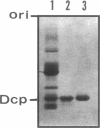
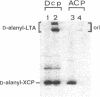
Abstract
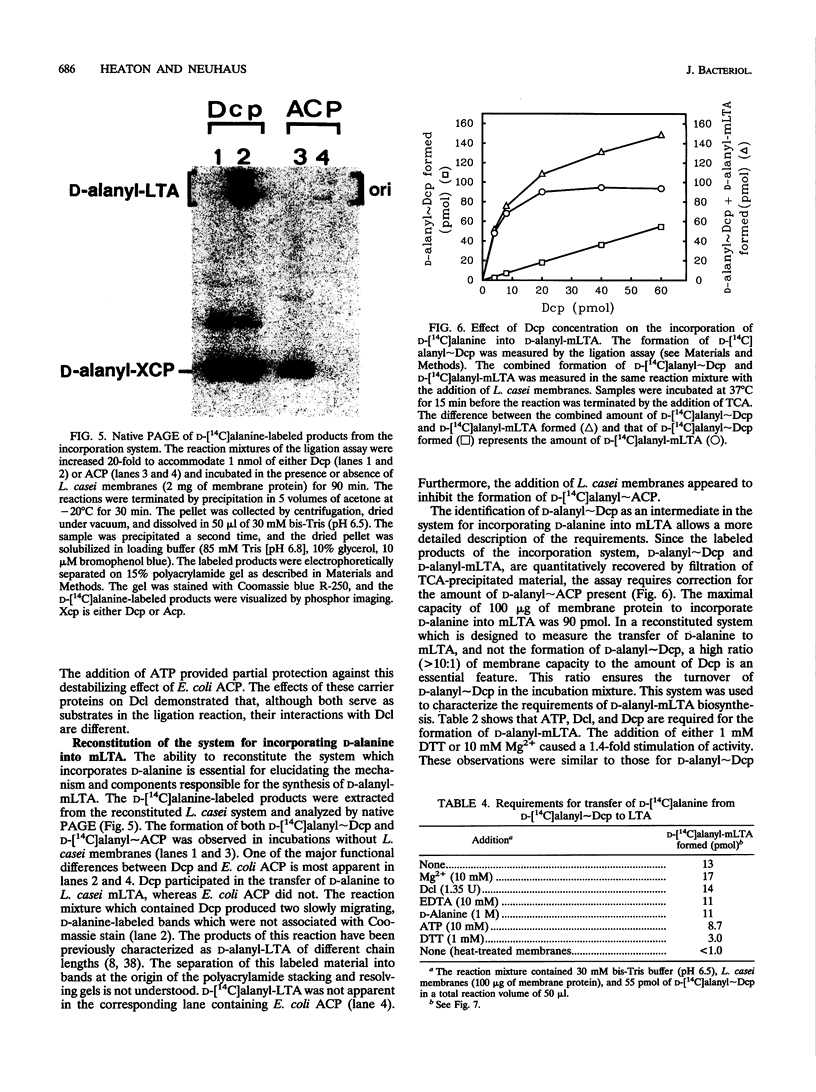
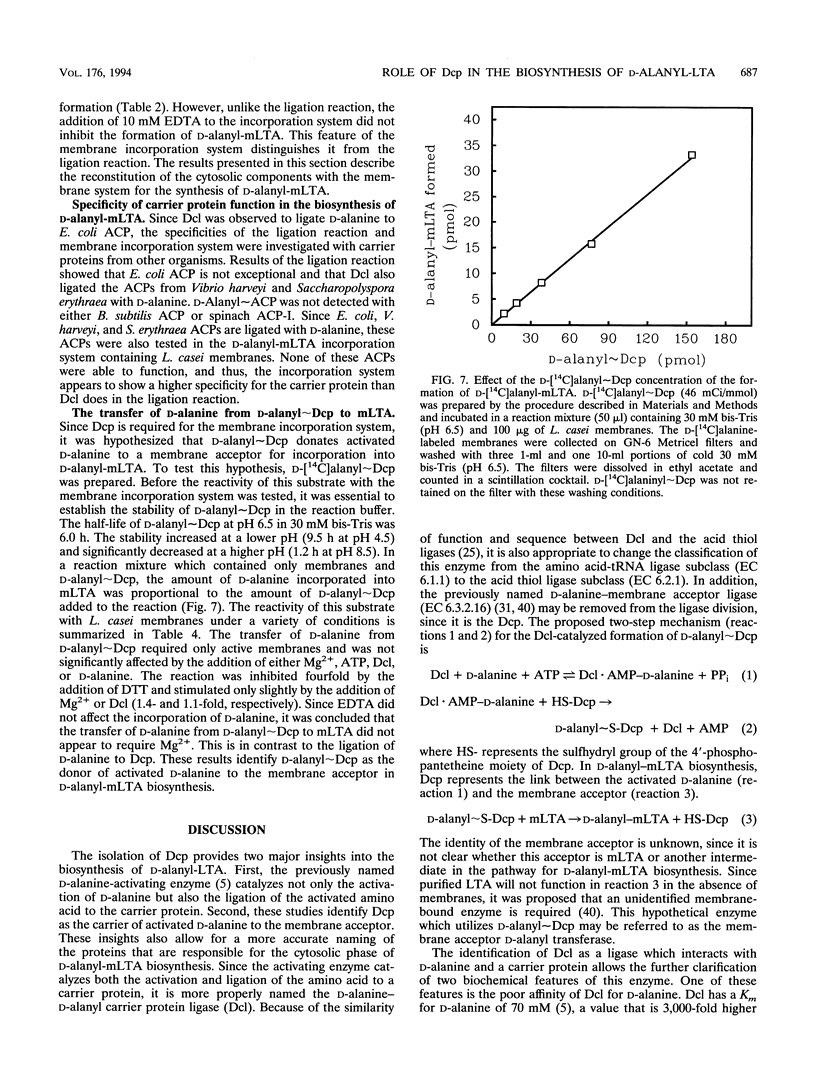
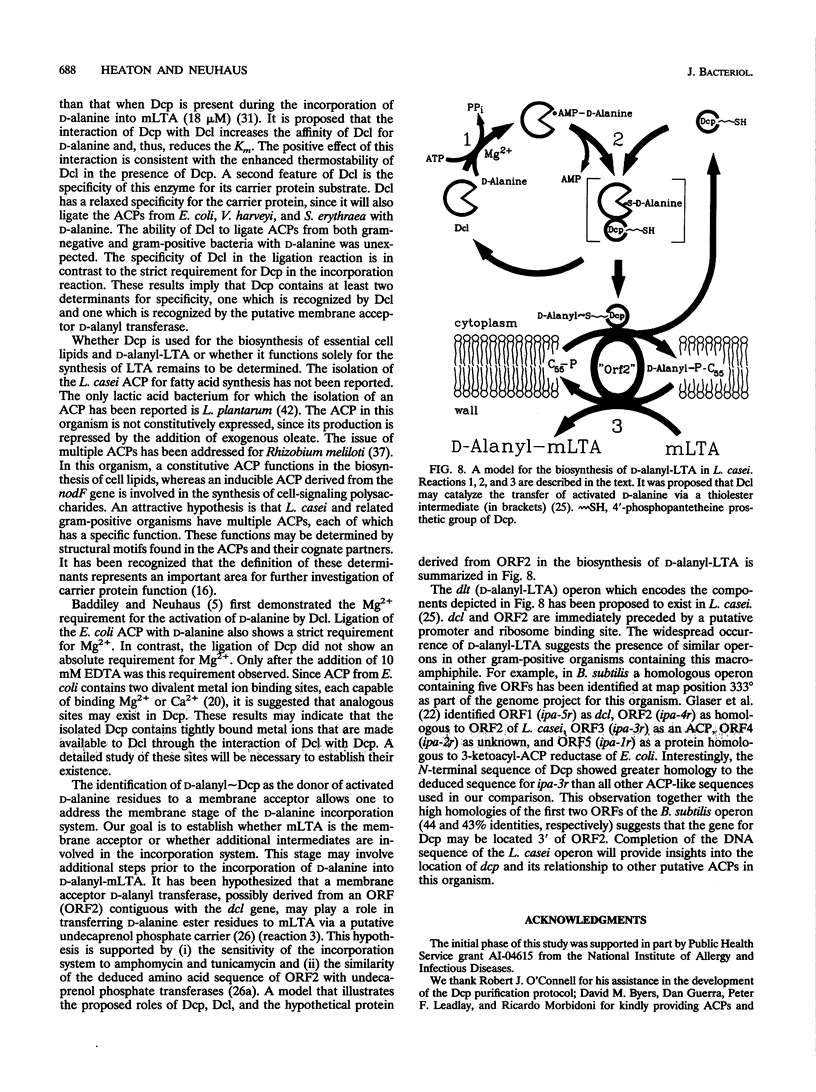
D-Alanyl-lipoteichoic acid (D-alanyl-LTA) is a widespread macroamphiphile which plays a vital role in the growth and development of gram-positive organisms. The biosynthesis of this polymer requires the enzymic activation of D-alanine for its transfer to the membrane-associated LTA (mLTA). A small, heat-stable, and acidic protein that is required for this transfer was purified to greater than 98% homogeneity from Lactobacillus casei ATCC 7469. This protein, previously named the D-alanine-membrane acceptor ligase (V. M. Reusch, Jr., and F. C. Neuhaus, J. Biol. Chem. 246:6136-6143, 1971), functions as the D-alanyl carrier protein (Dcp). The amino acid composition, beta-alanine content, and N-terminal sequence of this protein are similar to those of the acyl carrier proteins (ACPs) of fatty acid biosynthesis. The isolation of Dcp and its derivative, D-alanyl approximately Dcp, has allowed the characterization of two novel reactions in the pathway for D-alanyl-mLTA biosynthesis: (i) the ligation of Dcp with D-alanine and (ii) the transfer of D-alanine from D-alanyl approximately Dcp to a membrane acceptor. It has not been established whether the membrane acceptor is mLTA or another intermediate in the pathway for D-alanyl-mLTA biosynthesis. Since the D-alanine-activating enzyme (EC 6.1.1.13) catalyzes the ligation reaction, this enzyme functions as the D-alanine-Dcp ligase (Dcl). Dcl also ligated the ACPs from Escherichia coli, Vibrio harveyi, and Saccharopolyspora erythraea with D-alanine. In contrast to the relaxed specificity of Dcl in the ligation reaction, the transfer of D-alanine to the membrane acceptor was highly specific for Dcp and did not occur with other ACPs. This transfer was observed by using only D-[14C]alanyl approximately Dcp and purified L. casei membranes. Thus, D-alanyl approximately Dcp is an essential intermediate in the transfer of D-alanine from Dcl to the membrane acceptor. The formation of D-alanine esters of mLTA provides a mechanism for modulating the net anionic charge in the cell wall.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald A. R., Baddiley J., Heptinstall S. The alanine ester content and magnesium binding capacity of walls of Staphylococcus aureus H grown at different pH values. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 16;291(3):629–634. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BADDILEY J., DAVISON A. L. The occurrence and location of teichoic acids in lactobacilli. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Feb;24:295–299. doi: 10.1099/00221287-24-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BADDILEY J., NEUHAUS F. C. The enzymic activation of D-alanine. Biochem J. 1960 Jun;75:579–587. doi: 10.1042/bj0750579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddiley J. Bacterial cell walls and membranes. Discovery of the teichoic acids. Bioessays. 