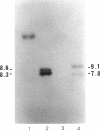
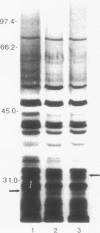
Abstract
Fimbrial production by Porphyromonas gingivalis was inactivated by insertion-duplication mutagenesis, using the cloned gene for the P. gingivalis major fimbrial subunit protein, fimA. by several criteria, this insertion mutation rendered P. gingivalis unable to produce fimbrilin or an intact fimbrial structure. A nonfimbriated mutant, DPG3, hemagglutinated sheep erythrocytes normally and was unimpaired in the ability to coaggregate with Streptococcus gordonii G9B. The cell surface hydrophobicity of DPG3 was also unaffected by the loss of fimbriae. However, DPG3 was significantly less able to bind to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite than wild-type P. gingivalis 381. This suggested that P. gingivalis fimbriae are important for adherence of the organism to saliva-coated oral surfaces. Further, DPG3 was significantly less able to cause periodontal bone loss in a gnotobiotic rat model of periodontal disease. These observations are consistent with other data suggesting that P. gingivalis fimbriae play an important role in the pathogenesis of human periodontal disease.
Full text
PDF


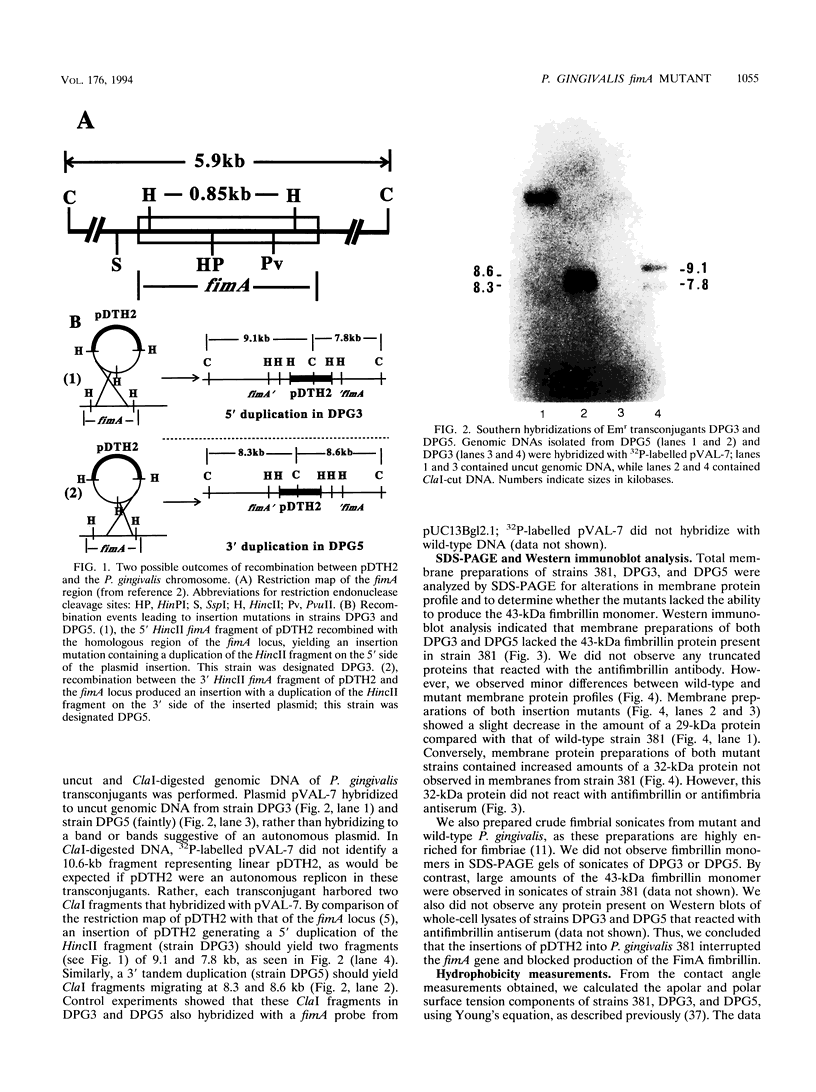

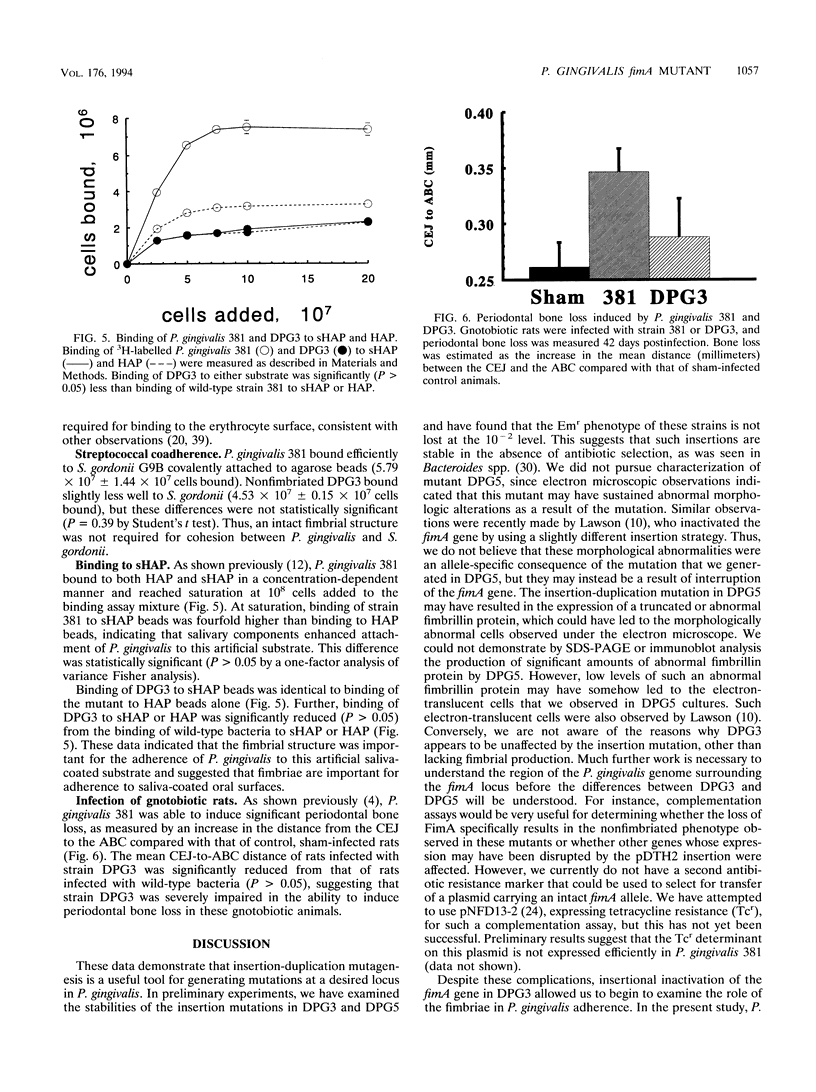


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark W. B., Bammann L. L., Gibbons R. J. Comparative estimates of bacterial affinities and adsorption sites on hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):846–853. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.846-853.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson D. P., Kubiniec M. A., Yoshimura F., Genco R. J. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the fimbrial subunit protein of Bacteroides gingivalis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1658–1665. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1658-1665.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., Bilalis G., Michel J. H., Malek R. Conjugal transfer of plasmid and transposon DNA from Escherichia coli into Porphyromonas gingivalis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 31;186(2):1012–1019. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90847-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. T., Klausen B., Sojar H. T., Bedi G. S., Sfintescu C., Ramamurthy N. S., Golub L. M., Genco R. J. Immunization with Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis fimbriae protects against periodontal destruction. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2926–2935. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2926-2935.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I. Comparative hydrophobicities of oral bacteria and their adherence to salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1190–1196. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1190-1196.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulbourne P. A., Ellen R. P. Evidence that Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis fimbriae function in adhesion to Actinomyces viscosus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5266–5274. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5266-5274.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie E. P., Salyers A. A. Use of targeted insertional mutagenesis to determine whether chondroitin lyase II is essential for chondroitin sulfate utilization by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):966–971. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.966-971.