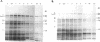Abstract
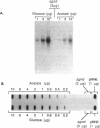
In Escherichia coli K-12 strain W3110, the amount of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase relative to that of total protein, i.e., the specific enzyme activity, increases about threefold during growth in minimal media over the range of growth rates with acetate and glucose as sole carbon sources. Previous work with gnd-lac operon and protein fusion strains indicated that two steps in the expression of the gnd gene are subject to growth rate-dependent control, with at least one step being posttranscriptional. With both Northern (RNA) and slot blot analyses, we found that the amount of gnd mRNA relative to that of total RNA was 2.5-fold higher in cells growing in glucose minimal medium than in cells grown on acetate. Therefore, since the total mRNA fraction of total RNA is essentially independent of the growth rate, the amount of gnd mRNA relative to that of total mRNA increases about 2.5-fold with increasing growth rate. This indicates that most of the growth rate-dependent increase in 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase can be accounted for by the growth rate-dependent increase in gnd mRNA level. We measured the decay of gnd mRNA mass in the two growth conditions after blocking transcription initiation with rifampin and found that the stability of gnd mRNA does not change with growth rate. We also used a gnd-lacZ protein fusion to measure the functional mRNA half-life and found that it too is growth rate independent. Thus, the growth rate-dependent increase in the level of gnd mRNA is due to an increase in gnd transcription, and this increase is sufficient to account for the growth rate regulation of the 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase level. The dilemma posed by interpretations of the properties of gnd-lac fusion strains and by direct measurement of gnd mRNA level is discussed.
Full text
PDF

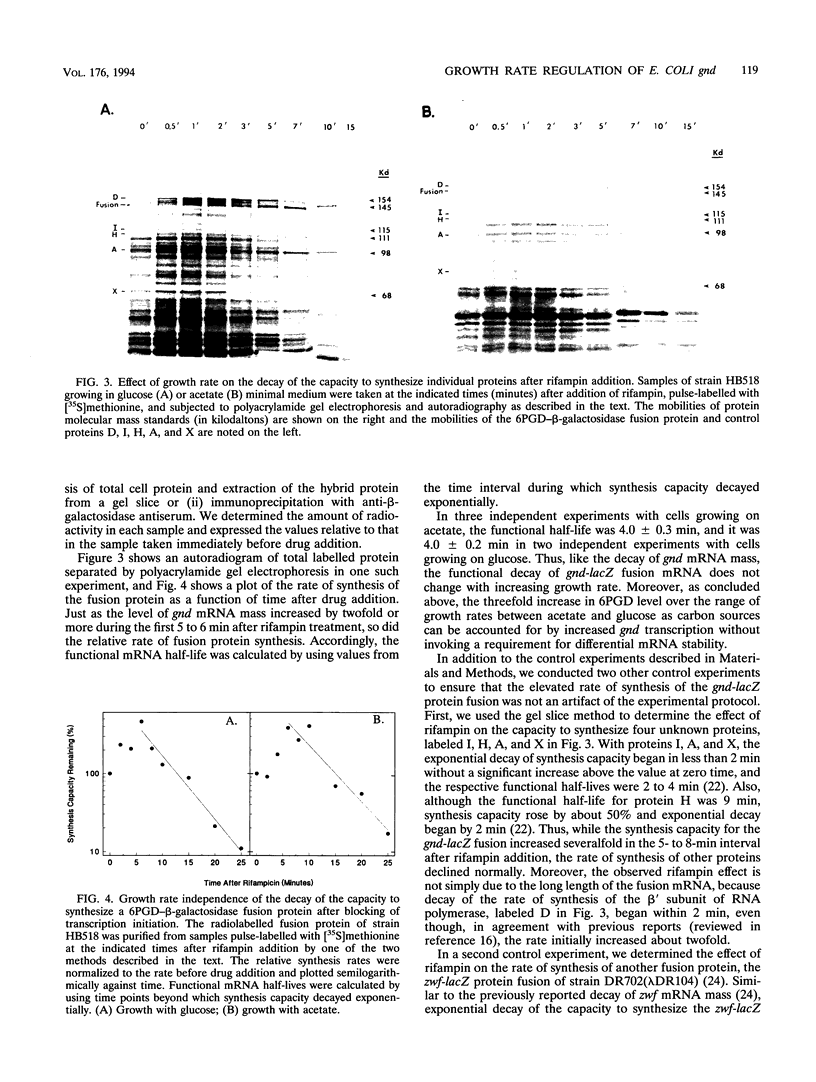
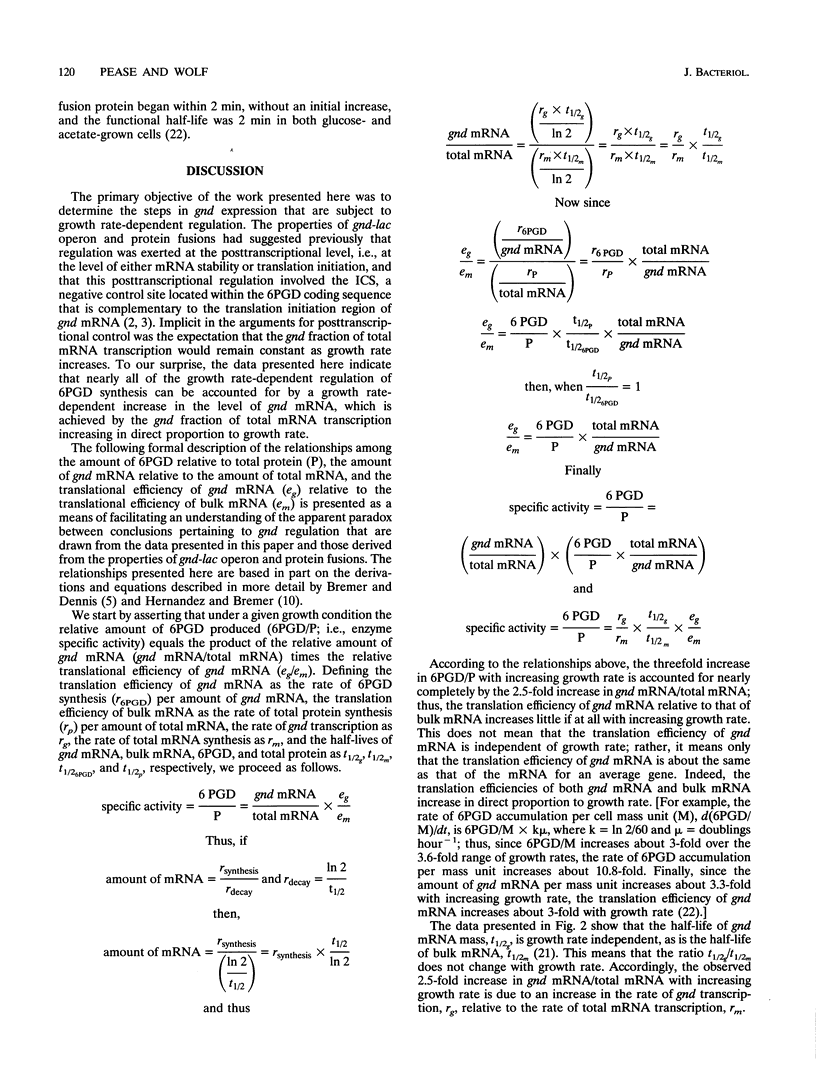


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker H. V., 2nd, Wolf R. E., Jr Essential site for growth rate-dependent regulation within the Escherichia coli gnd structural gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7669–7673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H. V., 2nd, Wolf R. E., Jr Growth rate-dependent regulation of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase level in Escherichia coli K-12: beta-galactosidase expression in gnd-lac operon fusion strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):771–781. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.771-781.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcak G. J., Wolf R. E., Jr Growth-rate-dependent expression and cloning of gnd alleles from natural isolates of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):365–371. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.365-371.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter-Muenchau P., Wolf R. E., Jr Growth-rate-dependent regulation of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase level mediated by an anti-Shine-Dalgarno sequence located within the Escherichia coli gnd structural gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1138–1142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. R., Nomura M. Changes in the half-life of ribosomal protein messenger RNA caused by translational repression. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90162-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. R., Nomura M. Translational regulation is responsible for growth-rate-dependent and stringent control of the synthesis of ribosomal proteins L11 and L1 in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4129–4133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. W., Vaughn V., Walter W. A., Neidhardt F. C., Gross C. A. Regulation of the promoters and transcripts of rpoH, the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory gene. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):419–432. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez V. J., Bremer H. Guanosine tetraphosphate (ppGpp) dependence of the growth rate control of rrnB P1 promoter activity in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11605–11614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. R., Barcak G. J., Wolf R. E., Jr Altered growth-rate-dependent regulation of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase level in hisT mutants of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1197–1205. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1197-1205.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg U., Nilsson G., von Gabain A. The differential stability of the Escherichia coli ompA and bla mRNA at various growth rates is not correlated to the efficiency of translation. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. A., Hayward R. S. Direct evidence for rifampicin-promoted readthrough of the partial terminator tL7 in the rpoBC operon of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):358–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00325706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasoff M. S., Baker H. V., 2nd, Wolf R. E., Jr DNA sequence of the Escherichia coli gene, gnd, for 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. Gene. 1984 Mar;27(3):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasoff M. S., Wolf R. E., Jr Molecular cloning, correlation of genetic and restriction maps, and determination of the direction of transcription of gnd of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):731–741. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.731-741.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Belasco J. G., Cohen S. N., von Gabain A. Growth-rate dependent regulation of mRNA stability in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):75–77. doi: 10.1038/312075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S., Reeh S. Functional mRNA half lives in E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 9;166(3):329–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00267626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. L., Pease A. J., Wolf R. E., Jr Genetic and physical analyses of the growth rate-dependent regulation of Escherichia coli zwf expression. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4660–4667. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4660-4667.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. L., Wolf R. E., Jr Molecular characterization of the Escherichia coli K-12 zwf gene encoding glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):968–977. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.968-977.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAECHTER M., MAALOE O., KJELDGAARD N. O. Dependency on medium and temperature of cell size and chemical composition during balanced grown of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Dec;19(3):592–606. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-3-592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf R. E., Jr, Prather D. M., Shea F. M. Growth-rate-dependent alteration of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase levels in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):1093–1096. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.1093-1096.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Belasco J. G., Schottel J. L., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Decay of mRNA in Escherichia coli: investigation of the fate of specific segments of transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]