1989 Jun;10(6):207–210. doi: 10.1002/bies.950100607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddiley J. Teichoic acids in cell walls and membranes of bacteria. Essays Biochem. 1972;8:35–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigan V. M., Childs W. C., 3rd, Neuhaus F. C. Biosynthesis of D-alanyl-lipoteichoic acid in Lactobacillus casei: D-alanyl-lipophilic compounds as intermediates. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):239–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.239-250.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs W. C., 3rd, Neuhaus F. C. Biosynthesis of D-alanyl-lipoteichoic acid: characterization of ester-linked D-alanine in the in vitro-synthesized product. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):293–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.293-301.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs W. C., 3rd, Taron D. J., Neuhaus F. C. Biosynthesis of D-alanyl-lipoteichoic acid by Lactobacillus casei: interchain transacylation of D-alanyl ester residues. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1191–1195. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1191-1195.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coley J., Duckworth M., Baddiley J. The occurrence of lipoteichoic acids in the membranes of gram-positive bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Dec;73(3):587–591. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-3-587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. L., Boyce S. G., Lueking D. R. Purification and characterization of Rhodobacter sphaeroides acyl carrier protein. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2740–2746. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debellé F., Sharma S. B. Nucleotide sequence of Rhizobium meliloti RCR2011 genes involved in host specificity of nodulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 25;14(18):7453–7472. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.18.7453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E. E., Kessler R. E., Clewell D. B. Identification of pheromone-induced surface proteins in Streptococcus faecalis and evidence of a role for lipoteichoic acid in formation of mating aggregates. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):6–12. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.6-12.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst-Fonberg M. L., Tucker M. M., Fonberg I. B. The amphiphilicity of ACP helices: a means of macromolecular interaction? FEBS Lett. 1987 May 11;215(2):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W. Physiology of lipoteichoic acids in bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1988;29:233–302. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60349-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Rösel P., Koch H. U. Effect of alanine ester substitution and other structural features of lipoteichoic acids on their inhibitory activity against autolysins of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):467–475. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.467-475.