Abstract
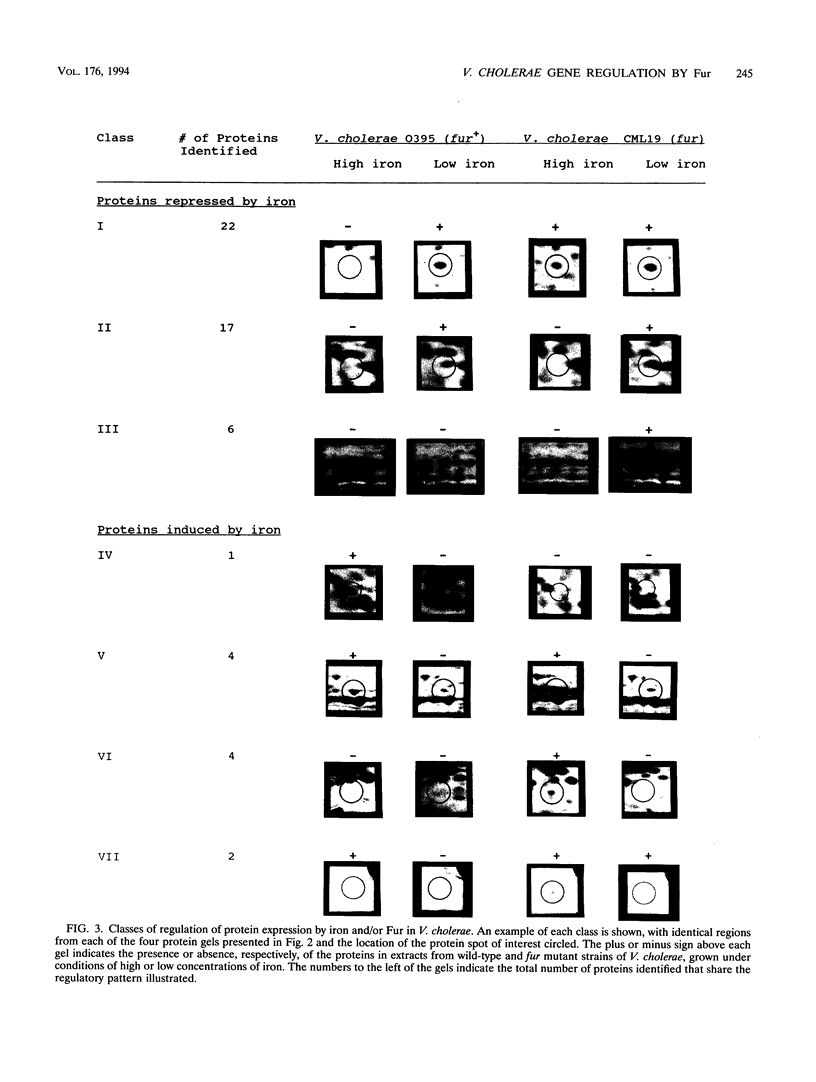
Iron concentration influences the expression of a number of genes involved in iron uptake and virulence in bacteria. In Escherichia coli, coordinate regulation of these genes by iron depends on the product of the fur gene, which acts as an iron-responsive, DNA-binding repressor protein. Several genes in Vibrio cholerae are also repressed by iron; and a fur gene, homologous to E. coli fur, has been previously cloned from this organism. The present study was undertaken to define the roles of Fur and iron in regulating gene expression in V. cholerae. V. cholerae strains with a mutation in fur by virtue of suicide plasmid integration into this gene showed derepressed expression of two previously characterized, iron-regulated genes, irgA and viuA, in high concentrations of iron; even in the fur mutants, however, residual two- to threefold regulation by iron persisted. The fur mutant strains constructed by suicide plasmid integration required antibiotic selection to maintain the mutation. To analyze further the effect of Fur and iron on gene regulation in V. cholerae without the need for antibiotic selection, we used in vivo marker exchange to construct a nonrevertible V. cholerae fur mutant. This V. cholerae fur mutant grew significantly less well in Luria-Bertani medium than the wild-type parent but grew slightly better than the wild type under iron-restricted conditions. The V. cholerae fur mutant was unable to utilize a number of carbon sources including glycerol, acetate, succinate, lactate, and fumarate, that supported growth of the wild-type strain on minimal media. We utilized two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of whole-cell protein extracts from the fur mutant and wild-type strains following growth in conditions of either low or high concentrations of iron to identify proteins regulated by iron and/or Fur. Twenty-two proteins were negatively regulated by iron in the wild-type strain but constitutively expressed in the fur mutant, consistent with the model of Fur as an iron-dependent repressor. However, many other proteins were regulated in a different manner by iron and/or Fur. Seventeen proteins were negatively regulated by iron but independent of Fur, suggesting the presence of an additional iron-dependent repressor(s). Six proteins were strongly iron regulated in the fur mutant but hardly expressed at all in the wild-type strain regardless of the iron concentration, suggesting an interaction between Fur and another iron regulatory mechanism. There were 11 proteins that were induced rather than repressed by iron, in four different regulatory classes. Gene regulation in V. cholerae by Fur and iron is much more complex than previously thought and is reminiscent of the Lrp regulon in E.coli.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagg A., Neilands J. B. Ferric uptake regulation protein acts as a repressor, employing iron (II) as a cofactor to bind the operator of an iron transport operon in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 25;26(17):5471–5477. doi: 10.1021/bi00391a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagg A., Neilands J. B. Molecular mechanism of regulation of siderophore-mediated iron assimilation. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):509–518. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.509-518.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomfield I. C., Vaughn V., Rest R. F., Eisenstein B. I. Allelic exchange in Escherichia coli using the Bacillus subtilis sacB gene and a temperature-sensitive pSC101 replicon. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1447–1457. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J. The significance of iron in infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1127–1138. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterton J. R., Stoebner J. A., Payne S. M., Calderwood S. B. Cloning, sequencing, and transcriptional regulation of viuA, the gene encoding the ferric vibriobactin receptor of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3729–3738. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3729-3738.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderwood S. B., Mekalanos J. J. Confirmation of the Fur operator site by insertion of a synthetic oligonucleotide into an operon fusion plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):1015–1017. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.1015-1017.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderwood S. B., Mekalanos J. J. Iron regulation of Shiga-like toxin expression in Escherichia coli is mediated by the fur locus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4759–4764. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4759-4764.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. Genetics and molecular biology of siderophore-mediated iron transport in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):517–530. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.517-530.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Grandis S., Ginsberg J., Toone M., Climie S., Friesen J., Brunton J. Nucleotide sequence and promoter mapping of the Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxin operon of bacteriophage H-19B. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4313–4319. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4313-4319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. Construction of an eae deletion mutant of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by using a positive-selection suicide vector. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4310–4317. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4310-4317.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsting B. R., Atkinson M. R., Ninfa A. J., Matthews R. G. Characterization of the regulon controlled by the leucine-responsive regulatory protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1109–1118. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1109-1118.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. W., Hall H. K. Effect of Salmonella typhimurium ferric uptake regulator (fur) mutations on iron- and pH-regulated protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4317–4323. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4317-4323.