Abstract
The ribosome translocation step that occurs during protein synthesis is a highly conserved, essential activity of all cells. The precise movement of one codon that occurs following peptide bond formation is regulated by elongation factor G (EF-G) in eubacteria or elongation factor 2 (EF-2) in eukaryotes. To begin to understand molecular interactions that regulate this process, a genetic selection was developed with the aim of obtaining conditional-lethal alleles of the gene (fusA) that encodes EF-G in Escherichia coli. The genetic selection depends on the observation that resistant strains arose spontaneously in the presence of sublethal concentrations of the antibiotic kanamycin. Replica plating was performed to obtain mutant isolates from this collection that were restrictive for growth at 42 degrees C. Two tightly temperature-sensitive strains were characterized in detail and shown to harbor single-site missense mutations within fusA. The fusA100 mutant encoded a glycine-to-aspartic acid change at codon 502. The fusA101 allele encoded a glutamine-to-proline alteration at position 495. Induction kinetics of beta-galactosidase activity suggested that both mutations resulted in slower elongation rates in vivo. These missense mutations were very near a small group of conserved amino acid residues (positions 483 to 493) that occur in EF-G and EF-2 but not EF-Tu. It is concluded that these sequences encode a specific domain that is essential for efficient translocase function.
Full text
PDF

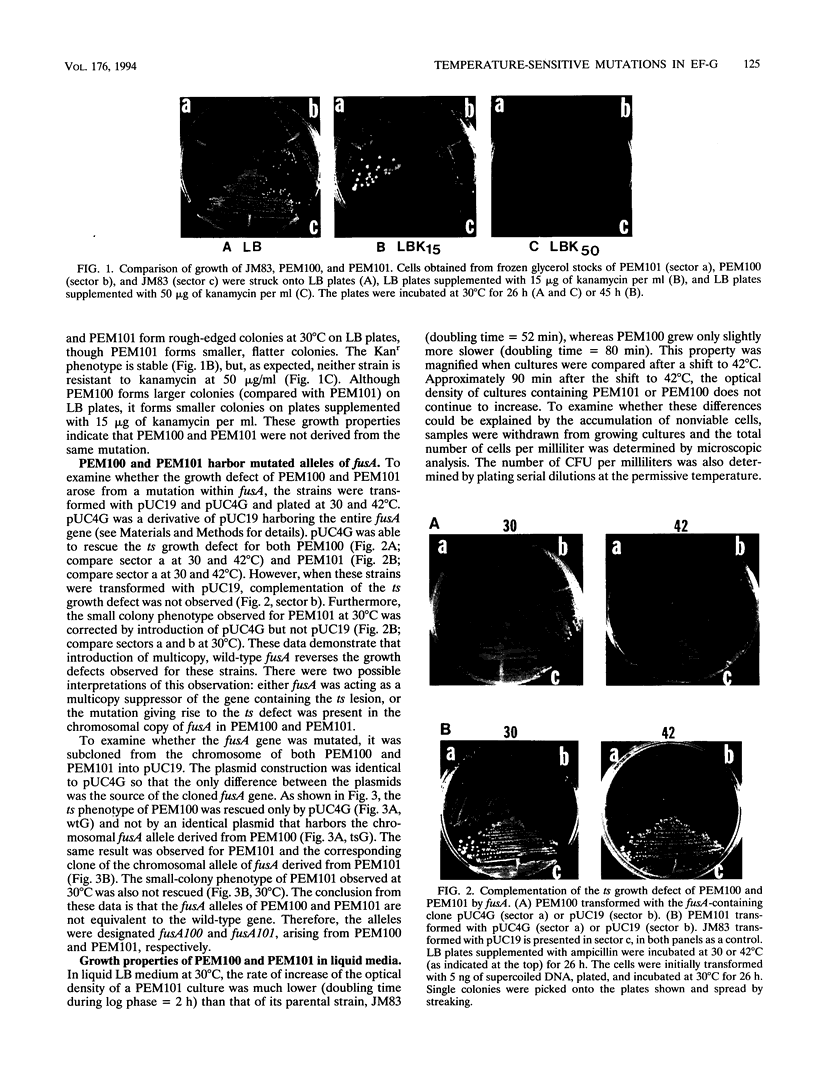
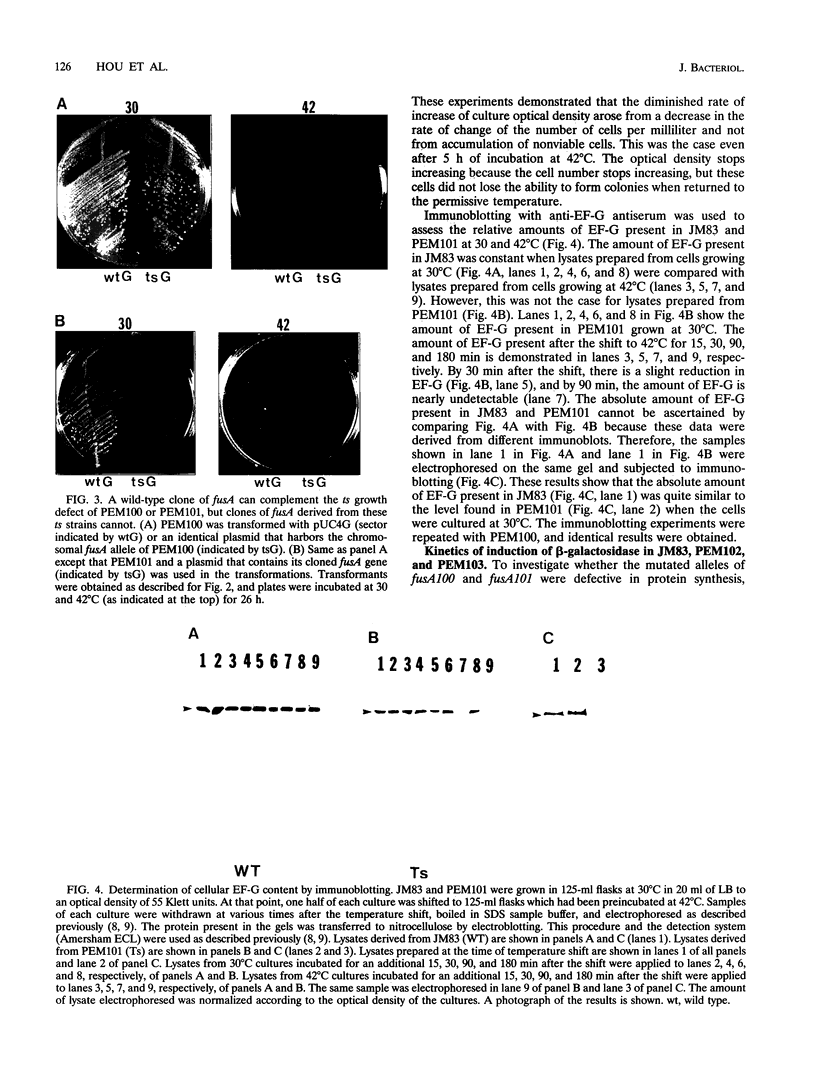



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. 4.5S RNA: does form predict function? New Biol. 1991 May;3(5):430–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. Mutations in the gene for EF-G reduce the requirement for 4.5S RNA in the growth of E. coli. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):825–833. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90620-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabañas M. J., Vázquez D., Modolell J. Inhibition of ribosomal translocation by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 14;83(3):991–997. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammarano P., Palm P., Creti R., Ceccarelli E., Sanangelantoni A. M., Tiboni O. Early evolutionary relationships among known life forms inferred from elongation factor EF-2/EF-G sequences: phylogenetic coherence and structure of the archaeal domain. J Mol Evol. 1992 May;34(5):396–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00162996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollop N., March P. E. A GTP-binding protein (Era) has an essential role in growth rate and cell cycle control in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2265–2270. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2265-2270.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollop N., March P. E. Localization of the membrane binding sites of Era in Escherichia coli. Res Microbiol. 1991 Feb-Apr;142(2-3):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90045-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel E., Koka M., Nakamoto T. Requirement of an Escherichia coli 50 S ribosomal protein component for effective interaction of the ribosome with T and G factors and with guanosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):805–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskunas S. R., Lindahl L., Nomura M. Identification of two copies of the gene for the elongation factor EF-Tu in E. coli. Nature. 