulon of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):210–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.210-216.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., MacNeil T., MacNeil D., Brill W. J. Regulation and characterization of protein products coded by the nif (nitrogen fixation) genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):267–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.267-279.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Isolation of an iron-molybdenum cofactor from nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3249–3253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. IV. Simple method of purification to homogeneity of nitrogenase components from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 30;305(2):445–454. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Stacey G., Brill W. J. Electron transport to nitrogenase. Purification and characterization of pyruvate:flavodoxin oxidoreductase. The nifJ gene product. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):12064–12068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. C., Harris G. S., Orme-Johnson W. H. Electrophoretic studies on the assembly of the nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein from the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifD and nifK gene products. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):24007–24016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]