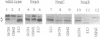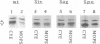Abstract
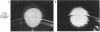
Myxococcus xanthus is a gram-negative gliding bacterium that exhibits a complex life cycle. Exposure of M. xanthus to chemicals like dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) at nondeleterious concentrations or the depletion of nutrients caused several negative responses by the cells. DMSO (> 0.1 M) or nutrient depletion triggered a repellent response: cell swarming was inhibited and FrzCD (a methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein) was demethylated; higher concentrations of DMSO (> 0.3 M) or prolonged starvation induced an additional response which involved cellular morphogenesis: DMSO caused cells to convert from rod-shaped vegetative cells to spherical, environmentally resistant "DMSO spores," and starvation induced myxospore formation in the fruiting bodies. In order to investigate the nature of these responses, we isolated a number of mutants defective in negative chemotaxis and/or sporulation. Characterization of these mutants indicated that negative chemotaxis plays an important role in colony swarming and in developmental aggregation. In addition, the results revealed some of the major interrelationships between the signal transduction pathways which respond to negative stimuli: (i) DMSO exposure and starvation were initially sensed by different systems, the neg system for DMSO and the stv system for starvation; (ii) the repellent response signals triggered by DMSO or starvation were then relayed by the frz signal transduction system; mutants defective in these responses showed altered FrzCD methylation patterns; and (iii) the morphogenesis signals in response to DMSO or starvation utilize a group of genes involved in sporulation (spo).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacon K., Rosenberg E. Ribonucleic acid synthesis during morphogenesis in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1883–1889. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1883-1889.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard R. P., Parish J. H. Mutants of Myxococcus xanthus insensitive to glycerol-induced myxospore formation. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Aug 28;104(3):289–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00447339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J. M., Geisselsoder J., Zusman D. R. Isolation of bacteriophage MX4, a generalized transducing phage for Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M., GIBSON S. M. A SYSTEM FOR STUDYING MICROBIAL MORPHOGENESIS: RAPID FORMATION OF MICROCYSTS IN MYXOCOCCUS XANTHUS. Science. 1964 Oct 9;146(3641):243–244. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3641.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Biosynthesis and self-assembly of protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride M. J., Köhler T., Zusman D. R. Methylation of FrzCD, a methyl-accepting taxis protein of Myxococcus xanthus, is correlated with factors affecting cell behavior. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4246–4257. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4246-4257.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleary W. R., McBride M. J., Zusman D. R. Developmental sensory transduction in Myxococcus xanthus involves methylation and demethylation of FrzCD. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4877–4887. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4877-4887.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison C. E., Zusman D. R. Myxococcus xanthus mutants with temperature-sensitive, stage-specific defects: evidence for independent pathways in development. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1036–1042. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1036-1042.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Analysis of Myxococcus xanthus cell types by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3334–3341. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3334-3341.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Genetic analysis of Myxococcus xanthus and isolation of gene replacements after transduction under conditions of limited homology. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):744–748. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.744-748.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi W., Köhler T., Zusman D. R. Chemotaxis plays a role in the social behaviour of Myxococcus xanthus. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(3):601–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi W., Zusman D. R. The two motility systems of Myxococcus xanthus show different selective advantages on various surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3378–3382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]