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isogai H., Isogai E., Yoshimura F., Suzuki T., Kagota W., Takano K. Specific inhibition of adherence of an oral strain of Bacteroides gingivalis 381 to epithelial cells by monoclonal antibodies against the bacterial fimbriae. Arch Oral Biol. 1988;33(7):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(88)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Y., Sojar H. T., Bedi G. S., Genco R. J. Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis fimbrillin: size, amino-terminal sequence, and antigenic heterogeneity. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):383–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.383-389.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Y., Sojar H. T., Bedi G. S., Genco R. J. Synthetic peptides analogous to the fimbrillin sequence inhibit adherence of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1662–1670. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1662-1670.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Ellen R. P. Relative adherence of Bacteroides species and strains to Actinomyces viscosus on saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. J Dent Res. 1989 Sep;68(9):1308–1312. doi: 10.1177/00220345890680090301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund B., Lindberg F. P., Båga M., Normark S. Globoside-specific adhesins of uropathogenic Escherichia coli are encoded by similar trans-complementable gene clusters. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1293–1301. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1293-1301.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund B., Lindberg F., Marklund B. I., Normark S. The PapG protein is the alpha-D-galactopyranosyl-(1----4)-beta-D-galactopyranose-binding adhesin of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5898–5902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Davies J., Grundström T., Kihlström E., Normark S. Surface charge and hydrophobicity of Salmonella, E. coli, Gonococci in relation to their tendency to associate with animal cells. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1980;Suppl 24:135–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D., Holt S. C. Biology of asaccharolytic black-pigmented Bacteroides species. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):134–152. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.134-152.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Ni Eidhin D., Deslauriers M., Lamy L. The hemagglutinating adhesin HA-Ag2 of Bacteroides gingivalis is distinct from fimbrilin. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1991 Feb;6(1):6–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1991.tb00444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Nagata H., Amano A., Takagaki M., Shizukuishi S., Tsunemitsu A., Aimoto S. Inhibitory effects of human salivary histatins and lysozyme on coaggregation between Porphyromonas gingivalis and Streptococcus mitis. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3284–3286. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3284-3286.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peros W. J., Etherden I., Gibbons R. J., Skobe Z. Alteration of fimbriation and cell hydrophobicity by sublethal concentrations of tetracycline. J Periodontal Res. 1985 Jan;20(1):24–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1985.tb00406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz S., Ellen R. P., Grove D. A. Bacteroides gingivalis-Actinomyces viscosus cohesive interactions as measured by a quantitative binding assay. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2391–2397. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2391-2397.