Abstract
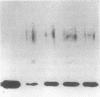
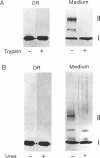
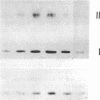
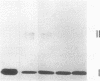
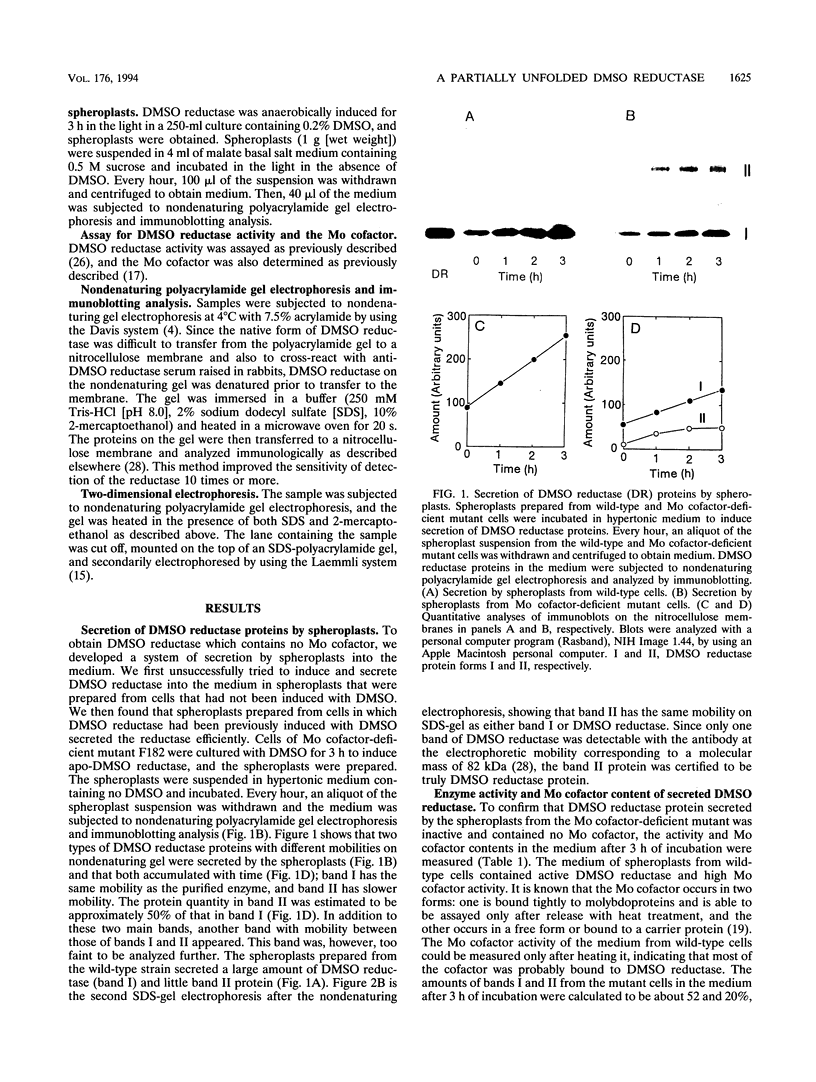
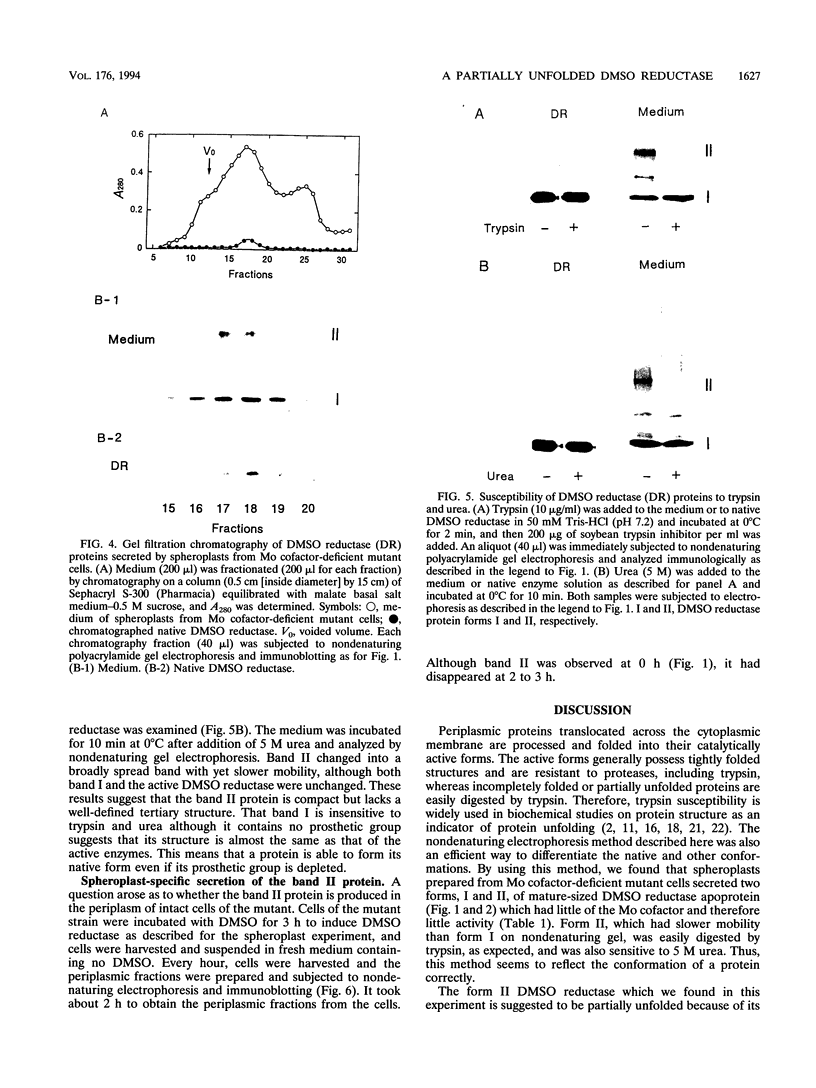
Spheroplasts prepared from a molybdenum cofactor-deficient mutant of Rhodobacter sphaeroides f. sp. denitrificans secreted dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) reductase which had no molybdenum cofactor and therefore no activity, whereas those from wild-type cells secreted the active reductase. The inactive DMSO reductase proteins were separated by nondenaturing electrophoresis into two forms: form I, with the same mobility as the native enzyme, and form II, with slower mobility. Both forms had the same mobility on denaturing gel. Form I and active DMSO reductase had the same profile on gel filtration chromatography. Form II was eluted a little faster than the native enzyme, suggesting that DMSO reductase form II was not an aggregated form but a compactly folded form very similar to the native enzyme. Form II was digested by trypsin and denatured with urea, whereas form I was unaffected, like native DMSO reductase. These results suggested that form II was a partially unfolded but compactly folded apoprotein of DMSO reductase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anfinsen C. B. Principles that govern the folding of protein chains. Science. 1973 Jul 20;181(4096):223–230. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4096.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkowitz R. A., Joly J. C., Wickner W. Translocation can drive the unfolding of a preprotein domain. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):243–253. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05650.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. Protein folding. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):1–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2700001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elöve G. A., Chaffotte A. F., Roder H., Goldberg M. E. Early steps in cytochrome c folding probed by time-resolved circular dichroism and fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 4;31(30):6876–6883. doi: 10.1021/bi00145a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Schmid F. X. The mechanism of protein folding. Implications of in vitro refolding models for de novo protein folding and translocation in the cell. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 6;29(9):2205–2212. doi: 10.1021/bi00461a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto Y., Fink A. L. Conformational states of beta-lactamase: molten-globule states at acidic and alkaline pH with high salt. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):945–952. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz P. M., Criscimagna N. L. Stable intermediates can be trapped during the reversible refolding of urea-denatured rhodanese. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2576–2583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeguchi M., Kuwajima K., Mitani M., Sugai S. Evidence for identity between the equilibrium unfolding intermediate and a transient folding intermediate: a comparative study of the folding reactions of alpha-lactalbumin and lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6965–6972. