Abstract
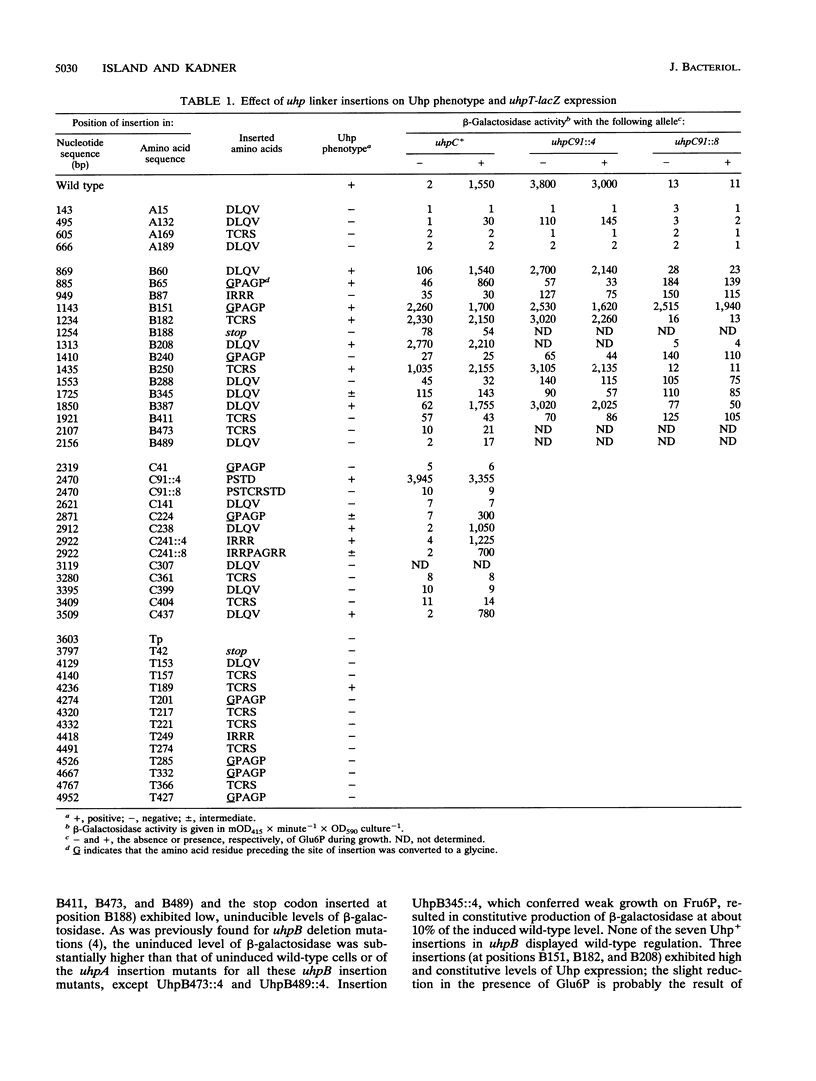
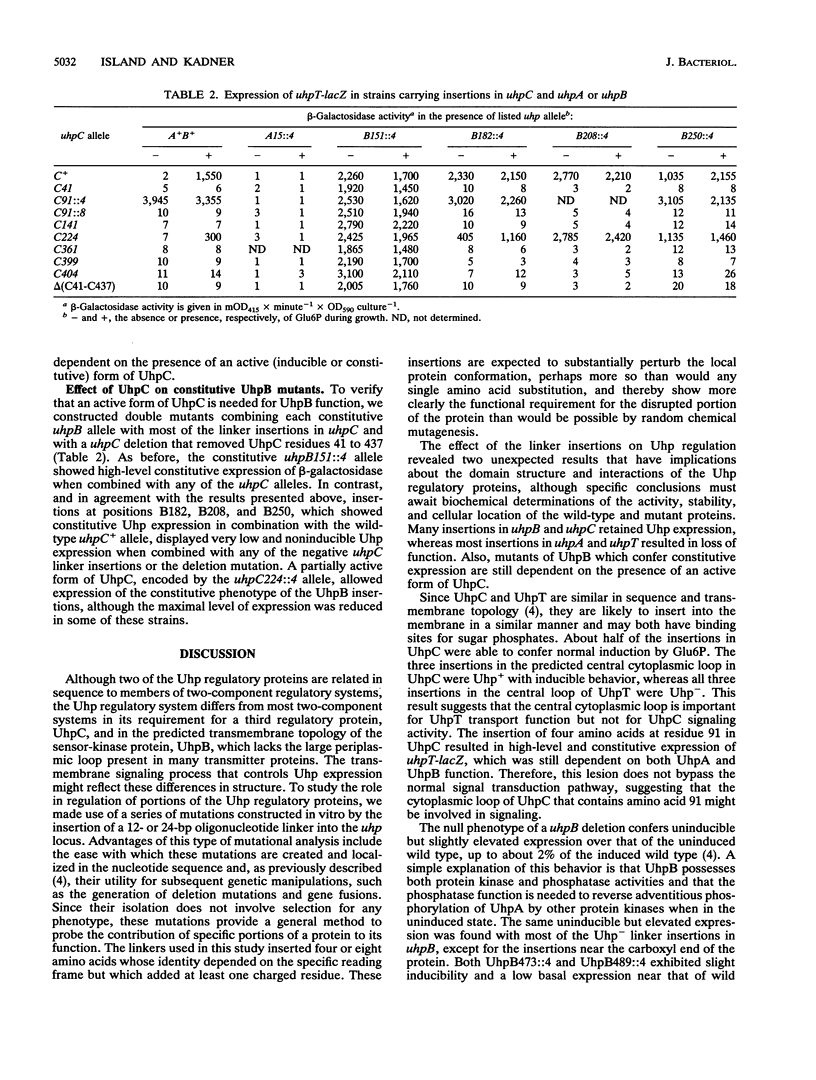
Expression of the Escherichia coli uhpT gene, encoding the sugar phosphate transport protein, is induced by extracellular glucose-6-phosphate and requires the function of the uhpABC regulatory genes. The UhpA and UhpB proteins are related to the response-regulator and sensor-kinase proteins of two-component regulatory systems, whereas the UhpC protein is related to UhpT and homologous transport proteins. To investigate the role of segments of the membrane-associated UhpB and UhpC regulatory proteins, a series of mutations were constructed in vitro by insertion of a 12- or 24-bp oligonucleotide linker at 44 sites within the uhpABCT locus. The effect of these mutations on regulation of a uhpT-lacZ transcriptional reporter was assayed with the mutated uhp alleles in single copy on the chromosome. All but one of the insertions in uhpA or uhpT were inactive for transcription activation or transport, respectively. In contrast, about half of the insertions in uhpB and uhpC retained Uhp expression, and insertions at four sites in uhpB and at one site in uhpC conferred high-level constitutive expression. The constitutive mutants in UhpB resulted from insertions in the nonpolar amino-terminal half of the protein, and all insertions in that half of UhpB affected Uhp expression in some manner, which suggests that the transmembrane segments of UhpB might negatively regulate the kinase activity of the carboxyl portion. The constitutive behavior of all but one of these uhpB alleles was dependent on the presence of active forms of both UhpA and UhpC, which suggests that UhpB and UhpC act jointly as a complex in the signaling process.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheng H. C., van Patten S. M., Smith A. J., Walsh D. A. An active twenty-amino-acid-residue peptide derived from the inhibitor protein of the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):655–661. doi: 10.1042/bj2310655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Wallace J. C., Brown J. P. Finding protein similarities with nucleotide sequence databases. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:111–132. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House C., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase C contains a pseudosubstrate prototope in its regulatory domain. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1726–1728. doi: 10.1126/science.3686012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Island M. D., Wei B. Y., Kadner R. J. Structure and function of the uhp genes for the sugar phosphate transport system in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2754–2762. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2754-2762.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang S. Q., Yu G. Q., Li Z. G., Hong J. S. Genetic evidence for modulation of the activator by two regulatory proteins involved in the exogenous induction of phosphoglycerate transport in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4304–4308. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4304-4308.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadner R. J., Shattuck-Eidens D. M. Genetic control of the hexose phosphate transport system of Escherichia coli: mapping of deletion and insertion mutations in the uhp region. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1052–1061. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1052-1061.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofoid E. C., Parkinson J. S. Transmitter and receiver modules in bacterial signaling proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):4981–4985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.4981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A. D., Kadner R. J. Topology of the Escherichia coli uhpT sugar-phosphate transporter analyzed by using TnphoA fusions. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1688–1693. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1688-1693.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel T. J., Nelson D. M., Brauer C. L., Kadner R. J. Promoter elements required for positive control of transcription of the Escherichia coli uhpT gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2763–2770. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2763-2770.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohno T., Noji S., Taniguchi S., Saito T. The narX and narL genes encoding the nitrate-sensing regulators of Escherichia coli are homologous to a family of prokaryotic two-component regulatory genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):2947–2957. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Kofoid E. C. Communication modules in bacterial signaling proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:71–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N. N., Wang E., Yashphe J., Torriani A. Nucleotide pool in pho regulon mutants and alkaline phosphatase synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):205–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.205-211.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando J. J., Maurer M. C., Bolen E. J., Grisham C. M. Role of cofactors in protein kinase C activation. Cell Signal. 1992 Nov;4(6):595–609. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(92)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattuck-Eidens D. M., Kadner R. J. Exogenous induction of the Escherichia coli hexose phosphate transport system defined by uhp-lac operon fusions. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):203–209. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.203-209.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa H., Makino K., Nakata A. Regulation of the pho regulon in Escherichia coli K-12. Genetic and physiological regulation of the positive regulatory gene phoB. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 15;168(3):477–488. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Lukat G. S., Stock A. M. Bacterial chemotaxis and the molecular logic of intracellular signal transduction networks. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:109–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Buechler J. A., Yonemoto W. cAMP-dependent protein kinase: framework for a diverse family of regulatory enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:971–1005. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston L. A., Kadner R. J. Identification of uhp polypeptides and evidence for their role in exogenous induction of the sugar phosphate transport system of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3546–3555. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3546-3555.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston L. A., Kadner R. J. Role of uhp genes in expression of the Escherichia coli sugar-phosphate transport system. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3375–3383. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3375-3383.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Compartmentation in the induction of the hexose-6-phosphate transport system of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):470–475. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.470-475.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. L., Goldrick D., Hong J. S. Identification of the products and nucleotide sequences of two regulatory genes involved in the exogenous induction of phosphoglycerate transport in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4299–4303. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4299-4303.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. Q., Hong J. S. Identification and nucleotide sequence of the activator gene of the externally induced phosphoglycerate transport system of Salmonella typhimurium. Gene. 1986;45(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]