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. B., Boyko S. A., Calderwood S. B. Positive transcriptional regulation of an iron-regulated virulence gene in Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1125–1129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. B., Boyko S. A., Calderwood S. B. Transcriptional regulation by iron of a Vibrio cholerae virulence gene and homology of the gene to the Escherichia coli fur system. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6863–6870. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6863-6870.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. B., DiRita V. J., Calderwood S. B. Identification of an iron-regulated virulence determinant in Vibrio cholerae, using TnphoA mutagenesis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):55–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.55-60.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantke K. Regulation of ferric iron transport in Escherichia coli K12: isolation of a constitutive mutant. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):288–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00269672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantke K. Selection procedure for deregulated iron transport mutants (fur) in Escherichia coli K 12: fur not only affects iron metabolism. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Nov;210(1):135–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00337769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovde C. J., Calderwood S. B., Mekalanos J. J., Collier R. J. Evidence that glutamic acid 167 is an active-site residue of Shiga-like toxin I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2568–2572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin C. M., Boyko S. A., Calderwood S. B. Cloning, sequencing, and transcriptional regulation of the Vibrio cholerae fur gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1897–1903. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1897-1903.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin C. M., Calderwood S. B. Cloning and genetic analysis of the Vibrio vulnificus fur gene and construction of a fur mutant by in vivo marker exchange. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):706–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.706-715.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin C. M., Calderwood S. B. Role of iron in regulation of virulence genes. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1993 Apr;6(2):137–149. doi: 10.1128/cmr.6.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Swartz D. J., Pearson G. D., Harford N., Groyne F., de Wilde M. Cholera toxin genes: nucleotide sequence, deletion analysis and vaccine development. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):551–557. doi: 10.1038/306551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Inouye H., Oliver D., Beckwith J. Mutations that alter the signal sequence of alkaline phosphatase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):366–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.366-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. W., Cox C. D., Vasil M. L. Coordinate regulation of siderophore and exotoxin A production: molecular cloning and sequencing of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa fur gene. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2589–2598. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2589-2598.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. W., Storey D. G., Vasil A. I., Vasil M. L. Regulation of toxA and regA by the Escherichia coli fur gene and identification of a Fur homologue in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103 and PA01. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2823–2831. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U. Construction and properties of a new cloning vehicle, allowing direct screening for recombinant plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;178(2):475–477. doi: 10.1007/BF00270503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäffer S., Hantke K., Braun V. Nucleotide sequence of the iron regulatory gene fur. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):110–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00383321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel S. P., Payne S. M. Effect of iron limitation on growth, siderophore production, and expression of outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):148–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.148-155.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staggs T. M., Perry R. D. Fur regulation in Yersinia species. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(17):2507–2516. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staggs T. M., Perry R. D. Identification and cloning of a fur regulatory gene in Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):417–425. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.417-425.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staskawicz B., Dahlbeck D., Keen N., Napoli C. Molecular characterization of cloned avirulence genes from race 0 and race 1 of Pseudomonas syringae pv. glycinea. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5789–5794. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5789-5794.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoebner J. A., Butterton J. R., Calderwood S. B., Payne S. M. Identification of the vibriobactin receptor of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3270–3274. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3270-3274.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoebner J. A., Payne S. M. Iron-regulated hemolysin production and utilization of heme and hemoglobin by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2891–2895. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2891-2895.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Wee S., Herrero M., Neilands J. B. Operator sequences of the aerobactin operon of plasmid ColV-K30 binding the ferric uptake regulation (fur) repressor. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2624–2630. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2624-2630.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]