1975 Oct 9;257(5526):458–462. doi: 10.1038/257458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Kawano G., Tanaka N. Association of fusidic acid sensitivity with G factor in a protein-synthesizing system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 9;33(5):769–773. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kischa K., Möller W., Stöffler G. Reconstitution of a GTPase activity by a 50S ribosomal protein and E. coli. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 8;233(36):62–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio233062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno K., Uchida T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S., Nakanishi T., Fukui T., Ohtsuka E., Ikehara M., Okada Y. Amino acid sequence of mammalian elongation factor 2 deduced from the cDNA sequence: homology with GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):4978–4982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.4978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March P. E., Inouye M. Characterization of the lep operon of Escherichia coli. Identification of the promoter and the gene upstream of the signal peptidase I gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7206–7213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March P. E. Membrane-associated GTPases in bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(10):1253–1257. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi M., Nishimura T., Komai T., Tanaka N. Interaction of kanamycin and related antibiotics with the large subunit of ribosomes and the inhibition of translocation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 29;84(2):358–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):389–394. doi: 10.1038/327389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Robertson J. M., Noller H. F. Interaction of elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu with a conserved loop in 23S RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):362–364. doi: 10.1038/334362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter Dahlfors A. A., Kurland C. G. Novel mutants of elongation factor G. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 20;215(4):549–557. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R., Hess W., Finkelstein S., Ellis D. Induction kinetics of the L-arabinose operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):9–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.9-14.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sköld S. E. Chemical crosslinking of elongation factor G to the 23S RNA in 70S ribosomes from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4923–4932. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocchini-Valentini G. P., Felicetti L., Rinaldi G. M. Mutants of Escherichia coli blocked in protein synthesis: mutants with an altered G factor. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:463–468. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weijland A., Harmark K., Cool R. H., Anborgh P. H., Parmeggiani A. Elongation factor Tu: a molecular switch in protein biosynthesis. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(6):683–688. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zengel J. M., Archer R. H., Lindahl L. The nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli fus gene, coding for elongation factor G. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):2181–2192. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.2181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]