Abstract
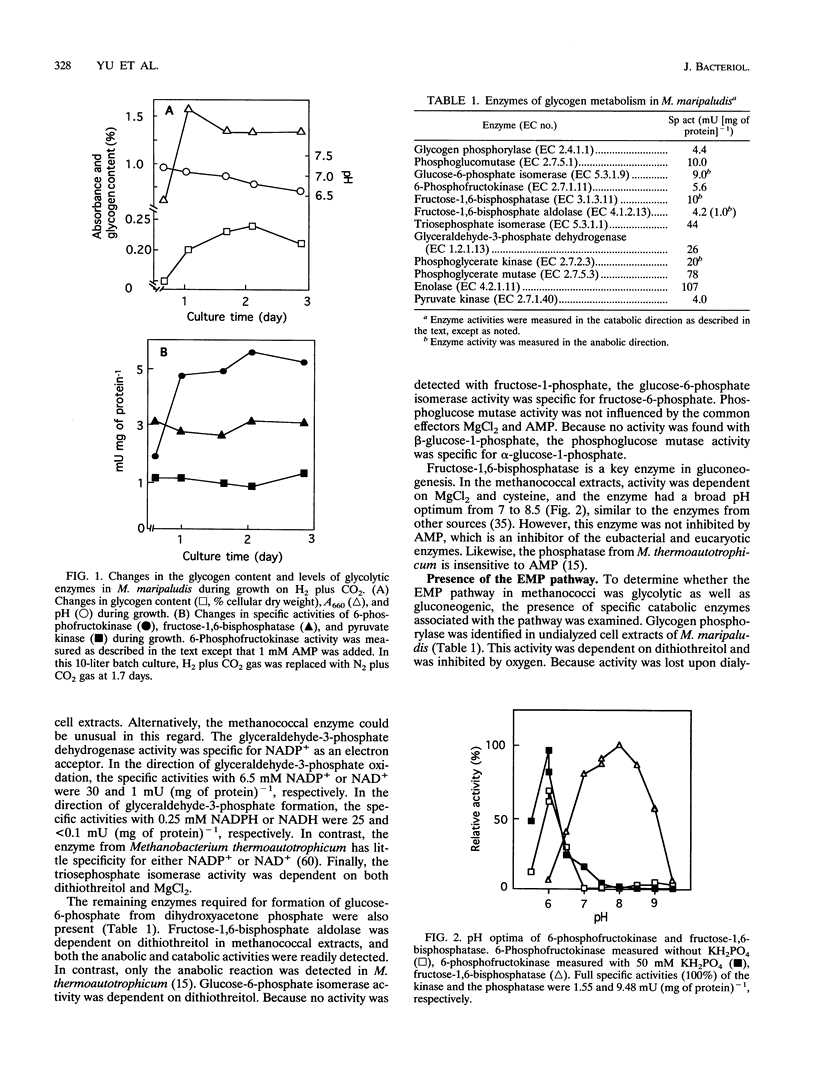
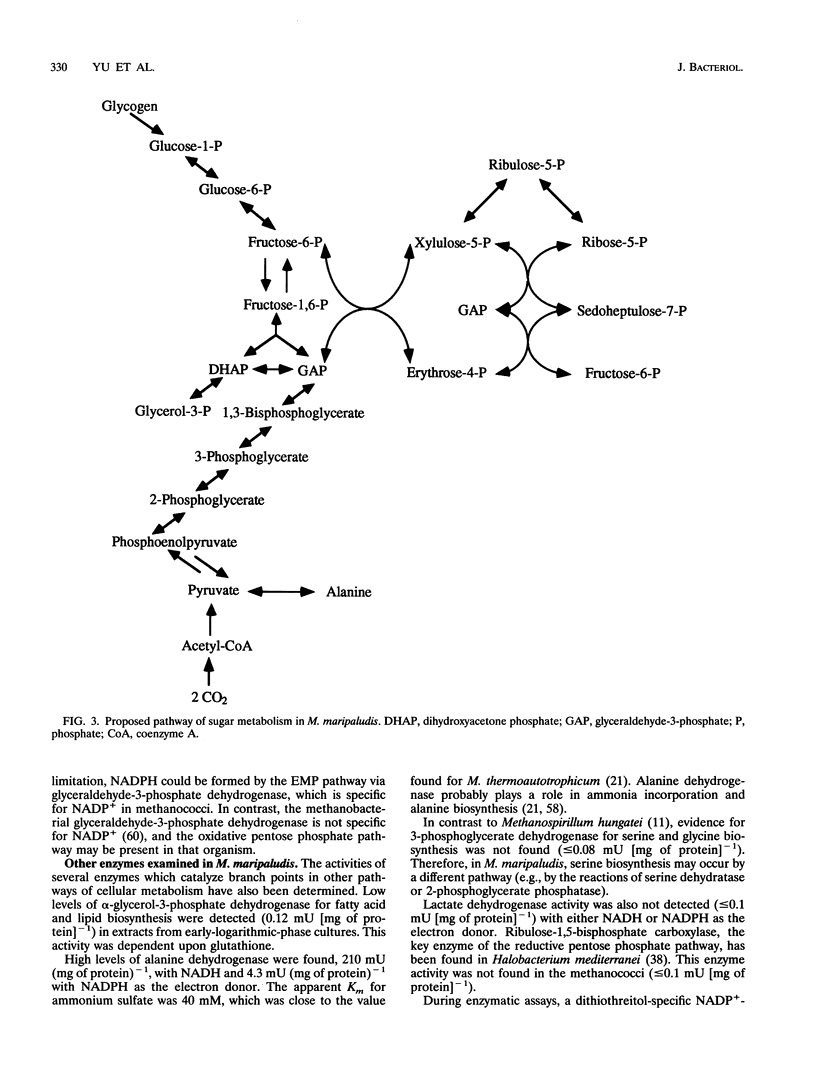
Methanococcus maripaludis, a facultatively autotrophic archaebacterium that grows with H2 or formate as the electron donor, does not assimilate sugars and other complex organic substrates. However, glycogen is biosynthesized intracellularly and commonly reaches values of 0.34% of the cellular dry weight in the early stationary phase. To determine the pathway of glycogen catabolism, specific enzymes of sugar metabolism were assayed in cell extracts. The following enzymes were found (specific activity in milliunits per milligram of protein): glycogen phosphorylase, 4.4; phosphoglucomutase, 10; glucose-6-phosphate isomerase, 9; 6-phosphofructokinase, 5.6, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, 10; fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase, 4.2; triosephosphate isomerase, 44; glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, 26; phosphoglycerate kinase, 20; phosphoglycerate mutase, 78; enolase, 107; and pyruvate kinase, 4.0. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was NADP+ dependent, and the pyruvate kinase required MnCl2. The 6-phosphofructokinase had an unusually low pH optimum of 6.0. Four nonoxidative pentose-biosynthetic enzymes were found (specific activity in milliunits per milligram of protein): transketolase, 12; transaldolase, 24; ribulose-5-phosphate-3-epimerase, 55; and ribulose-5-phosphate isomerase, 100. However, the key enzymes of the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway, the reductive pentose phosphate pathway, and the classical and modified Entner-Duodoroff pathways were not detected. Thus, glycogen appears to be catabolized by the Embden-Meyerhoff-Parnas pathway. This result is in striking contrast to the nonmethanogenic archaebacteria that have been examined, among which the Entner-Doudoroff pathway is common. A dithiothreitol-specific NADP(+)-reducing activity was also found (8.5 mU/mg of protein). Other thiol compounds, such as cysteine hydrochloride, reduced glutathione, and 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid, did not replace dithiothreitol for this activity. The physiological significance of this activity is not known.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CZOK R., BUECHER T. Crystallized enzymes from the myogen of rabbit skeletal muscle. Adv Protein Chem. 1960;15:315–415. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60311-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. S., Segel I. H. Purification and properties of glycogen phosphorylase from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 20;127(1):175–186. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessio G., Josse J. Glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase, phosphoglycerate kinase, and phosphoglyceromutase of Escherichia coli. Simultaneous purification and physical properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4319–4325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J. Central metabolism of the archaebacteria: an overview. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):58–64. doi: 10.1139/m89-009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrichs D., Meyer M., Schmidt B., Andreesen J. R. Purification of NADPH-dependent electron-transferring flavoproteins and N-terminal protein sequence data of dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenases from anaerobic, glycine-utilizing bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2088–2095. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2088-2095.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenreich W., Bacher A. Biosynthesis of 5-hydroxybenzimidazolylcobamid (factor III) in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23840–23849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekiel I., Smith I. C., Sprott G. D. Biosynthetic pathways in Methanospirillum hungatei as determined by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):316–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.316-326.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esnouf M. P., Harris R. P., McVittie J. D. Triosephosphate isomerase from chicken and rabbit muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1982;89(Pt 500):579–583. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)89100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando J., Enser M., Pontremoli S., Horecker B. L. Purification and properties of rabbit muscle fructose 1,6-diphosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Aug;126(2):599–606. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G., Pontremoli S., Horecker B. L. The specific fructose diphosphatase of Escherichia coli: properties and partial purification. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Apr;114(1):4–12. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90298-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSHI J. G., HANDLER P. PHOSPHOGLUCOMUTASE. I. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF PHOSPHOGLUCOMUTASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2741–2751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. J., Nagle D. P., Jr, Whitman W. B. Methanogens and the diversity of archaebacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):135–177. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.135-177.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemerer V. R., Griffin C. C., Brand L. Phosphofructokinase from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:91–98. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp R. G. Phosphofructokinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:71–77. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenealy W. R., Thompson T. E., Schubert K. R., Zeikus J. G. Ammonia assimilation and synthesis of alanine, aspartate, and glutamate in Methanosarcina barkeri and Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1357–1365. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1357-1365.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandelwal R. L., Spearman T. N., Hamilton I. R. Purification and properties of glycogen phosphorylase from Streptococcus salivarius. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jan;154(1):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochetov G. A. Transketolase from yeast, rat liver, and pig liver. Methods Enzymol. 1982;90(Pt E):209–223. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Yuan J. H., Goldberg E. Lactate dehydrogenase isozymes from mouse. Methods Enzymol. 1982;89(Pt 500):351–358. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)89063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry O. H., Passonneau J. V. Phosphoglucomutase kinetics with the phosphates of fructose, glucose, mannose, ribose, and galactose. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):910–916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOLTMANN E. A. ISOLATION OF CRYSTALLINE PHOSPHOGLUCOSE ISOMERASE FROM RABBIT MUSCLE. J Biol Chem. 1964 May;239:1545–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive C., Levy H. R. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Methods Enzymol. 1975;41:196–201. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)41046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODWELL V. W., TOWNE J. C., GRISOLIA S. The kinetic properties of yeast and muscle phosphoglyceric acid mutase. J Biol Chem. 1957 Oct;228(2):875–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawal N., Kelkar S. M., Altekar W. Alternative routes of carbohydrate metabolism in halophilic archaebacteria. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1988 Dec;25(6):674–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum I. Y., Sallach H. J. D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase from wheat germ-1. Methods Enzymol. 1975;41:285–289. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)41065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. 3-phosphoglycerate kinase of skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:127–134. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42105-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh J. S., Whitman W. B. Pathway of acetate assimilation in autotrophic and heterotrophic methanococci. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5327–5329. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5327-5329.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring T. G., Wold F. Enolase from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:323–329. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIETZ A., OCHOA S. Fluorokinase and pyruvic kinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Dec;78(2):477–493. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90372-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsolas O., Joris L. Transaldolase. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:290–297. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B., Sanwal B. D. The control of pyruvate kinases of Escherichia coli. I. Physicochemical and regulatory properties of the enzyme activated by fructose 1,6-diphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):265–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. B. Glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase of chicken breast muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1975;41:245–249. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)41056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing R. Y., Whitman W. B. Characterization of amino acid aminotransferases of Methanococcus aeolicus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):541–548. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.541-548.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing R. Y., Whitman W. B. Sulfometuron methyl-sensitive and -resistant acetolactate synthases of the archaebacteria Methanococcus spp. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4486–4492. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4486-4492.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Fuchs G., Kenealy W., Thauer R. K. Oxidoreductases involved in cell carbon synthesis of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):604–613. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.604-613.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