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamitani S., Akiyama Y., Ito K. Identification and characterization of an Escherichia coli gene required for the formation of correctly folded alkaline phosphatase, a periplasmic enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):57–62. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim P. S., Baldwin R. L. Intermediates in the folding reactions of small proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:631–660. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima K. The molten globule state as a clue for understanding the folding and cooperativity of globular-protein structure. Proteins. 1989;6(2):87–103. doi: 10.1002/prot.340060202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima K., Yamaya H., Miwa S., Sugai S., Nagamura T. Rapid formation of secondary structure framework in protein folding studied by stopped-flow circular dichroism. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 31;221(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80363-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J., Langer T., Boteva R., Schramel A., Horwich A. L., Hartl F. U. Chaperonin-mediated protein folding at the surface of groEL through a 'molten globule'-like intermediate. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):36–42. doi: 10.1038/352036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama S., Fujita Y., Mizushima S. SecD is involved in the release of translocated secretory proteins from the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):265–270. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05652.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza J. A., Rogers E., Lorimer G. H., Horowitz P. M. Unassisted refolding of urea unfolded rhodanese. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13587–13591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minsky A., Summers R. G., Knowles J. R. Secretion of beta-lactamase into the periplasm of Escherichia coli: evidence for a distinct release step associated with a conformational change. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4180–4184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohgushi M., Wada A. 'Molten-globule state': a compact form of globular proteins with mobile side-chains. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Hoshino Y., Kitamura H. Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides forma sp. denitrificans, a denitrifying strain as a subspecies of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Jul;108(3):265–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00454851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Kurihara F. N. Purification and properties of dimethylsulfoxide reductase containing a molybdenum cofactor from a photodenitrifier, Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides f.s. denitrificans. J Biochem. 1987 Jul;102(1):191–197. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwagen E., Babul J. Stabilization of the globular structure of ferricytochrome c by chloride in acidic solvents. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5135–5140. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida Y., Takai M., Satoh T., Takami S. Molybdenum requirement for translocation of dimethyl sulfoxide reductase to the periplasmic space in a photodenitrifier, Rhodobacter sphaeroides f. sp. denitrificans. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3277–3281. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3277-3281.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]