Abstract
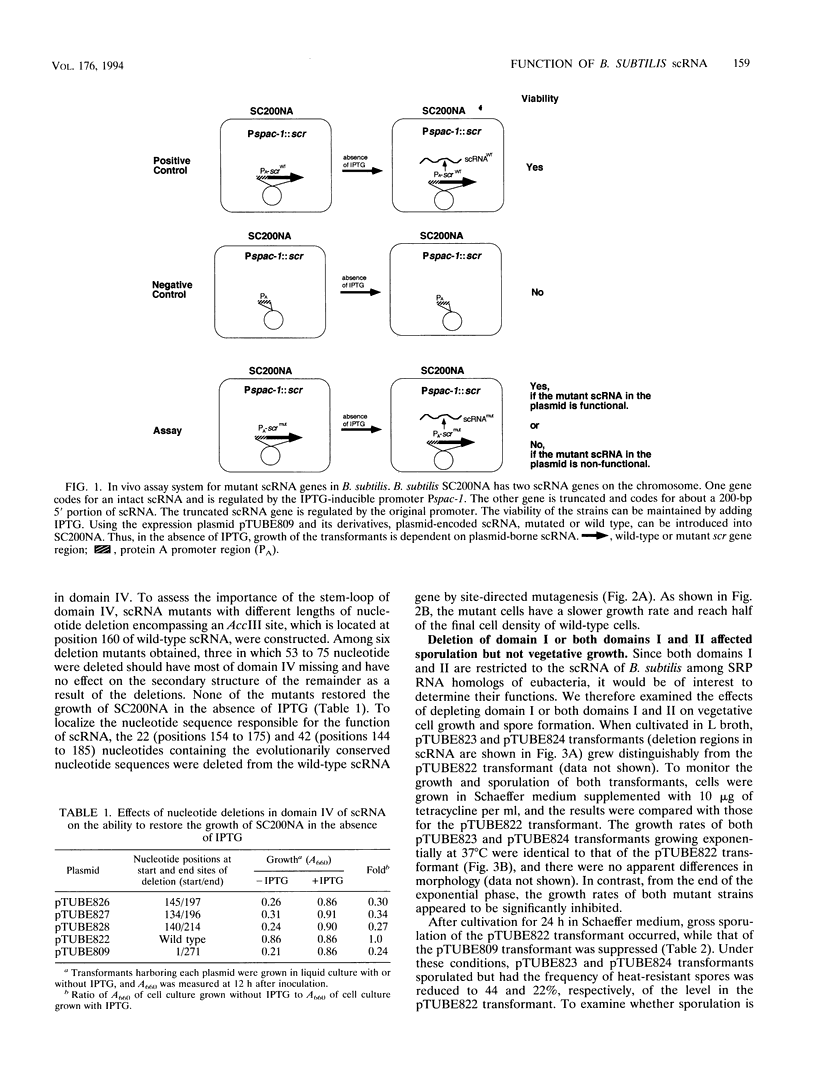
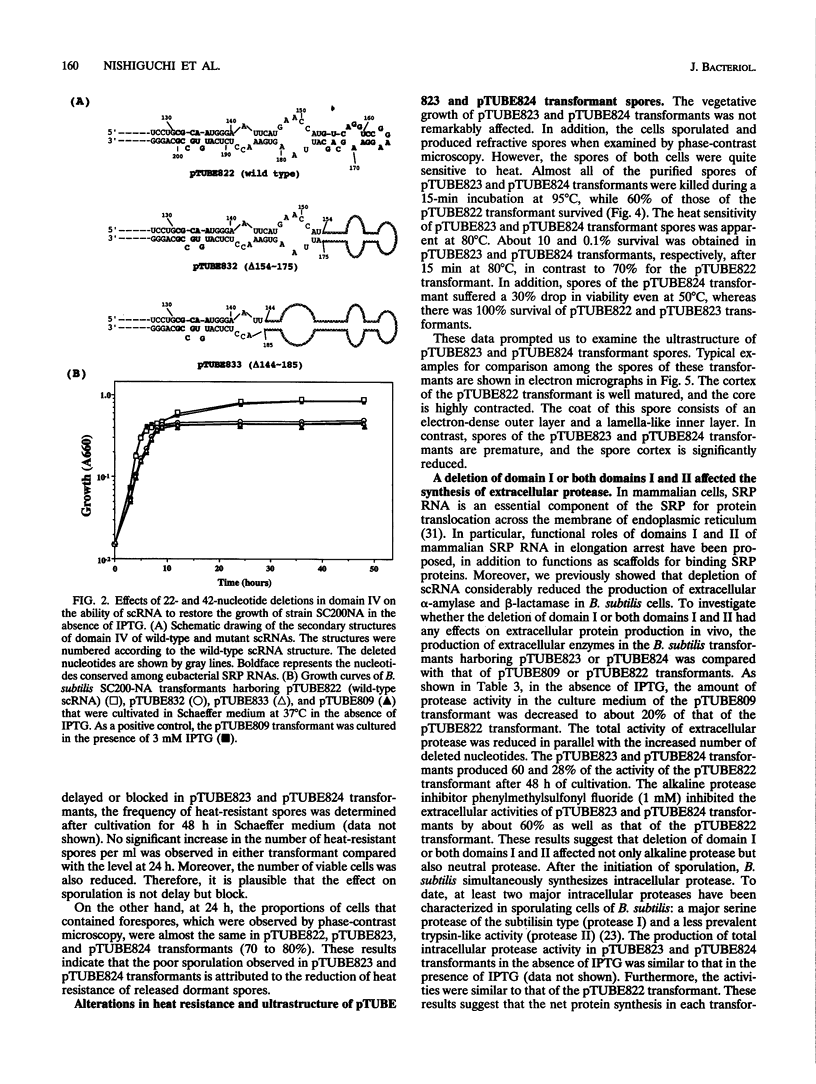
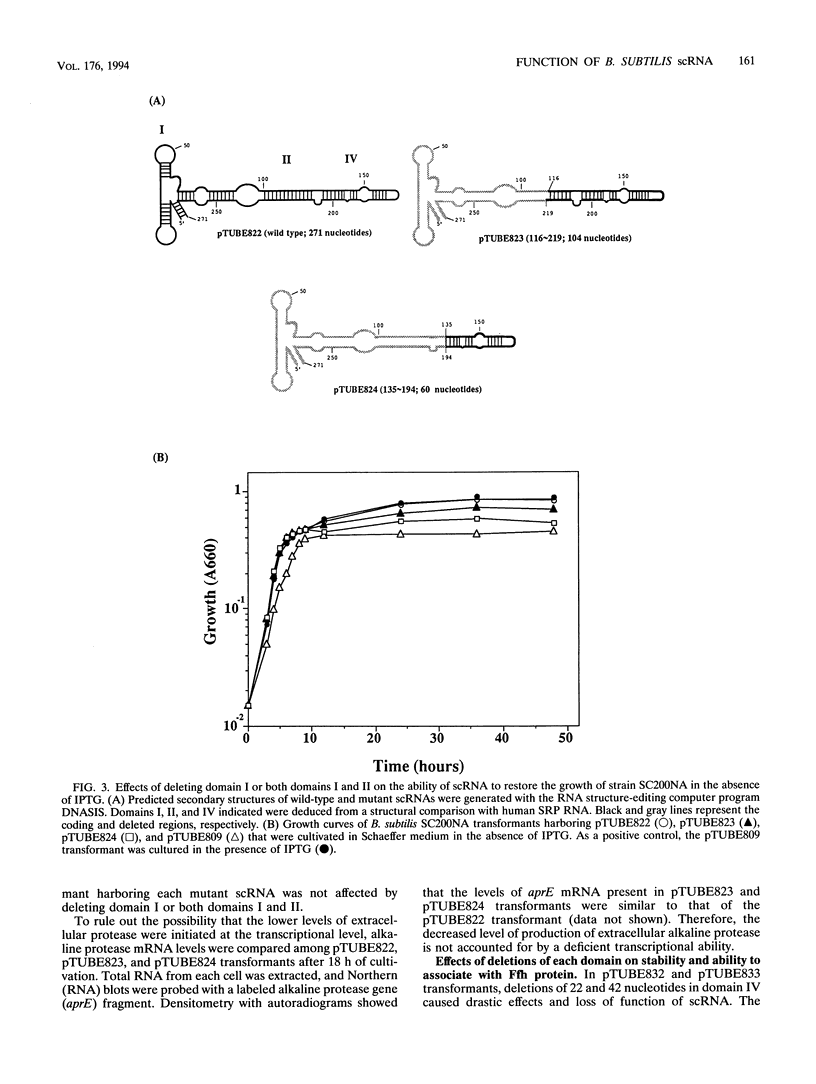
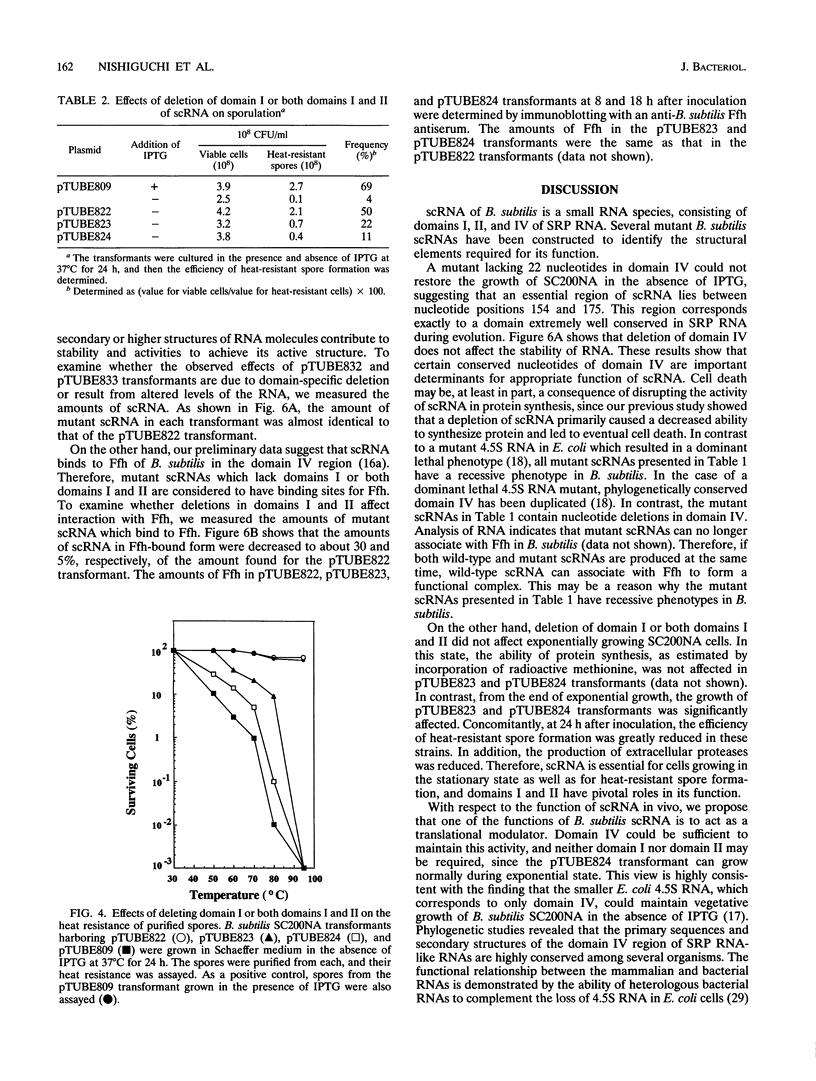
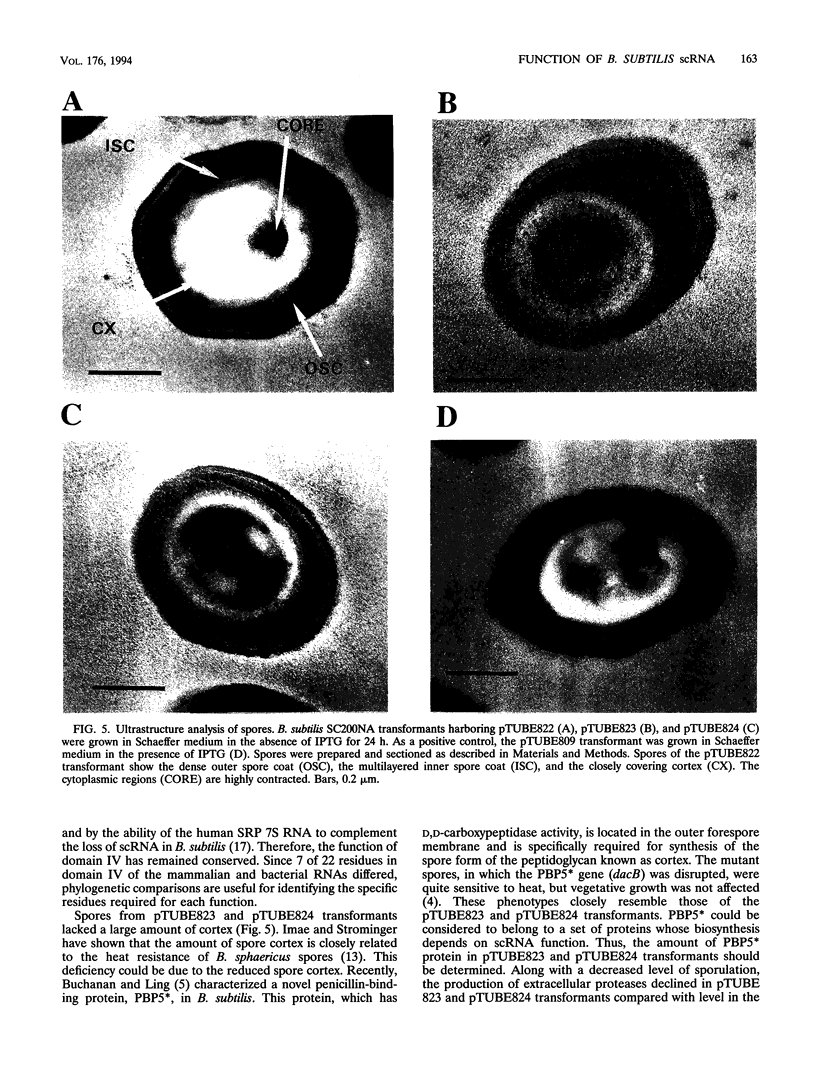
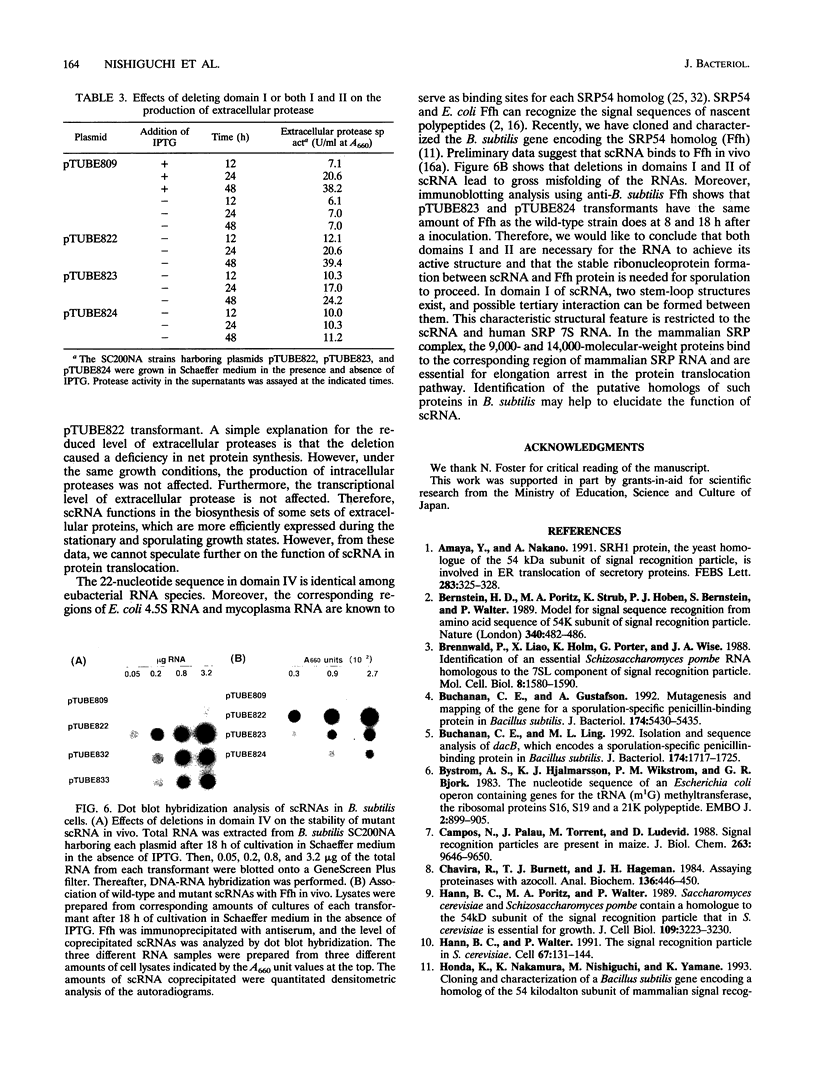
Bacillus subtilis small cytoplasmic RNA (scRNA; 271 nucleotides) is a member of the signal recognition particle (SRP) RNA family, which has evolutionarily conserved primary and secondary structures. The scRNA consists of three domains corresponding to domains I, II, and IV of human SRP 7S RNA. To identify the structural determinants required for its function, we constructed mutant scRNAs in which individual domains or conserved nucleotides were deleted, and their importance was assayed in vivo. The results demonstrated that domain IV of scRNA is necessary to maintain cell viability. On the other hand, domains I and II were not essential for vegetative growth but were preferentially required for the RNA to achieve its active structure, and assembled ribonucleoprotein between Ffh and scRNA is required for sporulation to proceed. This view is highly consistent with the fact that the presence of domains I and II is restricted to sporeforming B. subtilis scRNA among eubacterial SRP RNA-like RNAs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaya Y., Nakano A. SRH1 protein, the yeast homologue of the 54 kDa subunit of signal recognition particle, is involved in ER translocation of secretory proteins. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 3;283(2):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80619-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Poritz M. A., Strub K., Hoben P. J., Brenner S., Walter P. Model for signal sequence recognition from amino-acid sequence of 54K subunit of signal recognition particle. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):482–486. doi: 10.1038/340482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennwald P., Liao X., Holm K., Porter G., Wise J. A. Identification of an essential Schizosaccharomyces pombe RNA homologous to the 7SL component of signal recognition particle. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1580–1590. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan C. E., Gustafson A. Mutagenesis and mapping of the gene for a sporulation-specific penicillin-binding protein in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5430–5435. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5430-5435.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan C. E., Ling M. L. Isolation and sequence analysis of dacB, which encodes a sporulation-specific penicillin-binding protein in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1717–1725. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1717-1725.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byström A. S., Hjalmarsson K. J., Wikström P. M., Björk G. R. The nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli operon containing genes for the tRNA(m1G)methyltransferase, the ribosomal proteins S16 and L19 and a 21-K polypeptide. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):899–905. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos N., Palau J., Torrent M., Ludevid D. Signal recognition-like particles are present in maize. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9646–9650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavira R., Jr, Burnett T. J., Hageman J. H. Assaying proteinases with azocoll. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):446–450. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann B. C., Poritz M. A., Walter P. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe contain a homologue to the 54-kD subunit of the signal recognition particle that in S. cerevisiae is essential for growth. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3223–3230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann B. C., Walter P. The signal recognition particle in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90577-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. M., Zagorski J., Fournier M. J. Cloning and sequence analysis of the Escherichia coli 4.5 S RNA gene. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 25;178(3):509–531. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imae Y., Strominger J. L. Relationship between cortex content and properties of Bacillus sphaericus spores. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):907–913. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.907-913.