Abstract
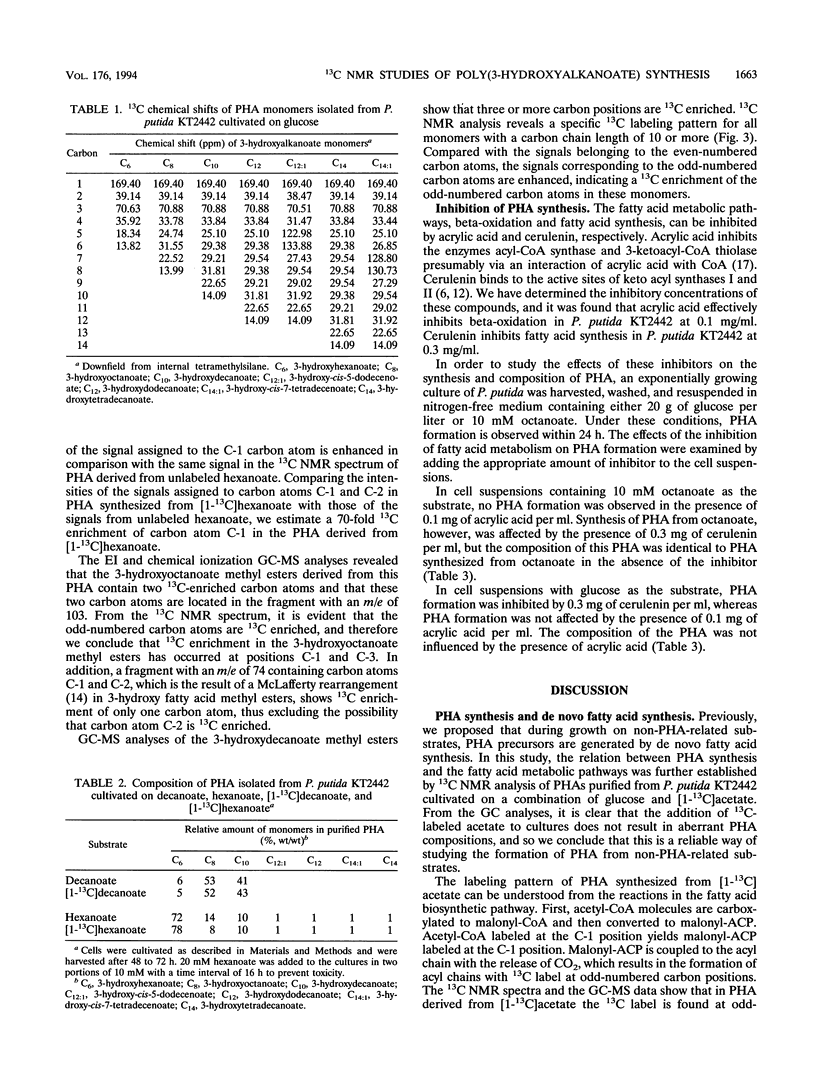
The formation of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) (PHAs) in Pseudomonas putida KT2442 from various carbon sources was studied by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, gas chromatography, and gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy. By using [1-13C]decanoate, the relation between beta-oxidation and PHA formation was confirmed. The labeling pattern in PHAs synthesized from [1-13C]acetate corresponded to the formation of PHAs via de novo fatty acid biosynthesis. Studies with specific inhibitors of the fatty acid metabolic pathways demonstrated that beta-oxidation and de novo fatty acid biosynthesis function independently in PHA formation. Analysis of PHAs derived from [1-13C]hexanoate showed that both fatty acid metabolic routes can function simultaneously in the synthesis of PHA. Furthermore, evidence is presented that during growth on medium-chain-length fatty acids, PHA precursors can be generated by elongation of these fatty acids with an acetyl coenzyme A molecule, presumably by a reverse action of 3-ketothiolase.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagdasarian M., Lurz R., Rückert B., Franklin F. C., Bagdasarian M. M., Frey J., Timmis K. N. Specific-purpose plasmid cloning vectors. II. Broad host range, high copy number, RSF1010-derived vectors, and a host-vector system for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl H., Gross R. A., Lenz R. W., Fuller R. C. Pseudomonas oleovorans as a Source of Poly(beta-Hydroxyalkanoates) for Potential Applications as Biodegradable Polyesters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):1977–1982. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.1977-1982.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funabashi H., Kawaguchi A., Tomoda H., Omura S., Okuda S., Iwasaki S. Binding site of cerulenin in fatty acid synthetase. J Biochem. 1989 May;105(5):751–755. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood G. W., Anderson A. J., Ewing D. F., Dawes E. A. Accumulation of a Polyhydroxyalkanoate Containing Primarily 3-Hydroxydecanoate from Simple Carbohydrate Substrates by Pseudomonas sp. Strain NCIMB 40135. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3354–3359. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3354-3359.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huijberts G. N., Eggink G., de Waard P., Huisman G. W., Witholt B. Pseudomonas putida KT2442 cultivated on glucose accumulates poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) consisting of saturated and unsaturated monomers. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):536–544. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.536-544.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman G. W., de Leeuw O., Eggink G., Witholt B. Synthesis of poly-3-hydroxyalkanoates is a common feature of fluorescent pseudomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Aug;55(8):1949–1954. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.1949-1954.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackowski S., Rock C. O. Acetoacetyl-acyl carrier protein synthase, a potential regulator of fatty acid biosynthesis in bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7927–7931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lageveen R. G., Huisman G. W., Preusting H., Ketelaar P., Eggink G., Witholt B. Formation of Polyesters by Pseudomonas oleovorans: Effect of Substrates on Formation and Composition of Poly-(R)-3-Hydroxyalkanoates and Poly-(R)-3-Hydroxyalkenoates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):2924–2932. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.2924-2932.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIJSSE G. J. FATTY-ACID ACCUMULATION BY ACRYLATE INHIBITION OF BETA-OXIDATION IN ALKANE-OXIDIZING PSEUDOMONAS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 20;84:195–197. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timm A., Steinbüchel A. Formation of polyesters consisting of medium-chain-length 3-hydroxyalkanoic acids from gluconate by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other fluorescent pseudomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3360–3367. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3360-3367.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waard P., van der Wal H., Huijberts G. N., Eggink G. Heteronuclear NMR analysis of unsaturated fatty acids in poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates). Study of beta-oxidation in Pseudomonas putida. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):315–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


