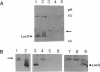
Abstract
Insertions, replacement mutations, and deletions were introduced via single or double crossover recombination into the lacE (enzyme IIlac) and lacG (phospho-beta-galactosidase) genes of the Lactococcus lactis chromosomal lacABCDFEGX operon. LacG production was abolished in strains missing the lacG gene or carrying multicopy insertions in the lacE gene that affected expression of the lacG gene. However, these LacG-deficient strains could still ferment lactose slowly and were found to contain an enzymatic activity that hydrolyzed the chromogenic substrate o-nitrophenyl-beta-D-galactopyranoside phosphate. Induction of this phospho-beta-glycohydrolase activity coincided with the appearance of a new 55-kDa protein cross-reacting with anti-LacG antibodies that had a size similar to that of LacG but a higher isoelectric point (pI 5.2) and was not found in wild-type cells during growth on lactose. Since the phospho-beta-glycohydrolase activity and this protein with a pI of 5.2 were highly induced in both mutant and wild-type cells during growth on cellobiose that is likely to be transported via a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system, we propose that this induced activity is a phospho-beta-glucosidase that also hydrolyzes lactose-6-phosphate.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Plasmids, loss of lactose metabolism, and appearance of partial and full lactose-fermenting revertants in Streptococcus cremoris B1. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):367–377. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.367-377.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J., Daly C., Fitzgerald G. F. Chromosomal integration of plasmid DNA by homologous recombination in Enterococcus faecalis and Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis hosts harboring Tn919. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2677–2682. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2677-2682.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopin M. C., Chopin A., Rouault A., Galleron N. Insertion and amplification of foreign genes in the Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis chromosome. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jul;55(7):1769–1774. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.7.1769-1774.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connors M. J., Howard S., Hoch J., Setlow P. Determination of the chromosomal locations of four Bacillus subtilis genes which code for a family of small, acid-soluble spore proteins. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):412–416. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.412-416.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cords B. R., McKay L. L. Characterization of lactose-fermenting revertants from lactose-negative Streptococcus lactis C2 mutants. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):830–839. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.830-839.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos W. M., Gasson M. J. Structure and expression of the Lactococcus lactis gene for phospho-beta-galactosidase (lacG) in Escherichia coli and L. lactis. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jul;135(7):1833–1846. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-7-1833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos W. M., Simons G. Molecular cloning of lactose genes in dairy lactic streptococci: the phospho-beta-galactosidase and beta-galactosidase genes and their expression products. Biochimie. 1988 Apr;70(4):461–473. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feirtag J. M., Petzel J. P., Pasalodos E., Baldwin K. A., McKay L. L. Thermosensitive plasmid replication, temperature-sensitive host growth, and chromosomal plasmid integration conferred by Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris lactose plasmids in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.539-548.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J. Plasmid complements of Streptococcus lactis NCDO 712 and other lactic streptococci after protoplast-induced curing. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutterson N. I., Koshland D. E., Jr Replacement and amplification of bacterial genes with sequences altered in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4894–4898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Banner C. D., Ollington J. F., Losick R., Hoch J. A., O'Connor M. B., Sonenshein A. L. Mapping a cloned gene under sporulation control by inserttion of a drug resistance marker into the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):90–98. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.90-98.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holo H., Nes I. F. High-Frequency Transformation, by Electroporation, of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris Grown with Glycine in Osmotically Stabilized Media. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3119–3123. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3119-3123.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inamine J. M., Lee L. N., LeBlanc D. J. Molecular and genetic characterization of lactose-metabolic genes of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):855–862. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.855-862.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Crow V. L., Lee L. N., Garon C. F. Influence of the lactose plasmid on the metabolism of galactose by Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):878–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.878-884.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenhouts K. J., Gietema J., Kok J., Venema G. Chromosomal stabilization of the proteinase genes in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2568–2575. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2568-2575.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenhouts K. J., Kok J., Venema G. Campbell-like integration of heterologous plasmid DNA into the chromosome of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):394–400. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.394-400.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenhouts K. J., Kok J., Venema G. Replacement recombination in Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4794–4798. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4794-4798.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A. Stabilization of Lactose Metabolism in Streptococcus lactis C2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):360–367. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.360-367.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel B., Niaudet B., Ehrlich S. D. Intermolecular recombination during transformation of Bacillus subtilis competent cells by monomeric and dimeric plasmids. Plasmid. 1983 Jul;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méjean V., Claverys J. P., Vasseghi H., Sicard A. M. Rapid cloning of specific DNA fragments of Streptococcus pneumoniae by vector integration into the chromosome followed by endonucleolytic excision. Gene. 1981 Nov;15(2-3):289–293. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niaudet B., Goze A., Ehrlich S. D. Insertional mutagenesis in Bacillus subtilis: mechanism and use in gene cloning. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niaudet B., Jannière L., Ehrlich S. D. Integration of linear, heterologous DNA molecules into the Bacillus subtilis chromosome: mechanism and use in induction of predictable rearrangements. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):111–120. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.111-120.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Hall B. G. Characterization and nucleotide sequence of the cryptic cel operon of Escherichia coli K12. Genetics. 1990 Mar;124(3):455–471. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.3.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petzel J. P., McKay L. L. Molecular characterization of the integration of the lactose plasmid from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris SK11 into the chromosome of L. lactis subsp. lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):125–131. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.125-131.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polzin K. M., McKay L. L. Development of a lactococcal integration vector by using IS981 and a temperature-sensitive lactococcal replication region. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):476–484. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.476-484.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Mock M., Schwartz M. A technique for integrating any DNA fragment into the chromosome of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Reizer A., Saier M. H., Jr The cellobiose permease of Escherichia coli consists of three proteins and is homologous to the lactose permease of Staphylococcus aureus. Res Microbiol. 1990 Nov-Dec;141(9):1061–1067. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90079-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero D. A., Klaenhammer T. R. IS946-mediated integration of heterologous DNA into the genome of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):699–702. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.699-702.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnetz K., Toloczyki C., Rak B. Beta-glucoside (bgl) operon of Escherichia coli K-12: nucleotide sequence, genetic organization, and possible evolutionary relationship to regulatory components of two Bacillus subtilis genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2579–2590. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2579-2590.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos W. M., Boerrigter I., van Rooyen R. J., Reiche B., Hengstenberg W. Characterization of the lactose-specific enzymes of the phosphotransferase system in Lactococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22554–22560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos W. M., Vos P., de Haard H., Boerrigter I. Cloning and expression of the Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris SK11 gene encoding an extracellular serine proteinase. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Hassouni M., Henrissat B., Chippaux M., Barras F. Nucleotide sequences of the arb genes, which control beta-glucoside utilization in Erwinia chrysanthemi: comparison with the Escherichia coli bgl operon and evidence for a new beta-glycohydrolase family including enzymes from eubacteria, archeabacteria, and humans. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):765–777. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.765-777.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alen-Boerrigter I. J., Baankreis R., de Vos W. M. Characterization and overexpression of the Lactococcus lactis pepN gene and localization of its product, aminopeptidase N. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2555–2561. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2555-2561.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rooijen R. J., Gasson M. J., de Vos W. M. Characterization of the Lactococcus lactis lactose operon promoter: contribution of flanking sequences and LacR repressor to promoter activity. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2273–2280. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2273-2280.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rooijen R. J., de Vos W. M. Molecular cloning, transcriptional analysis, and nucleotide sequence of lacR, a gene encoding the repressor of the lactose phosphotransferase system of Lactococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18499–18503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rooijen R. J., van Schalkwijk S., de Vos W. M. Molecular cloning, characterization, and nucleotide sequence of the tagatose 6-phosphate pathway gene cluster of the lactose operon of Lactococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7176–7181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]