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaine B. P. Structure of the archaebacterial 7S RNA molecule. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 May;221(3):315–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00259394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luirink J., High S., Wood H., Giner A., Tollervey D., Dobberstein B. Signal-sequence recognition by an Escherichia coli ribonucleoprotein complex. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):741–743. doi: 10.1038/359741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Imai Y., Nakamura A., Yamane K. Small cytoplasmic RNA of Bacillus subtilis: functional relationship with human signal recognition particle 7S RNA and Escherichia coli 4.5S RNA. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2185–2192. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2185-2192.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Bernstein H. D., Strub K., Zopf D., Wilhelm H., Walter P. An E. coli ribonucleoprotein containing 4.5S RNA resembles mammalian signal recognition particle. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1111–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.1701272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Siegel V., Hansen W., Walter P. Small ribonucleoproteins in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Yarrowia lipolytica homologous to signal recognition particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4315–4319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Strub K., Walter P. Human SRP RNA and E. coli 4.5S RNA contain a highly homologous structural domain. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):4–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribes V., Römisch K., Giner A., Dobberstein B., Tollervey D. E. coli 4.5S RNA is part of a ribonucleoprotein particle that has properties related to signal recognition particle. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):591–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90454-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppen M. E., Van Alstine G. L., Band L. Control of intracellular serine protease expression in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):136–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.136-140.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römisch K., Webb J., Herz J., Prehn S., Frank R., Vingron M., Dobberstein B. Homology of 54K protein of signal-recognition particle, docking protein and two E. coli proteins with putative GTP-binding domains. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):478–482. doi: 10.1038/340478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson T. A Mycoplasma protein homologous to mammalian SRP54 recognizes a highly conserved domain of SRP RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5763–5770. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson T., Guindy Y. Nucleotide sequence of a Mycoplasma mycoides RNA which is homologous to E. coli 4.5S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4938–4938. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck J. C., Hartmann R. K., Toschka H. Y., Erdmann V. A. Transcription and processing of Bacillus subtilis small cytoplasmic RNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Feb;215(3):478–482. doi: 10.1007/BF00427046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck J. C., Lempicki R. A., Toschka H. Y., Erdmann V. A., Fournier M. J. Escherichia coli 4.5S RNA gene function can be complemented by heterologous bacterial RNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1284–1288. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1284-1288.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck J. C., Vogel D. W., Ulbrich N., Erdmann V. A. The Bacillus subtilis scRNA is related to the 4.5S RNA from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2719–2719. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Weiner A. M. Human genes and pseudogenes for the 7SL RNA component of signal recognition particle. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3303–3310. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02294.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood H., Luirink J., Tollervey D. Evolutionary conserved nucleotides within the E.coli 4.5S RNA are required for association with P48 in vitro and for optimal function in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 25;20(22):5919–5925. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.22.5919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]