Abstract
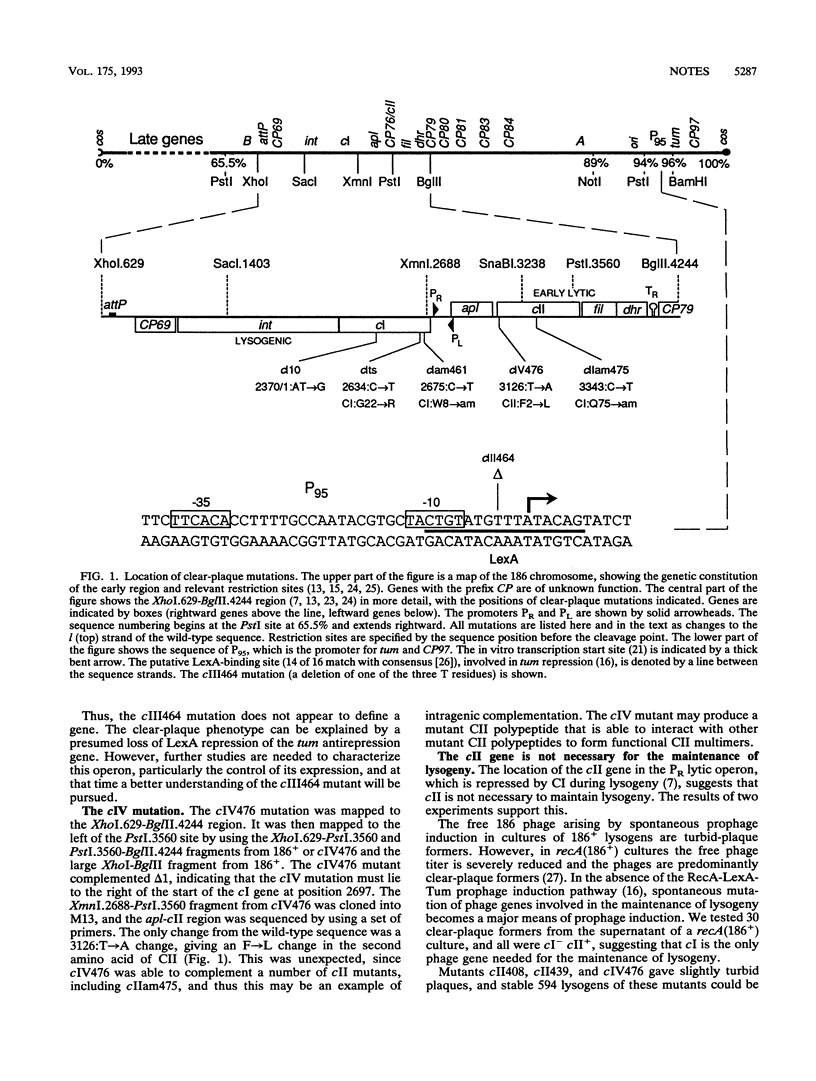
To identify the genes in coliphage 186 that are required for lysogeny, we isolated clear-plaque mutants. Complementation studies and DNA sequencing identified two genes, the cI gene for the immunity maintenance repressor and the cII gene, which is required only for the establishment of lysogeny. One mutant carried a change in the LexA-binding site controlling expression of the antirepression protein Tum.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin R. L., Barrand P., Fritsch A., Goldthwait D. A., Jacob F. Cohesive sites on the deoxyribonucleic acids from several temperate coliphages. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;17(2):343–357. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley C., Ling O. P., Egan J. B. Isolation of phage P2-186 intervarietal hybrids and 186 insertion mutants. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Sep 29;140(2):123–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00329780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. The steric effect in lysogenization by bacteriophage lambda. I. Lysogenization of a partially diploid strain of Escherichia coli K-12. Virology. 1965 Nov;27(3):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90112-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Improved detection of helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motifs in protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5019–5026. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Kalionis B., Egan J. B. Control of gene expression in the temperate coliphage 186. VIII. Control of lysis and lysogeny by a transcriptional switch involving face-to-face promoters. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90144-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garen A., Garen S., Wilhelm R. C. Suppressor genes for nonsense mutations. I. The Su-1, Su-2 and Su-3 genes of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):167–178. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. E., Yarmolinsky M. B. Integration-negative mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):487–505. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90423-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking S. M., Egan J. B. Genetic studies of coliphage 186. I. Genes associated with phage morphogenesis. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):1056–1067. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.1056-1067.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., WOLLMAN E. L. Sur les processus de conjugaison et de recombinaison chez Escherichia coli. I. L'induction par conjugaison ou induction zygotique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Oct;91(4):486–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalionis B., Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Control of gene expression in the P2-related template coliphages. III. DNA sequence of the major control region of phage 186. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 20;191(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90257-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Lecocq J. P. New versatile cloning and sequencing vectors based on bacteriophage M13. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE M. Mutations in the temperate phage P22 and lysogeny in Salmonella. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):22–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont I., Brumby A. M., Egan J. B. UV induction of coliphage 186: prophage induction as an SOS function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5492–5496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont I., Kalionis B., Egan J. B. Control of gene expression in the P2-related temperate coliphages. V. The use of sequence analysis of 186 Vir mutants to indicate presumptive repressor binding sites. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):379–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Tomizawa J. Absortive lysogenization of bacteriophage lambda b2 and residual immunity of non-lysogenic segregants. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jan 28;23(2):225–245. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard M., Egan J. B. Control of gene expression in P2-related coliphages: the in vitro transcription pattern of coliphage 186. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3599–3604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04123.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H., Egan J. B. DNA replication studies with coliphage 186. II. Depression of host replication by a 186 gene. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90523-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H., Puspurs A., Egan J. B. Control of gene expression in the P2-related temperate coliphage 186. VI. Sequence analysis of the early lytic region. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90539-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivaprasad A. V., Jarvinen R., Puspurs A., Egan J. B. DNA replication studies with coliphage 186. III. A single phage gene is required for phage 186 replication. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 5;213(3):449–463. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80207-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertman K. F., Mount D. W. Nucleotide sequence binding specificity of the LexA repressor of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.376-384.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods W. H., Egan J. B. Prophage induction of noninducible coliphage 186. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1349–1356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1349-1356.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