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Genco R. J. Black-pigmented Bacteroides species, Capnocytophaga species, and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease: virulence factors in colonization, survival, and tissue destruction. J Dent Res. 1984 Mar;63(3):412–421. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630031101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Genco R. J. Direct hemagglutination technique for differentiating Bacteroides asaccharolyticus oral strains from nonoral strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):371–373. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.371-373.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Gibbons R. J. Attachment of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subsp. asaccharolyticus to oral surfaces and its possible role in colonization of the mouth and of periodontal pockets. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):254–264. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.254-264.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Salyers A. A. Cell-associated pullulanase from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron: cloning, characterization, and insertional mutagenesis to determine role in pullulan utilization. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2116–2123. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2116-2123.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S. Microbiology of periodontal disease -- present status and future considerations. J Periodontol. 1977 Sep;48(9):497–504. doi: 10.1902/jop.1977.48.9.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sojar H. T., Lee J. Y., Bedi G. S., Cho M. I., Genco R. J. Purification, characterization and immunolocalization of fimbrial protein from Porphyromonas (bacteroides) gingivalis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91624-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Safulko K., Levine M. J. Adherence of Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis to Streptococcus sanguis in vitro. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):102–108. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.102-108.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlin B. E., Norgren M., Båga M., Normark S. Adhesion to human cells by Escherichia coli lacking the major subunit of a digalactoside-specific pilus-adhesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1800–1804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine P. J., Shoemaker N. B., Salyers A. A. Mobilization of Bacteroides plasmids by Bacteroides conjugal elements. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1319–1324. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1319-1324.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe K., Yamaji Y., Umemoto T. Correlation between cell-adherent activity and surface structure in Porphyromonas gingivalis. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1992 Dec;7(6):357–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1992.tb00636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Takahashi K., Nodasaka Y., Suzuki T. Purification and characterization of a novel type of fimbriae from the oral anaerobe Bacteroides gingivalis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):949–957. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.949-957.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J., Reynolds H. S., Slots J. Black-pigmented Bacteroides spp. in the human oral cavity. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):198–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.198-203.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]