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederick A. F., Kay L. E., Prestegard J. H. Location of divalent ion sites in acyl carrier protein using relaxation perturbed 2D NMR. FEBS Lett. 1988 Sep 26;238(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80222-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J., Swindell S., Maeda S., Dodd H. M. Molecular rearrangement of lactose plasmid DNA associated with high-frequency transfer and cell aggregation in Lactococcus lactis 712. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(21):3213–3223. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser P., Kunst F., Arnaud M., Coudart M. P., Gonzales W., Hullo M. F., Ionescu M., Lubochinsky B., Marcelino L., Moszer I. Bacillus subtilis genome project: cloning and sequencing of the 97 kb region from 325 degrees to 333 degrees. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Oct;10(2):371–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale R. S., Jordan K. N., Leadlay P. F. A small, discrete acyl carrier protein is involved in de novo fatty acid biosynthesis in Streptomyces erythraeus. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaton M. P., Neuhaus F. C. Biosynthesis of D-alanyl-lipoteichoic acid: cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the Lactobacillus casei gene for the D-alanine-activating enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4707–4717. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4707-4717.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heptinstall S., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. Teichoic acids and membrane function in bacteria. Nature. 1970 Feb 7;225(5232):519–521. doi: 10.1038/225519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. H., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. The function of teichoic acids in cation control in bacterial membranes. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;132(1):83–93. doi: 10.1042/bj1320083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELEMEN M. V., BADDILEY J. Structure of the intracellular glycerol teichoic acid from Lactobacillus casei A.T.C.C. 7469. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:246–254. doi: 10.1042/bj0800246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. A., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. Influence of alanyl ester residues on the binding of magnesium ions to teichoic acids. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):671–676. doi: 10.1042/bj1510671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer R., Neuhaus F. C. Biosynthesis of membrane teichoic acid. A role of the D-alanine-activating enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3196–3201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauël C., Young M., Margot P., Karamata D. The essential nature of teichoic acids in Bacillus subtilis as revealed by insertional mutagenesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Feb;215(3):388–394. doi: 10.1007/BF00427034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M., Fischer W. Trihexosyldiacylglycerol and acyltrihexosyldiacylglycerol as lipid anchors of the lipoteichoic acid of Lactobacillus casei DSM 20021. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Jan;359(1):1–11. doi: 10.1515/bchm.1978.359.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus F. C., Linzer R., Reusch V. M., Jr Biosynthesis of membrane teichoic acid: role of the D-alanine-activating enzyme and D-alanine: membrane acceptor ligase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):502–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ntamere A. S., Taron D. J., Neuhaus F. C. Assembly of D-alanyl-lipoteichoic acid in Lactobacillus casei: mutants deficient in the D-alanyl ester content of this amphiphile. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1702–1711. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1702-1711.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou L. T., Marquis R. E. Electromechanical interactions in cell walls of gram-positive cocci. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):92–101. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.92-101.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt M. W., Miller K. J., Lane W. S., Kennedy E. P. Isolation and characterization of the constitutive acyl carrier protein from Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5440–5444. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5440-5444.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. H., Ntamere A. S., Neuhaus F. C. D-alanyl-lipoteichoic acid in Lactobacillus casei: secretion of vesicles in response to benzylpenicillin. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 May;138(5):849–859. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-5-849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reusch V. M., Jr, Neuhaus F. C. D-Alanine: membrane acceptor ligase from Lactobacillus casei. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6136–6143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock C. O., Cronan J. E., Jr Acyl carrier protein from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1981;71(Pt 100):341–351. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)71043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabaitis J. E., Jr, Powell G. L. Acyl carrier protein metabolism and regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis by Lactobacillus plantarum. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4706–4712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe I. C., Shaw N. Atypical lipoteichoic acids of gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7065–7069. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7065-7069.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanaman T. C., Wakil S. J., Hill R. L. The complete amino acid sequence of the acyl carrier protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6420–6431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. B. Teichoic and teichuronic acids: biosynthesis, assembly, and location. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Jun;45(2):211–243. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.2.211-243.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]